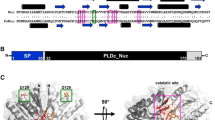
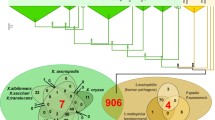
Abstract
Bacterial non-specific nucleases of the phospholipase D family are widely distributed among the members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Each genome mainly contains a single copy of a gene encoding a phospholipase D family protein. However, two distantly related isozymes (< 40% identity at the protein level) were identified by BLAST-analyses in the plant pathogenic competitor enterobacterium Pantoea agglomerans. The two nucleases PaNuc-1 and PaNuc-2 were produced in Escherichia coli. Identical gene constructs and expression conditions resulted in the production of PaNuc-1 in soluble form, while PaNuc-2 remained insoluble in inclusion bodies. PaNuc-2 was refolded and both proteins were purified by a combination of affinity and ion exchange chromatography. Proteolytic removal of the HIS-tag allowed the characterization of pure and mature tag-less proteins. Enzymatic properties of both isozymes revealed that they are non-specific nucleases, displaying activities against RNA, single- and double-stranded genomic DNA as well as circular plasmids. However, their biochemical activity profiles were clearly different, with PaNuc-1 being optimally active at 70 °C and pH 7.0, while PaNuc-2 was most active at 45 °C and pH 7.0. The enzymes retained > 90% nuclease activity at EDTA concentrations of 4 mM (PaNuc-2) and 20 mM (PaNuc-1), respectively. Different enzymatic properties suggest that the roles of PaNuc-1 and PaNuc-2 differ in the cell and might be the result of functional diversification after an ancient gene duplication event took place. The fact that both enzymes could be easily produced in recombinant form and their tolerance against metal ion chelators in combination with a broad substrate promiscuity might pave the way to versatile biotechnological applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Z, Authman S, Al-Ezee A (2017) Temperature effects on growth of the biocontrol agent Pantoea agglomerans (an oval isolate from Iraqi soils). J Adv Lab Res Biol 8:85–88
Bao Y, Higgins L, Zhang P, Chan SH, Laget S, Sweeney S, Lunnen K, Xu SY (2008) Expression and purification of BmrI restriction endonuclease and its N-terminal cleavage domain variants. Protein Expr Purif 58:42–52
Costa E, Usall J, Teixido N, Delgado J, Vinas I (2002) Water activity, temperature, and pH effects on growth of the biocontrol agent Pantoea agglomerans CPA-2. Can J Microbiol 48:1082–1088
Cruz AT, Cazacu AC, Allen CH (2007) Pantoea agglomerans, a plant pathogen causing human disease. J Clin Microbiol 45:1989–1992
Doronina NV, Kaparullina EN, Trotsenko YA, Nortemann B, Bucheli-Witschel M, Weilenmann HU, Egli T (2010) Chelativorans multitrophicus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Chelativorans oligotrophicus sp. nov., aerobic EDTA-degrading bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1044–1051
Elleuche S, Klippel B, von der Heyde A, Antranikian G (2013) Comparative analysis of two members of the metal ion-containing group III-alcohol dehydrogenases from Dickeya zeae. Biotechnol Lett 35:725–733
Espinosa-Cantu A, Ascencio D, Barona-Gomez F, DeLuna A (2015) Gene duplication and the evolution of moonlighting proteins. Front Genet 6:227
Gray HB Jr, Ostrander DA, Hodnett JL, Legerski RJ, Robberson DL (1975) Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res 2:1459–1492
Grazulis S, Manakova E, Roessle M, Bochtler M, Tamulaitiene G, Huber R, Siksnys V (2005) Structure of the metal-independent restriction enzyme BfiI reveals fusion of a specific DNA-binding domain with a nonspecific nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15797–15802
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Leiros I, Secundo F, Zambonelli C, Servi S, Hough E (2000) The first crystal structure of a phospholipase D. Structure 8:655–667
Li L, Rohrmann GF (2000) Characterization of a baculovirus alkaline nuclease. J Virol 74:6401–6407
MacLellan SR, Forsberg CW (2001) Properties of the major non-specific endonuclease from the strict anaerobe Fibrobacter succinogenes and evidence for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Microbiology 147:315–323
Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Geer LY, Geer RC, He J, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lanczycki CJ, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Wang Z, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zheng C, Bryant SH (2015) CDD: NCBI's conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D222–D226
Miltenyi S, Hübel T, Nölle V (2018) Process for sorting cells by microfabricated components using a nuclease. USA Patent US 10,018,541 B2, Jul. 10, 2018
Nielsen H (2017) Predicting secretory proteins with SignalP. Methods Mol Biol 1611:59–73
Pandya C, Farelli JD, Dunaway-Mariano D, Allen KN (2014) Enzyme promiscuity: engine of evolutionary innovation. J Biol Chem 289:30229–30236
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Pommer AJ, Wallis R, Moore GR, James R, Kleanthous C (1998) Enzymological characterization of the nuclease domain from the bacterial toxin colicin E9 from Escherichia coli. Biochem J 334(Pt 2):387–392
Ponting CP, Kerr ID (1996) A novel family of phospholipase D homologues that includes phospholipid synthases and putative endonucleases: identification of duplicated repeats and potential active site residues. Protein Sci 5:914–922
Rangarajan ES, Shankar V (2001) Sugar non-specific endonucleases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:583–613
Rudolph AE, Stuckey JA, Zhao Y, Matthews HR, Patton WA, Moss J, Dixon JE (1999) Expression, characterization, and mutagenesis of the Yersinia pestis murine toxin, a phospholipase D superfamily member. J Biol Chem 274:11824–11831
Schmitz S, Nölle V, Elleuche S (2019) A non-specific nucleolytic enzyme and its application potential in EDTA-containing buffer solutions. Biotechnol Lett 41:129–136
Singh A, Upadhyay V, Upadhyay AK, Singh SM, Panda AK (2015) Protein recovery from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli using mild solubilization process. Microb Cell Factories 14:41
Song Q, Zhang X (2008) Characterization of a novel non-specific nuclease from thermophilic bacteriophage GBSV1. BMC Biotechnol 8:43
Stuckey JA, Dixon JE (1999) Crystal structure of a phospholipase D family member. Nat Struct Biol 6:278–284
Yang W (2011) Nucleases: diversity of structure, function and mechanism. Q Rev Biophys 44:1–93
Zeida M, Wieser M, Yoshida T, Sugio T, Nagasawa T (1998) Purification and characterization of gallic acid decarboxylase from Pantoea agglomerans T71. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4743–4747
Zhao Y, Stuckey JA, Lohse DL, Dixon JE (1997) Expression, characterization, and crystallization of a member of the novel phospholipase D family of phosphodiesterases. Protein Sci 6:2655–2658
Acknowledgements
We thank Stefan Edelburg for the help with the VICTOR™ X4 Multilabel Plate Reader.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 171 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, S., Börner, P., Nölle, V. et al. Comparative analysis of two non-specific nucleases of the phospholipase D family from the plant pathogen competitor bacterium Pantoea agglomerans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 2635–2648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09644-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09644-y