Abstract.
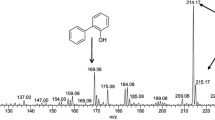
The dibenzothiophene (DBT) desulfurizing operon, dsz, was introduced into various benzothiophene (BT)-desulfurizing bacteria using a Rhodococcus-E. coli shuttle vector. Of the tested recombinant bacteria, only those from Rhodococcus sp. strain T09 grew with both DBT and BT as the sole sulfur source. These recombinant cells desulfurized not only alkylated BTs, but also various alkylated DBTs, producing alkylated hydroxybiphenyls as the desulfurized products. Recombinant strain T09 also desulfurized alkylated DBT in an oil-water, two-phase resting-cell reaction. The dsz operon had the same desulfurizing activity when inserted into the vector in either orientation, indicating that the promoter region of the operon was functional in strain T09.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 12 October 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsui, .T., Hirasawa, .K., Konishi, .J. et al. Microbial desulfurization of alkylated dibenzothiophene and alkylated benzothiophene by recombinant Rhodococcus sp. strain T09. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56, 196–200 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000549