Abstract
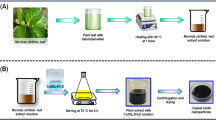
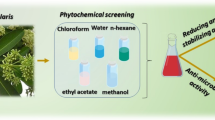
Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) synthesis using an environmentally benign approach, as well as their antibacterial properties. Copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O) of different concentrations (2 mM, 5 mM and 10 mM) and aqueous Nyctanthes arbor-tristis leaf extract were used to make the CuO NPs. The synthesised CuO NPs are characterised by UV–vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). UV–vis spectroscopy confirmed the presence of CuO NPs. The functional groups of the active components were identified using the FTIR spectra of the control (leaf extract) and CuO NPs. SEM pictures revealed that the particles were rectangular, truncated triangle and spherical in shape, with sizes ranging between 4.9 nm, 18.4 nm and 23.8 nm determined using X-ray diffraction. The antibacterial activity of the produced CuO NPs was further evaluated using the well diffusion method. By observing inhibition zones around each well, the nanoparticles were revealed to have broad antibacterial action against human pathogenic bacterial strains Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus withs the 7 ± 0.70-mm and 7 ± 0.21-mm inhibitory zone size respectively followed by 08 μg/mL and 2.5 μg/mL MIC respectively. Thus, these outputs concluded that the CuO NPs exhibited miraculous effect and it might be boon towards nanomedical science, pharmaceuticals and health industries.
Graphical abstract

Key points
• Biosynthesis of CuO nanoparticle
• Multifaceted utilization
• Broad spectrum antimicrobial activity








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ajtha B, Reddy AK, Reddy SP (2015) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Lantana camara leaf extract. Matter Sci Eng c 49:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.035
Amin F, Fozia KB, Alotaibi A, Qasim M, Ahmad I, Ullah B, Gul A, Zahoor S, Ahmad R (2021) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Aerva javanica leaf extract and their characterization and investigation of in vitro antimicrobial potential and cytotoxic activities. Evid Based Complement Altern 2021:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5589703
Assumpta CN, Lovasoa CR, Bashir AKH, Chinwe OI, Stephen CN, Subelia B, Ntwampe SKO, Fabian IE, Emmanuel II, Malik M (2019) Industrial textile effluent treatment and antibacterial effectiveness of Zea mays L. Dry husk mediated biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 375:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.004
Das D, Nath BC, Phukon P, Dolui SK (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial behavior of CuO nanoparticles. Col Surf b: Biointerf 101:430–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.002
Dilaveez R, Mahendiran D, Senthil K, Rahiman AK (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101
Dobrucka R (2018) Antioxidant and catalytic activity of biosynthesised CuO nanoparticles using extract of Galeopsidis herba. J Inorg & Org Polymers & Mat 28:812–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0750-2
Dong C, Zhang X, Cai H, Cao C (2016) Green synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles mediated by Osmanthus fragrans extract in aqueous solution. Optik 127(22):10378–10388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.08.055
Duraipandi D, Selvaraj MR (2017) Cissus quadrangularis mediated ecofriendly synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its antifungal studies against Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus Flavus. Mater Sci Eng C 80:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.130
Fan H, Yang L, Hua W, Wu X, Wu Z, Xie S, Zou B (2003) Controlled synthesis of monodispersed CuO nanocrystals15:37. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/15/1/007
Fardood ST, Ramzani A (2016) Green synthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles using coffee powder extract. J Nanostructures 6:167–171. https://doi.org/10.7508/JNS.2016.02.009
Fayezeh S, Leyla B, Hossein S, Saeed Y (2019) Controllable phyto-synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Capparis spinosa (caper) leaves and application in iron sensing. Microchem J 150:104–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104158
Ghidana AY, Al-Antarya TM, Awwad AM (2016) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum peels extract: effect on green peach Aphid. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 6:95–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.08.002
Gunalana S, Sivaraja RR, V, (2012) Green synthesised ZnO NPs against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog Mat Sci 22(6):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.11.01
Husen A, Siddiqi KS (2014) Phytosynthesis of nanoparticles: concept, controversy and application. Nano Res Lett 9:229. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-229
Jamdagini P, Khatri P, Rana JS (2016) Green synthesis of zincoxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J Saud University- Science 30(2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.10.002
Jayachandran A, Nar ASS (2021) Green synthesis and characterisation of ZnO NPs using Cayratia pedata leaf extract. Biochem Biophys Rep 26:100995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100995
Kasana RC, Panwar NR, Kaul R, Kumar P (2017) Biosynthesis and effects of copper nanoparticles on plants. Environ Chem Lett 15(2):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0615-5
Kerour A, Boudjadar S, Bourzami R, Allouche B (2018) Ecofriendly synthesis of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles and improvement of their solar photocatalytic activities. J Solid State Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2018.04.010
Kumar B, Smita K, Cumbal DA, Angulo ADY (2021) Biofabrication of copper oxide nanoparticles using Andean blackberry (Rubus glaucus Benth) fruit and leaf. J Saudi Chem S 21:S475–S480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2015.01.009
Kumar RV, Elgamiel R, Diamant Y, Gedanken A, Norwig, (2001) Sonochemical preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline copper oxide embedded in poly (vinyl alcohol) and its effect on crystal growth of copper oxide. Langmuir 17:1406–1410. https://doi.org/10.1021/la001331s
Mali SC, Dhaka A, Githala CK, Trivedi R (2020) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Celastrus paniculatus wild leaf extract and their photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 27:e00518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00518
Maryam B, Zeinab SZ, Bahar K (2018) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles/ clinoptilolite using Rheum palmatum L root extract high catalytic activity for reduction of 4-nitro phenol rhodamine B and methylene blue. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 81(3):724–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4239-1
Mehran A, Maryam R, Mojtaba T (2018) Effect of incubation time, CuSO4 and glucose concentrations on biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles with rectangular shape and antibacterial activity Taguchi method approach. Nano Biomed Eng 10(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.51051/nbe.v10i1
Mishra AK, Tiwari KN, Saini R (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle from leaf extract of Nyctanthes arbour-tristis L. and assessment of its antioxidant, antimicrobial response. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30:2266–2278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01392-w
Mohamed EA (2020) Green synthesis of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles using the extract of seedless dates. Heliyon 6:e03123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.e03123
Naika RH, Lingaraju K, Manjunath K, Kumar D, Nagaraju G, Suresh D, Nagabhushana H (2015) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity. J Taibah Univ Sci 9:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2014.04.006
Rajendran A, Siva E, Dhanraj C, Senthilkumar S (2018) A green and facile approach for the synthesis copper oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis flower extracts and its antibacterial activities. J Bioprocess Biotech 8(3):324. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9821.1000324
Rajesh KM, Ajitha B, Reddy YA, Suneetha Y, Reddy PS (2018) Assisted green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Syzygium aromaticum bud extract: physical, optical and antimicrobial properties. Optik 154:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.10.074
Salavati-Nissari M, Davar F (2009) Synthesis of copper and copper (I) oxide nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of a new precursor. Mater Lett 63:441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.11.023
Saruchi PT, Vaneet K (2019) Kinetics and thermodynamic studies for removal of methylene blue dye by biosynthesize copper oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity. J Env Health Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s4201-019-00354-1
Singh S, Kumar N, Kumar M, Agarwal JA, Mizaikoff B (2017) Electrochemical sensing and remediation of 4-nitrophenol using bio-synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 313:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.049
Sivaraj R, Rahman PKSM, Rajiv P, Narendhran S, Venckatesh R (2014) Biosynthesis and characterization of Acalypha indica mediated copper oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 129:255–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.03.027
Sonbol H, Ameen F, AlYahya S, Almansob A, Alwakeel S (2021) Padina boryana mediated green synthesis of crystalline palladium nanoparticles as potential nanodrug against multidrug resistant bacteria and cancer cells. Sci Rep 11:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84794-6
Swetha A, Satheesh KB, Jaison J, Murugesan M, Manisha V, Yen SC, Michael KC (2019) Phytosynthesized metal oxide nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 392:755–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01666-7
Tresye U, Hariths A A, Digha M (2017) Green method for synthesis of gold NPs using Polyscias scutellaria leaf extract under UV light and their catalytic activity to reduce methylene blue. J Nanomat 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/307936
Vanathi P, Rajiv P, Rajeshwari S (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Eichhornia mediated copper oxide nanoparticles and assessing their antifungal activity against plant. Pathogens Bull Mater Sci C 39:1165–1170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1276-x
Wang H, Xu JZ, Chen HY (2002) Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J Cryst Growth 244(1):88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01571-3
Xu JF, Ji W, Shen ZX, Tang SH, Ye XR, Jia DZ, Xin XQ (1999) Preparation and Characterization of CuO. Nanocrystals 147(2):516–519. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1999.8409
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to Principal of Govt. VYTPG Autonomous College, Durg (C.G.) India, for providing basic facilities for the completion of this research. The authors also thank to Vice Chancellor, Pt. Ravi Shankar University, Raipur (C.G.) India, for the inspiration towards the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N. A. conducted complete experimentation. A. K. K. consived, designed and supervised the research. A. K. analysed and evaluated the result data and outcomes. L. D. formatted and corrected the manuscript as well as supprted for result evaluation and draft designing. D. V. contributed as cowerker during this research. All authors approved this research manuscript for the publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Noorafsha, Kashyap, A.K., Kashyap, A. et al. Biosynthesis and biophysical elucidation of CuO nanoparticle from Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn Leaf. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 5823–5832 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12105-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12105-8