Abstract
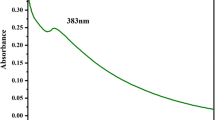
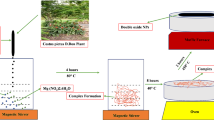
In recent years, the rapid increase in the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics has produced major health issues. Novel applications for these compounds have been developed by integrating modern technologies such as nanotechnology and material science with the innate antibacterial activity of metals. The current study demonstrated the synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) from Momordica charantia and Curcuma zedoaria plant extracts, as well as their antibacterial properties. The synthesis of ZnO NPs was confirmed via UV-visible spectroscopy, showing clear peaks at 375 and 350 nm for M. charantia and C. zedoaria, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis revealed crystals of irregular shapes for the majority of the nanoparticles synthesized from both plants. The existence of ZnO NPs was confirmed using X-ray diffraction while the particle size was calculated using Scherrer’s equation, which was 19.65 for C. zedoaria and 17.02 for M. charantia. Different functional groups were detected through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis. The antibacterial activity of the ZnO NPs at three different concentrations (250, 500, and 1000 µg/ml) was assessed against three different bacterial strains, i.e., Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), using disc diffusion methods. The ZnO nanoparticles showed promising antibacterial activity against bacterial strains. For C. zedoaria, the highest growth inhibition was observed at a concentration of 1000 µg/ml, which was 18, 19, and 18 mm as compared to antibiotics (15, 11, and 15.6 mm) against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, respectively. Similarly, at 1000 µg/ml of NPs, M. charantia showed the highest growth inhibition (18, 15, and 17 mm) as compared to antibiotics (15, 11, and 14.6 mm) against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, respectively. In conclusion, compared to pure plant extract and antibiotics, ZnO NPs at a higher concentration (1000 µg/ml) exhibited a significant difference in zone of inhibition against all the bacterial strains. Different concentrations of ZnO using M. charantia and C. zedoaria caused increments in the scavenging of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals and 2,2-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS). The nanoparticles extracted using C. zedoaria exhibited higher antioxidant activity than M. charantia. Greenly synthesized ZnO nanoparticles have remarkable antibacterial properties and antioxidant activity, making them a promising contender for future pharmaceutical application.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelbaky, A. S., Abd El-Mageed, T. A., Babalghith, A. O., Selim, S., & Mohamed, A. M. H. A. (2022). Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles using Pelargonium odoratissimum (L.) aqueous leaf extract and their antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. Antioxidants, 11, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081444
Dhawi, F., El-Beltagi, H. S., Abdel-Mobdy, Y. E., Salah, S. M., Ghaly, I. S., Abdel-Rahim, E. A., Soliman, A. M., & Mohamed, H. I. (2021). Synergistic impact of the pomegranate peels and its nanoparticles against the infection of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 30(1), 731-746.
Abou-Okeil, A. (2012). Ag nanoparticles growing onto cotton fabric using chitosan as a template. Journal of Natural Fibers, 9(2), 61-72.
Sithara, R., Selvakumar, P., Arun, C., Anandan, S., & Sivashanmugam, P. (2017). Economical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Acalypha hispida and its application in the detection of Mn (II) ions. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(6), 561-568.
Bukhari, A., Ijaz, I., Gilani, E., Nazir, A., Zain, H., Saeed, R., Alarfaji, S. S., Hussain, S., Aftab, R., & Naseer, Y. (2021). Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles using different plants’ parts for antimicrobial activity and anticancer activity: A review article. Coatings, 11, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111374
Pal, S. L., Jana, U. P. K., Manna, G. P., Mohanta, R., & Manavalan, R. (2011). Nanoparticle: An overview of preparation and characterization. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 1(6), 228-234.
Amer, A., Ghoneim, M., Shoala, T., & Mohamed, H. I. (2021). Comparative studies on French basil (Ocimum basilicum L. cv. Grand verde) as affected by alternatives spraying with humic, salicylic, and glycyrrhizic acids and their nanocomposites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 47196-47212.
Rana, R. A., Siddiqui, M. N., Skalicky, M., Brestic, M., Hossain, A., Kayesh, E., Popov, M., Hejnak, V., Gupta, D. R., Mahmud, N. U., et al. (2021). Prospects of nanotechnology in improving the productivity and quality of horticultural crops. Horticulturae, 7, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100332
Rahman, M. M., Islam, M. R., Akash, S., Harun-Or-Rashid, M., Ray, T. K., Rahaman, M. S., Islam, M., Anika, F., Hosain, M. K., Aovi, F. I., & Hemeg, H. A. (2022). Recent advancements of nanoparticles application in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: At a glance. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 153, 113305.
Haseeb, Q., Hamdani, S. D. A., Akram, A., Khan, D. A., Rajput, T. A. & Babar, M. M. (2020). Nanobiotechnology: Paving the way to personalized medicine. NanoBioMedicine, 17-32.
Lugani, Y., Sooch, B. S., Singh, P. & Kumar, S. (2021). Nanobiotechnology applications in food sector and future innovations. In Microbial biotechnology in food and health (pp. 197-225). Academic Press.
Ealia, S. A. M., Saravanakumar, M. P., (2017). November. A review on the classification, characterisation, synthesis of nanoparticles and their application. In IOP conference series: Materials science and engineering, IOP Publishing, 263(3), 032019.
Marouzi, S., Sabouri, Z., & Darroudi, M. (2021). Greener synthesis and medical applications of metal oxide nanoparticles. Ceramics International, 47(14), 19632-19650.
Hakkar, K. N., Mhatre, S. S., & Parikh, R. Y. (2010). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine: nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 6(2), 257-262.
Singh, P. Y., Kim, J., Wang, C., Mathiyalagan, R., & Yang, D. C. (2018). Weissella oryzae DC6-facilitated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial potential. Artificial cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 44(6), 1569-1575.
Alyamani, A. A., Albukhaty, S., Aloufi, S., AlMalki, F. A., Al-Karagoly, H., & Sulaiman, G. M. (2021). Green fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using phlomis leaf extract: Characterization and in vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties. Molecules, 26(20), 6140.
Abbasi, E., Milani, M., Fekri Aval, S., Kouhi, M., Akbarzadeh, A., Tayefi Nasrabadi, H., Nikasa, P., Joo, S. W., Hanifehpour, Y., Nejati-Koshki, K., & Samiei, M. (2016). Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 42(2), 173-180.
Prakash, P., Gnanaprakasam, P., Emmanuel, R., Arokiyaraj, S., & Saravanan, M. (2013). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mimusops elengi, Linn. for enhanced antibacterial activity against multi drug resistant clinical isolates. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 108, 255-259.
García-Barrasa, J., López-de-Luzuriaga, J., & Monge, M. (2011). Silver nanoparticles synthesis through chemical methods in solution and biomedical applications. Open Chemistry, 9(1), 7-19.
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B. L., & Ikram, S. (2016). A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. Journal of Advanced Research, 7(1), 17-28.
Das, R. K., Pachapur, V. L., Lonappan, L., Naghdi, M., Pulicharla, R., Maiti, S., Cledon, M., Dalila, L. M. A., Sarma, S. J., & Brar, S. K. (2017). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Plants, animals and microbial aspects. Nanotechnology for Environmental Engineering, 2(1), 1-21.
Rautela, A., & Rani, J. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tectona grandis seeds extract: Characterization and mechanism of antimicrobial action on different microorganisms. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 10(1), 1-10.
Rafique, M., Sadaf, I., Rafique, M. S., & Tahir, M. B. (2017). A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 45(7), 1272-1291.
Mogazy, A. M., Mohamed, H. I., & El-Mahdy, O. M. (2022). Calcium and iron nanoparticles: A positive modulator of innate immune responses in strawberry plants against Botrytis cinerea. Process Biochemistry, 115, 128-145.
Galvin, P., Thompson, D., Ryan, K. B., McCarthy, A., Moore, A. C., Burke, C. S., Dyson, M., MacCraith, B. D., Gun’ko, Y. K., Byrne, M. T., & Volkov, Y. (2012). Nanoparticle-based drug delivery: Case studies for cancer and cardiovascular applications. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69(3), 389-404.
Muthuvel, A., Jothibas, M., & Manoharan, C. (2020). Effect of chemically synthesis compared to biosynthesized ZnO-NPs using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their photocatalytic antibacterial and in vitro antioxidant activity. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8, 103705.
Espitia, P. J. P., Soares, N. D. F. F., Coimbra, J. S. D. R., de Andrade, N. J., Cruz, R. S., & Medeiros, E. A. A. (2012). Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food Bioprocess Technology, 5(5), 1447-1464.
Paškevičius, Š, Starkevič, U., Misiūnas, A., Vitkauskienė, A., Gleba, Y., & Ražanskienė, A. (2017). Plant-expressed pyocins for control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One, 12(10), e0185782.
Schroth, M. N., Cho, J. J., Green, S. K., & Kominos, S. D. (2018). Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in agricultural areas. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 67(8), 1191-1201.
Schwarz-Linek, J., Arlt, J., Jepson, A., Dawson, A., Vissers, T., Miroli, D., & Poon, W. W. C. (2016). Escherichia coli as a model active colloid: A practical introduction. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 137, 2-16.
Allocati, N., Masulli, M., Alexeyev, M. F., & Di Ilio, C. (2013). Escherichia coli in Europe: An overview. International Journal of Environmental Research, 10(12), 6235-6254.
Jin, T., Mohammad, M., Pullerits, R., & Ali, A. (2021). Bacteria and host interplay in staphylococcus aureus septic arthritis and sepsis. Pathogens, 10(2), 158.
Lobo, R., Prabhu, K. S., Shirwaikar, A., & Shirwaikar, A. (2009). Curcuma zedoaria Rosc. (white turmeric): A review of its chemical, pharmacological and ethnomedicinal properties. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 61(1), 13-21.
Gharge, S., Hiremath, S. I., Kagawad, P., Jivaje, K., Palled, M. S., & Suryawanshi, S. S. (2021). Curcuma zedoaria Rosc (Zingiberaceae): A review on its chemical, pharmacological and biological activities. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7(1), 1-9.
Jia, S., Shen, M., Zhang, F., & Xie, J. (2017). Recent advances in Momordica charantia: Functional components and biological activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2555.
Tan, S. P., Kha, T. C., Parks, S. E., & Roach, P. D. (2016). Bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) bioactive composition and health benefits: A review. Food Reviews International, 32(2), 181-202.
Abdelbaky, A. S., & Diab, Y. M. (2021). Effect of various extraction methods and solvent types on yield phenolic and flavonoid content and antioxidant activity of Spathodea nilotica leaves. Egypt Journal of Chemistry, 64, 7483-7489.
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, M. M., Sherris, J. C., & Turck, M. (1966). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 45, 493-496.
Re, R., Pellegrini, N., Proteggente, A., Pannala, A., Yang, M., & Rice-Evans, C. (1999). Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 26(9-10), 1231-1237.
Park, H. R., Park, E., Rim, A. R., Jeon, K. I., Huang, J. H., & Lee, S. C. (2006). Antioxidant activity of extracts from Acanthopanax senticosus. African Journal Biotechnology, 5(23), 2388-2396.
Li, S., Shen, Y., Xie, A., Yu, X., Qiu, L., Zhang, L., & Zhang, Q. (2007). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chemistry, 9(8), 852-858.
Garibo, D., Borbón-Nuñez, H. A., de León, J. N. D., García Mendoza, E., Estrada, I., Toledano-Magaña, Y., Tiznado, H., Ovalle-Marroquin, M., Soto-Ramos, A. G., Blanco, A., & Rodríguez, J. A. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1-11.
Yousaf, H., Mehmood, A., Ahmad, K. S., & Raffi, M. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications as an alternative antibacterial and antioxidant agents. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 112, 110901.
Soares, A. M., Gonçalves, L. M., Ferreira, R. D., de Souza, J. M., Fangueiro, R., Alves, M. M., Carvalho, F. A., Mendes, A. N., & Cantanhêde, W. (2020). Immobilization of papain enzyme on a hybrid support containing zinc oxide nanoparticles and chitosan for clinical applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 243, 116498.
Thi, T. U. D., Nguyen, T. T., Thi, Y. D., Thi, K. H. T., Phan, B. T., & Pham, K. N. (2020). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using orange fruit peel extract for antibacterial activities. RSC Advances, 10(40), 23899-23907.
Soto-Robles, C. A., Luque, P. A., Gómez-Gutiérrez, C. M., Nava, O., Vilchis-Nestor, A. R., Lugo-Medina, E., Ranjithkumar, R., & Castro-Beltrán, A. (2019). Study on the effect of the concentration of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract on the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. Results in Physics, 15, 102807.
Awwad, A. M., Amer, M. W., Salem, N. M., & Abdeen, A. O. (2020). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using Ailanthus altissima fruit extracts and antibacterial activity. Chemistry International, 6(3), 151-159.
Mydeen, S. S., Kumar, R. R., Kottaisamy, M., & Vasantha, V. S. (2020). Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles through extract from Prosopis juliflora plant leaf: Antibacterial activities and a new approach by rust-induced photocatalysis. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 24(5), 393-406.
Aldeen, T. S., Mohamed, H. E. A., & Maaza, M. (2022). ZnO nanoparticles prepared via a green synthesis approach: Physical properties, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 160, 110313.
Vijayakumar, S., Vaseeharan, B., Malaikozhundan, B., & Shobiya, M. (2016). Laurus nobilis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Characterization and biomedical applications. Biomed Pharmaceutical, 84, 1213-1222.
Vijayakumar, S., Arulmozhi, P., Kumar, N., Sakthivel, B., Kumar, S. P., & Praseetha, P. K. (2020). Acalypha fruticosa L. leaf extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Characterization and antimicrobial activities. Materials Today: Proceedings, 23, 73-80.
Getie, S., Belay, A., Chandra Reddy, A. R., & Belay, Z. (2017). Synthesis and characterizations of zinc oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology, 8, 71-80.
Soren, S., Kumar, S., Mishra, S., Jena, P. K., Verma, S. K., & Parhi, P. (2018). Evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant potential of the zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by aqueous and polyol method. Microbial Pathogenesis, 119, 145-151.
Agarwal, H., Menon, S., Kumar, S. V., & Rajeshkumar, S. (2018). Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 286, 60-70.
Jayaseelan, C., Rahuman, A. A., Kirthi, A. V., Marimuthu, S., Santhoshkumar, T., Bagavan, A., & Rao, K. B. (2012). Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 90, 78-84.
Mthana, M. S., Mthiyane, D. M. N., Onwudiwe, D. C., & Singh, M. (2022). Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Capsicum chinense fruit extract and their in vitro cytotoxicity and antioxidant assay. Applied Science, 12, 4451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094451
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohsin Ihsan, Israr Ud Din, Khadija Alam, Iqbal Munir, Heba I. Mohamed, Fahimullah Khan: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ihsan, M., Din, I.U., Alam, K. et al. Green Fabrication, Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Plant Extract of Momordica charantia and Curcuma zedoaria and Their Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3546–3565 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04309-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04309-5