Abstract
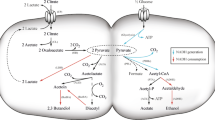
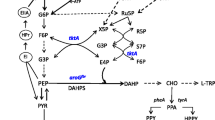
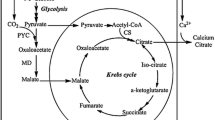
Cinnamic acid (CA) is the chemical basis for bulk production of flavoring reagents and chemical intermediates, and it can be fermented from biomass. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) has been used exclusively in the bacterial fermentation of sugar biomass in which the fermentation intermediate phenylalanine is deaminated to CA. Here, we designed an alternative metabolic pathway for fermenting glucose to CA. An Escherichia coli strain that generates phenylalanine in this pathway also produces Wickerhamia fluorescens phenylpyruvate reductase and ferments glucose to d-phenyllactate (d-PhLA) (Fujita et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97: 8887–8894, 2013). Thereafter, phenyllactate dehydratase encoded by fldABCI genes in Clostridium sporogenes converts the resulting d-PhLA into CA. The phenyllactate dehydratase expressed by fldABCI in the d-PhLA-producing bacterium fermented glucose to CA, but d-PhLA fermentation and phenyllactate dehydration were aerobic and anaerobic processes, respectively, which disrupted high-yield CA fermentation in single batch cultures. We overcame this disruption by sequentially culturing the two strains under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. We optimized the incubation periods of the respective aeration steps to produce 1.7 g/L CA from glucose, which exceeded the yield from PAL-dependent glucose fermentation to CA 11-fold. This process is a novel, efficient alternative to conventional PAL-dependent CA production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmichael AJ, Earle MJ, Holbrey JD, McCormac PB, Seddon KR (1999) The heck reaction in ionic liquids: a multiphasic catalyst system. Org Lett 1:997–1000. doi:10.1021/ol9907771
Chong J, Poutaraud A, Hugueney P (2009) Metabolism and roles of stilbenes in plants. Plant Sci 177:143–155. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.05.012
Cui JD, Qiu JQ, Fan XW, Jia SR, Tan ZL (2014) Biotechnological production and applications of microbial phenylalanine ammonia lyase: a recent review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 34:258–268. doi:10.3109/07388551.2013.791660
Dickert S, Pierik AJ, Linder D, Buckel W (2000) The involvement of coenzyme A esters in the dehydration of (R)-phenyllactate to (E)-cinnamate by Clostridium sporogenes. Eur J Biochem 267:3874–3884. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01427.x
Dickert S, Pierik AJ, Buckel W (2002) Molecular characterization of phenyllactate dehydratase and its initiator from Clostridium sporogenes. Mol Microbiol 44:49–60. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02867.x
Djurdjevic I, Zelder O, Buckel W (2011) Production of glutaconic acid in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:320–322. doi:10.1128/aem.02049-10
Fujii T, Shimizu M, Doi Y, Fujita T, Ito T, Miura D, Wariishi H, Takaya N (2011) Novel fungal phenylpyruvate reductase belongs to D-isomer-specific 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1814:1669–1676. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.05.024
Fujita T, Nguyen HD, Ito T, Zhou S, Osada L, Tateyama S, Kaneko T, Takaya N (2013) Microbial monomers custom-synthesized to build true bio-derived aromatic polymers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8887–8894. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5078-4
Hans M, Sievers J, Muller U, Bill E, Vorholt JA, Linder D, Buckel W (1999) 2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydratase from Clostridium symbiosum. Eur J Biochem 265:404–414. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00748.x
Hans M, Buckel W, Bill E (2000) The iron-sulfur clusters in 2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydratase from Acidaminococcus fermentans. Biochemical and spectroscopic investigations. Eur J Biochem 267:7082–7093. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01809.x
Herrmann KM (1995) The shikimate pathway: early steps in the biosynthesis of aromatic compounds. Plant Cell 7:907–919. doi:10.1105/tpc.7.7.907
Humphreys JM, Chapple C (2002) Rewriting the lignin roadmap. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:224–229. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00257-1
Johnson JR (2011) The Perkin reaction and related reactions. Org React 1:210–265. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or001.08
Jones G (2011) The Knoevenagel condensation. Org React 15:204–599. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or015.02
Kaneko T, Thi TH, Shi DJ, Akashi M (2006) Environmentally degradable, high-performance thermoplastics from phenolic phytomonomers. Nat Mater 5:966–970. doi:10.1038/nmat1778
Kawaguchi H, Uematsu K, Ogino C, Teramura H, Niimi-Nakamura S, Tsuge Y, Hasunuma T, Oinuma K, Takaya N, Kondo A (2014) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of kraft pulp by recombinant Escherichia coli for phenyllactic acid production. Biochem Eng J 88:188–194. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2014.04.014
Kawaguchi H, Teramura H, Uematsu K, Hara KY, Hasunuma T, Hirano K, Sazuka T, Kitano H, Tsuge Y, Kahar P, Niimi-Nakamura S, Oinuma K, Takaya N, Kasuga S, Ogino C, Kondo A (2015) Phenyllactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of pretreated sorghum bagasse. Bioresour Technol 182:169–178. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.097
Kikuchi Y, Tsujimoto K, Kurahashi O (1997) Mutational analysis of the feedback sites of phenylalanine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:761–762
Limem I, Guedon E, Hehn A, Bourgaud F, Chekir Ghedira L, Engasser JM, Ghoul M (2008) Production of phenylpropanoid compounds by recombinant microorganisms expressing plant-specific biosynthesis genes. Process Biochem 43:463–479. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2008.02.001
Mack M, Bendrat K, Zelder O, Eckel E, Linder D, Buckel W (1994) Location of the two genes encoding glutaconate coenzyme A-transferase at the beginning of the hydroxyglutarate operon in Acidaminococcus fermentans. Eur J Biochem 226:41–51. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00t41.x
Nguyen HD, Kaneko T, Takaya N, Fujita T, Ito T (2016) Fermentation of aromatic lactate monomer and its polymerization to produce highly thermoresistant bioplastics. Polym J 48:81–89. doi:10.1038/pj.2015.80
Nijkamp K, van Luijk N, de Bont JA, Wery J (2005) The solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 as host for the production of cinnamic acid from glucose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:170–177. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-1973-7
Noda S, Miyazaki T, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Kondo A (2012) Production of Streptoverticillium cinnamoneum transglutaminase and cinnamic acid by recombinant Streptomyces lividans cultured on biomass-derived carbon sources. Bioresour Technol 104:648–651. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.045
Perrenoud A, Sauer U (2005) Impact of global transcriptional regulation by ArcA, ArcB, Cra, Crp, Cya, Fnr, and Mlc on glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:3171–3179. doi:10.1128/JB.187.9.3171-3179.2005
Pitsch C, Simon H (1982) The stereochemical course of the water elimination from (2R)-phenyllactate in the amino acid fermentation of Clostridium sporogenes. Hoppe Seyler’s Z Physiol Chem 363:1253–1257
Roscoe EH (1881) Indigo and its artificial production. Nature 24:227–231
Sova M (2012) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of cinnamic acid derivatives. Mini-Rev Med Chem 12:749–767. doi:10.2174/138955712801264792#sthash.yoWU70ge.dpuf
Sprenger GA (2007) From scratch to value: engineering Escherichia coli wild type cells to the production of L-phenylalanine and other fine chemicals derived from chorismate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:739–749. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-0931-y
Surburg H, Panten J (2006) Common fragrance and flavor materials: preparation, properties and uses. WILEY-VCH, Weinheim
Thiemann T (2007) Solventless Wittig olefination with fluorinated benzaldehydes. J Chem Res 2007:336–341. doi:10.3184/030823407X225464
Vannelli T, Wei Qi W, Sweigard J, Gatenby AA, Sariaslani FS (2007) Production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid from glucose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli by expression of heterologous genes from plants and fungi. Metab Eng 9:142–151. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2006.11.001
Vargas-Tah A, Gosset G (2015) Production of cinnamic and p-hydroxycinnamic acids in engineered microbes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:116. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2015.00116
Vargas-Tah A, Martínez LM, Hernández-Chávez G, Rocha M, Martínez A, Bolívar F, Gosset G (2015) Production of cinnamic and p-hydroxycinnamic acid from sugar mixtures with engineered Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 14:1–12. doi:10.1186/s12934-014-0185-1
Xiang L, Moore BS (2005) Biochemical characterization of a prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia lyase. J Bacteriol 187:4286–4289. doi:10.1128/JB.187.12.4286-4289.2005
Zhang X, Liu CJ (2015) Multifaceted regulations of gateway enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Mol Plant 8:17–27. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.001
Acknowledgments
We thank Norma Foster for critical reading of the manuscript. This study was supported by the Advanced Low Carbon Technology Research and Development Program (5100270) from the Japan Science and Technology Agency [JST-ALCA].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Shunsuke Masuo and Yuta Kobayashi contributed equally to this work as first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuo, S., Kobayashi, Y., Oinuma, KI. et al. Alternative fermentation pathway of cinnamic acid production via phenyllactic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 8701–8709 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7623-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7623-4