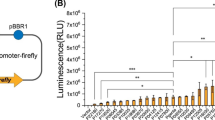
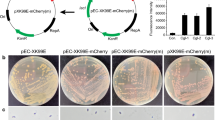
Abstract
Corynebacterium glutamicum is a non-pathogenic, non-sporulating Gram-positive soil bacterium that has been used for the industrial production of various proteins and chemicals. To achieve enhanced and economical production of target molecules, the development of strong auto-inducible promoters is desired, which can be activated without expensive inducers and has significant advantages for industrial-scale use. Here, we developed a stationary-phase gene expression system by engineering a sigma factor B (SigB)-dependent promoter that can be activated during the transition phase between exponential and stationary growth phases in C. glutamicum. First, the inducibilities of three well-known SigB-dependent promoters were examined using super-folder green fluorescent protein as a reporter protein, and we found that promoter of cg3141 (P cg3141 ) exhibited the highest inducibility. Next, a synthetic promoter library was constructed by randomizing the flanking and space regions of P cg3141 , and the stationary-phase promoters exhibiting high strengths were isolated via FACS-based high-throughput screening. The isolated synthetic promoter (P4-N14) showed a 3.5-fold inducibility and up to 20-fold higher strength compared to those of the original cg3141 promoter. Finally, the use of the isolated P4-N14 for fed-batch cultivation was verified with the production of glutathione S-transferase as a model protein in a lab-scale (5-L) bioreactor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker J, Wittmann C (2012) Bio-based production of chemicals, materials and fuels–Corynebacterium glutamicum as versatile cell factory. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:631–640
Brune I, Götker S, Schneider J, Rodionov DA, Tauch A (2012) Negative transcriptional control of biotin metabolism genes by the TetR-type regulator BioQ in biotin-auxotrophic Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. J Biotechnol 159:225–234
Cao Y, Xian M (2011) Production of phloroglucinol by Escherichia coli using a stationary-phase promoter. Biotechnol Lett 33:1853–1858
Choi JW, Yim SS, Lee SH, Kang TJ, Park SJ, Jeong KJ (2015) Enhanced production of gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) in recombinant Corynebacterium gluatamicum by expressing glutamate decarboxylase active in expanded pH range. Microb Cell Factories 1:1–11
Chou CH, Aristidou AA, Meng SY, Bennett GN, San KY (1995) Characterization of a pH-inducible promoter system for high-level expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:186–192
Donovan RS, Robinson C, Glick B (1996) Review: optimizing inducer and culture conditions for expression of foreign proteins under the control of the lac promoter. J Ind Microbiol 16:145–154
Ehira S, Shirai T, Teramoto H, Inui M, Yukawa H (2008) Group 2 sigma factor SigB of Corynebacterium glutamicum positively regulates glucose metabolism under conditions of oxygen deprivation. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5146–5152
Halgasova N, Bukovska G, Ugorcakova J, Timko J, Kormanec J (2002) The Brevibacterium flavum sigma factor SigB has a role in the environmental stress response. FEMS Microbiol Lett 216:77–84
Hammer K, Mijakovic I, Jensen PR (2006) Synthetic promoter libraries–tuning of gene expression. Trends Biotechnol 24:53–55
Hansen LH, Knudsen S, Sørensen SJ (1998) The effect of the lacY gene on the induction of IPTG inducible promoters, studied in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Curr Microbiol 36:341–347
Huang D, Holtz WJ, Maharbiz MM (2012) A genetic bistable switch utilizing nonlinear protein degradation. J Biol Eng 6:9
Ikeda M, Nakagawa S (2003) The Corynebacterium glutamicum genome: features and impacts on biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:99–109
Jensen PR, Hammer K (1998) The sequence of spacers between the consensus sequences modulates the strength of prokaryotic promoters. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:82–87
Kalinowski J, Bathe B, Bartels D, Bischoff N, Bott M, Burkovski A, Dusch N, Eggeling L, Eikmanns BJ, Gaigalat L, Goesmann A, Hartmann M, Huthmacher K, Krämer R, Linke B, McHardy AC, Meyer F, Möckel B, Pfefferle W, Pühler A, Rey DA, Rückert C, Rupp O, Sahm H, Wendisch VF, Woegräbe I, Tauch A (2003) The complete Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 genome sequence and its impact on the production of L-aspartate-derived amino acids and vitamins. J Biotechnol 104:5–25
Khosla C, Bailey JE (1989) Characterization of the oxygen-dependent promoter of the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 171:5595–6004
Kinoshita S, Udaka S, Shimono M (1957) Studies on the amino acid fermentation. J Gen Appl Microbiol 3:193–205
Larisch C, Nakunst D, Hüser AT, Tauch A, Kalinowski J (2007) The alternative sigma factor SigB of Corynebacterium glutamicum modulates global gene expression during transition from exponential growth to stationary phase. BMC Genomics 8:4
Lipscomb ML, Mark CM, Dhinakar SK (2004) Production of a secreted glycoprotein from an inducible promoter system in a perfusion bioreactor. Biotechnol Prog 20:1402–1407
Liu X, Yang Y, Zhang W, Sun Y, Peng F, Jeffrey L, Harvey L, McNeil B, Bai Z (2015) Expression of recombinant protein using Corynebacterium glutamicum: progress, challenges and applications. Criti Rev Biotechnol 15:1–13
Mijakovic I, Petranovic D, Jensen PR (2005) Tunable promoters in systems biology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:329–335
Miksch G, Bettenworth F, Friehs K, Flaschel E, Saalbach A, Twellmann T, Nattkemper TW (2005) Libraries of synthetic stationary-phase and stress promoters as a tool for fine-tuning of expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 120:25–37
Nishimura T, Teramoto H, Inui M, Yukawa H (2014) Corynebacterium glutamicum ArnR controls expression of nitrate reductase operon narKGHJI and nitric oxide (NO)-detoxifying enzyme gene hmp in an NO-responsive manner. J Bacteriol 196:60–69
Nishimura T, Teramoto H, Vertès AA, Inui M, Yukawa H (2008) ArnR, a novel transcriptional regulator, represses expression of the narKGHJI operon in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol 190:3264–3273
Nocadello S, Swennen EF (2012) The new pLAI (lux regulon based auto-inducible) expression system for recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 11:1–10
Okai N, Takahashi C, Hatada K, Ogino C, Kondo A (2014) Disruption of pknG enhances production of gamma-aminobutyric acid by Corynebacterium glutamicum expressing glutamate decarboxylase. AMB Express 4:20
Oguiza JA, Marcos AT, Martin JF (1997) Transcriptional analysis of the sigA and sigB genes of Brevibacterium lactofermentum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:111–117
Panahi R, Vasheghani-Farahani E, Shojaosadati S, Bambai B (2014) Auto-inducible expression system based on the SigB-dependent ohrB promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Biol 48:852–857
Park JH, Kwon HW, Jeong KJ (2013) Development of a plasmid display system with an Oct-1 DNA-binding domain suitable for in vitro screening of engineered proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 116:246–252
Park JU, Jo JH, Kim YJ, Chung SS, Lee JH, Lee HH (2008) Construction of heat-inducible expression vector of Corynebacterium glutamicum and C. ammoniagenes: fusion of lambda operator with promoters isolated from C. ammoniagenes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:639–647
Park KJ, Lee CH, Kim A, Jeong KJ, Kim CH, Kim YS (2012) Death receptors 4 and 5 activate Nox1 NADPH oxidase through riboflavin kinase to induce reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem 287:3313–3325
Park SH, Kim HU, Kim TY, Park JS, Kim SS, Lee SY (2014) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production. Nat Commun 5:4618
Pátek M, Nešvera J (2011) Sigma factors and promoters in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 154:101–113
Pédelacq JD, Cabantous S, Tran T, Terwilliger TC, Waldo GS (2006) Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 24:79–88
Platzen L, Koch-Koerfges A, Weil B, Brocker M, Bott M (2014) Role of flavohaemoprotein Hmp and nitrate reductase NarGHJI of Corynebacterium glutamicum for coping with nitrite and nitrosative stress. FEMS Microbiol Lett 350:239–248
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, Third edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Puhler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Takahashi C, Shirakawa J, Tsuchidate T, Okai N, Hatada K, Nakayama H, Tateno T, Ogino C, Kondo A (2012) Robust production of gamma-amino butyric acid using recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum expressing glutamate decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. Enzym Microb Technol 51:171–176
Wanner BL, Wilmes MR, Young DC (1988) Control of bacterial alkaline phosphatase synthesis and variation in an Escherichia coli K-12 phoR mutant by adenyl cyclase, the cyclic AMP receptor protein, and the phoM operon. J Bacteriol 170:1092–1102
Woo HM, Park JB (2014) Recent progress in development of synthetic biology platforms and metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 180:43–51
Yim SS, An SJ, Kang M, Lee J, Jeong KJ (2013) Isolation of fully synthetic promoters for high-level gene expression in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:2959–2969
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of Global Frontier Project (Grant no. NRF-2014M3A6A8066443) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant no. NRF-2015R1A2A2A01007674) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 246 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.J., Yim, S.S., Choi, J.W. et al. Development of a potential stationary-phase specific gene expression system by engineering of SigB-dependent cg3141 promoter in Corynebacterium glutamicum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 4473–4483 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7297-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7297-y