Abstract
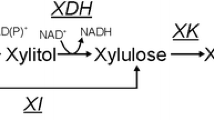
Xylose is present with glucose in lignocellulosic streams available for valorisation to biochemicals. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has excellent characteristics as a host for the bioconversion, except that it strongly prefers glucose to xylose, and the co-consumption remains a challenge. Further, since xylose is not a natural substrate of S. cerevisiae, the regulatory response it induces in an engineered strain cannot be expected to have evolved for its utilisation. Xylose-induced effects on metabolism and gene expression during anaerobic growth of an engineered strain of S. cerevisiae on medium containing both glucose and xylose medium were quantified. The gene expression of S. cerevisiae with an XR-XDH pathway for xylose utilisation was analysed throughout the cultivation: at early cultivation times when mainly glucose was metabolised, at times when xylose was co-consumed in the presence of low glucose concentrations, and when glucose had been depleted and only xylose was being consumed. Cultivations on glucose as a sole carbon source were used as a control. Genome-scale dynamic flux balance analysis models were simulated to analyse the metabolic dynamics of S. cerevisiae. The simulations quantitatively estimated xylose-dependent flux dynamics and challenged the utilisation of the metabolic network. A relative increase in xylose utilisation was predicted to induce the bi-directionality of glycolytic flux and a redox challenge even at low glucose concentrations. Remarkably, xylose was observed to specifically delay the glucose-dependent repression of particular genes in mixed glucose-xylose cultures compared to glucose cultures. The delay occurred at a cultivation time when the metabolic flux activities were similar in the both cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrehman D, Monteiro PT, Teixeira MC, Mira NP, Lourenço AB, dos Santos SC, Cabrito TR, Francisco AP, Madeira SC, Aires RS, Oliveira AL, Sá-Correia I, Freitas AT (2011) YEASTRACT: providing a programmatic access to curated transcriptional regulatory associations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through a web services interface. Nucleic Acids Res 39:136–140
Aristidou A, Penttilä M (2000) Metabolic engineering applications to renewable resource utilization. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:187–198
Aung HW, Henry SA, Walker LP (2013) Revising the representation of fatty acid, glycerolipid, and glycerophospholipid metabolism in the consensus model of yeast metabolism. Ind Biotechnol 9:215–228
Bergdahl B, Sandström AG, Borgström C, Boonyawan T, van Niel EW, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2013) Engineering yeast hexokinase 2 for improved tolerance toward xylose-induced inactivation. PLoS ONE 8:e75055
Bertilsson M, Andersson J, Lidén G (2008) Modeling simultaneous glucose and xylose uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from kinetics and gene expression of sugar transporters. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:369–377
Brandriss MC, Magasanik B (1979) Genetics and physiology of proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: enzyme induction by proline. J Bacteriol 140:498–503
Brat D, Boles E, Wiedemann B (2009) Functional expression of a bacterial xylose isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2304–2311
Bruinenberg PM, de Bot PHM, van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1983) The role of redox balances in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:287–292
Cadière A, Galeote V, Dequin S (2010) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae zinc factor protein Stb5p is required as a basal regulator of the pentose phosphate pathway. FEMS Yeast Res 10:819–827
Castrillo JI, Zeef LA, Hoyle DC, Zhang N, Hayes A, Gardner DC, Cornell MJ, Petty J, Hakes L, Wardleworth L, Rash B, Brown M, Dunn WB, Broadhurst D, O’Donoghue K, Hester SS, Dunkley TP, Hart SR, Swainston N, Li P, Gaskell SJ, Paton NW, Lilley KS, Kell DB, Oliver SG (2007) Growth control of the eukaryote cell: a systems biology study in yeast. J Biol 6:4
Cherest H, Davidian JC, Thomas D, Benes V, Ansorge W, Surdin-Kerjan Y (1997) Molecular characterization of two high affinity sulfate transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 145:627–635
Demeke MM, Dietz H, Li Y, Foulquié-Moreno MR, Mutturi S, Deprez S, Den Abt T, Bonini BM, Liden G, Dumortier F, Verplaetse A, Boles E, Thevelein JM (2013) Development of a D-xylose fermenting and inhibitor tolerant industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high performance in lignocellulose hydrolysates using metabolic and evolutionary engineering. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:89
Dunn CD, Jensen RE (2003) Suppression of a defect in mitochondrial protein import identifies cytosolic proteins required for viability of yeast cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 165:35–45
Eliasson A, Boles E, Johansson B, Osterberg M, Thevelein JM, Spencer-Martins I, Juhnke H, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Xylulose fermentation by mutant and wild-type strains of Zygosaccharomyces and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:376–382
Feddersen S, Neergaard TB, Knudsen J, Faergeman NJ (2007) Transcriptional regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis is linked to fatty acid metabolism by an acyl-CoA-binding-protein-dependent mechanism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 407:219–230
Fendt SM, Oliveira AP, Christen S, Picotti P, Dechant RC, Sauer U (2010) Unraveling condition-dependent networks of transcription factors that control metabolic pathway activity in yeast. Mol Syst Biol 6:432
Fernández R, Herrero P, Fernández MT, Moreno F (1986) Mechanism of inactivation of hexokinase PII of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by D-xylose. J Gen Microbiol 132:3467–3472
Fernández R, Herrero P, Fernández E, Fernández T, López-Boado YS, Moreno F (1988) Autophosphorylation of yeast hexokinase PII. J Gen Microbiol 134:2493–2498
Futschik ME, Carlisle B (2005) Noise-robust soft clustering of gene expression time-course data. J Bioinforma Comput Biol 3:965–988
Gancedo JM (1998) Yeast carbon catabolite repression. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:334–361
Gsell M, Mascher G, Schuiki I, Ploier B, Hrastnik C, Daum G (2013) Transcriptional response to deletion of the phosphatidylserine decarboxylase Psd1p in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 8:e77380
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gardonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiology 148:2783–2788
Heinisch JJ, Müller S, Schlüter E, Jacoby J, Rodicio R (1998) Investigation of two yeast genes encoding putative isoenzymes of phosphoglycerate mutase. Yeast 14:203–213
Herrgård MJ, Swainston N, Dobson P, Dunn WB, Arga KY, Arvas M, Blüthgen N, Borger S, Costenoble R, Heinemann M, Hucka M, Le Novère N, Li P, Liebermeister W, Mo ML, Oliveira AP, Petranovic D, Pettifer S, Simeonidis E, Smallbone K, Spasić I, Weichart D, Brent R, Broomhead DS, Westerhoff HV, Kirdar B, Penttilä M, Klipp E, Palsson BØ, Sauer U, Oliver SG, Mendes P, Nielsen J, Kell DB (2008) A consensus yeast metabolic reconstruction obtained from a community approach to systems biology. Nat Biotechnol 26:1155–1160
Hjersted JL, Henson MA (2009) Steady-state and dynamic flux balance analysis of ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IET Syst Biol 3:167–179
Huberts DH, Niebel B, Heinemann M (2012) A flux-sensing mechanism could regulate the switch between respiration and fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 12:118–128
Huh WK, Falvo JV, Gerke LC, Carroll AS, Howson RW, Weissman JS, O’Shea EK (2003) Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425:686–691
Jeppsson M, Johansson B, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2002) Reduced oxidative pentose phosphate pathway flux in recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains improves the ethanol yield from xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1604–1609
Jeppsson M, Johansson B, Jensen PR, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2003) The level of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity strongly influences xylose fermentation and inhibitor sensitivity in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Yeast 20:1263–1272
Jeppsson M, Bengtsson O, Franke K, Lee H, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2006) The expression of a Pichia stipitis xylose reductase mutant with higher K(M) for NADPH increases ethanol production from xylose in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:665–673
Jin YS, Laplaza JM, Jeffries TW (2004) Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose metabolism exhibits a respiratory response. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6816–6825
Jouhten P, Wiebe M, Penttilä M (2012) Dynamic flux balance analysis of the metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during the shift from fully respirative or respirofermentative metabolic states to anaerobiosis. FEBS J 279:3338–3354
Karhumaa K, Påhlman AK, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Levander F, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2009) Proteome analysis of the xylose-fermenting mutant yeast strain TMB 3400. Yeast 26:371–382
Kim JH, Block DE, Mills DA (2010) Simultaneous consumption of pentose and hexose sugars: an optimal microbial phenotype for efficient fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:1077–1085
Kim SR, Park YC, Jin YS, Seo JH (2013) Strain engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced xylose metabolism. Biotechnol Adv 31:851–861
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Kötter P, Amore R, Hollenberg CP, Ciriacy M (1990) Isolation and characterization of the Pichia-stipitis xylitol dehydrogenase gene, Xyl2, and construction of a xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces-cerevisiae transformant. Curr Genet 18:493–500
Krahulec S, Petschacher B, Wallner M, Longus K, Klimacek M, Nidetzky B (2010) Fermentation of mixed glucose-xylose substrates by engineered strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: role of the coenzyme specificity of xylose reductase, and effect of glucose on xylose utilization. Microb Cell Factories 9:16
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MSM, de Laat WTAM, den Ridder JJJ, Op den Camp HJM, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylose isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae? FEMS Yeast Res 4:69–78
Kuyper M, Hartog MM, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJ, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 5:399–409
Larochelle M, Drouin S, Robert F, Turcotte B (2006) Oxidative stress-activated zinc cluster protein Stb5 has dual activator/repressor functions required for pentose phosphate pathway regulation and NADPH production. Mol Cell Biol 26:6690–6701
Linck A, Vu XK, Essl C, Hiesl C, Boles E, Oreb M (2014) On the role of GAPDH isoenzymes during pentose fermentation in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 14:389–398
Madhavan A, Tamalampudi S, Ushida K, Kanai D, Katahira S, Srivastava A, Fukuda H, Bisaria VS, Kondo A (2009) Xylose isomerase from polycentric fungus Orpinomyces: gene sequencing, cloning, and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for bioconversion of xylose to ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1067–1078
Mahadevan R, Edwards JS, Doyle FJ III (2002) Dynamic flux balance analysis of diauxic growth in Escherichia coli. Biophys J 83:1331–1340
Martínez JL, Bordel S, Hong KK, Nielsen J (2014) Gcn4p and the Crabtree effect of yeast: drawing the causal model of the Crabtree effect in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and explaining evolutionary trade-offs of adaptation to galactose through systems biology. FEMS Yeast Res 14:654–662
Matsushika A, Goshima T, Hoshino T (2014) Transcription analysis of recombinant industrial and laboratory Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains reveals the molecular basis for fermentation of glucose and xylose. Microb Cell Factories 13:16
Mayer FV, Heath R, Underwood E, Sanders MJ, Carmena D, McCartney RR, Leiper FC, Xiao B, Jing C, Walker PA, Haire LF, Ogrodowicz R, Martin SR, Schmidt MC, Gamblin SJ, Carling D (2011) ADP regulates SNF1, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Metab 14:707–714
Meadows ML, Karnik R, Lam H, Forestell S, Snedecor B (2010) Application of dynamic flux balance analysis to an industrial Escherichia coli fermentation. Metab Eng 12:150–160
Meinander NQ, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1997) Influence of cosubstrate concentration on xylose conversion by recombinant, XYL1-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a comparison of different sugars and ethanol as cosubstrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1959–1964
Mojzita D, Hohmann S (2006) Pdc2 coordinates expression of the THI regulon in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Genet Genomics 276:147–161
Molin M, Norbeck J, Blomberg A (2003) Dihydroxyacetone kinases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are involved in detoxification of dihydroxyacetone. J Biol Chem 278:1415–1423
Monteiro PT, Mendes N, Teixeira MC, d’Orey S, Tenreiro S, Mira N, Pais H, Francisco AP, Carvalho AM, Lourenço A, Sá-Correia I, Oliveira AL, Freitas AT (2008) YEASTRACT-DISCOVERER: new tools to improve the analysis of transcriptional regulatory associations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 36:132–136
Norbeck J, Blomberg A (1997) Metabolic and regulatory changes associated with growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in 1.4 M NaCl. Evidence for osmotic induction of glycerol dissimilation via the dihydroxyacetone pathway. J Biol Chem 272:5544–5554
Oliveira AP, Patil KR, Nielsen J (2008) Architecture of transcriptional regulatory circuits is knitted over the topology of bio-molecular interaction networks. BMC Syst Biol 2:17
Özcan S, Johnston M (1995) Three different regulatory mechanisms enable yeast hexose transporter (HXT) genes to be induced by different levels of glucose. Mol Cell Biol 15:1564–1572
Pahlman AK, Granath K, Ansell R, Hohmann S, Adler L (2001) The yeast glycerol 3-phosphatases Gpp1p and Gpp2p are required for glycerol biosynthesis and differentially involved in the cellular responses to osmotic, anaerobic, and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 276:3555–3563
Patil KR, Nielsen J (2005) Uncovering transcriptional regulation of metabolism by using metabolic network topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:2685–2689
Pitkänen JP, Aristidou A, Salusjärvi L, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2003) Metabolic flux analysis of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using continuous culture. Metab Eng 5:16–31
R Development Core Team (2005) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
R Development Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rachidi N, Martinez MJ, Barre P, Blondin B (2000) Saccharomyces cerevisiae PAU genes are induced by anaerobiosis. Mol Microbiol 35:1421–1430
Regenberg B, Grotkjaer T, Winther O, Fausbøll A, Akesson M, Bro C, Hansen LK, Brunak S, Nielsen J (2006) Growth-rate regulated genes have profound impact on interpretation of transcriptome profiling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biol 7:R107
Rintala E, Toivari M, Pitkänen JP, Wiebe MG, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2009) Low oxygen levels as a trigger for enhancement of respiratory metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Genomics 10:461
Rizzi M, Erlemann P, Bui-Thanh NA, Dellweg H (1988) Xylose fermentation by yeast. 4. Purification and kinetics of xylose reductase from Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:148–154
Rizzi M, Harwart K, Erlemann P, Bui-Thanh NA, Dellweg H (1989) Purification and properties of the NAD+-xylitol dehydrogenase from the yeast Pichia stipitis. J Ferment Bioeng 67:20–24
Runquist D, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Bettiga M (2009) Increased expression of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and gluconeogenesis in anaerobically growing xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 8:49
Saint-Prix F, Bönquist L, Dequin S (2004) Functional analysis of the ALD gene family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during anaerobic growth on glucose: the NADP+-dependent Ald6p and Ald5p isoforms play a major role in acetate formation. Microbiology 150:2209–2220
Sainz J, Pizarro F, Pérez-Correa JR, Agosin E (2003) Modeling of yeast metabolism and process dynamics in batch fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:818–828
Salusjärvi L, Pitkänen JP, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2006) Transcription analysis of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals novel responses to xylose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 128:237–261
Salusjärvi L, Kankainen M, Soliymani R, Pitkänen JP, Penttilä M, Ruohonen L (2008) Regulation of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 7:18
Salusjärvi L, Kaunisto S, Holmström S, Vehkomäki ML, Koivuranta K, Pitkänen JP, Ruohonen L (2013) Overexpression of NADH-dependent fumarate reductase improves D-xylose fermentation in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:1383–1392
Santiago TC, Mamoun CB (2003) Genome expression analysis in yeast reveals novel transcriptional regulation by inositol and choline and new regulatory functions for Opi1p, Ino2p, and Ino4p. J Biol Chem 278:38723–38730
Schellenberger J, Que R, Fleming RMT, Thiele I, Orth JD, Feist AM, Zielinski DC, Bordbar A, Lewis NE, Rahmanian S, Kang J, Hyduke DR, Palsson BØ (2011) Quantitative prediction of cellular metabolism with constraint-based models: the COBRA Toolbox v2.0. Nat Protoc 6:1290–1307
Shirra MK, McCartney RR, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Schmidt MC, Arndt KM (2008) A chemical genomics study identifies Snf1 as a repressor of GCN4 translation. J Biol Chem 283:35889–35898
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:1–25
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry R, Huber W (eds) Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and bioconductor. Springer, New York, pp 397–420
Subtil T, Boles E (2012) Competition between pentoses and glucose during uptake and catabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:14
Teixeira MC, Monteiro P, Jain P, Tenreiro S, Fernandes AR, Mira NP, Alenquer M, Freitas AT, Oliveira AL, Sá-Correia I (2006) The YEASTRACT database: a tool for the analysis of transcription regulatory associations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 34:446–451
Toivari MH, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2001) Conversion of xylose to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae: importance of xylulokinase (XKS1) and oxygen availability. Metab Eng 3:236–249
Toivari MH, Salusjärvi L, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2004) Endogenous xylose pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3681–3686
Turcotte B, Liang XB, Robert F, Soontorngun N (2010) Transcriptional regulation of nonfermentable carbon utilization in budding yeast. FEMS Yeast Res 10:2–13
Turkia H, Siren H, Pitkanen JP, Wiebe M, Penttilä M (2010) Capillary electrophoresis for the monitoring of carboxylic acid production by Gluconobacter oxydans. J Chromatogr A 1217:1537–1542
Valadi H, Valadi A, Ansell R, Gustafsson L, Adler L, Norbeck J, Blomberg A (2004) NADH-reductive stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induces the expression of the minor isoform of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (TDH1). Curr Genet 45:90–95
Vandenbol M, Jauniaux JC, Grenson M (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PUT4 proline-permease-encoding gene: similarities between CAN1, HIP1 and PUT4 permeases. Gene 83:153–159
Varma A, Palsson BO (1994) Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Microbiology 60:3724–3731
Verduyn C, Postma E, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1992) Effect of benzoic acid on metabolic fluxes in yeasts: a continuous-culture study on the regulation of respiration and alcoholic fermentation. Yeast 8:501–517
Vyas VK, Kuchin S, Carlson M (2001) Interaction of the repressors Nrg1 and Nrg2 with the Snf1 protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 158:563–572
Wahlbom CF, Cordero Otero RR, van Zyl WH, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Jönsson LJ (2003) Molecular analysis of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant with improved ability to utilize xylose shows enhanced expression of proteins involved in transport, initial xylose metabolism, and the pentose phosphate pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:740–746
Walfridsson M, Bao X, Anderlund M, Lilius G, Bülow L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1996) Ethanolic fermentation of xylose with Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring the Thermus thermophilus xylA gene, which expresses an active xylose (glucose) isomerase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4648–4651
Watanabe S, Saleh AA, Pack SP, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein engineered NADP+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 130:316–319
Westergaard SL, Oliveira AP, Bro C, Olsson L, Nielsen J (2007) A systems biology approach to study glucose repression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:134–145
Wolak N, Kowalska E, Kozik A, Rapala-Kozik M (2014) Thiamine increases the resistance of baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae against oxidative, osmotic and thermal stress, through mechanisms partly independent of thiamine diphosphate-bound enzymes. FEMS Yeast Res 14:1249–1262
Woods RA, Gietz RD (2001) High-efficiency transformation of plasmid DNA into yeast. Methods Mol Biol 177:85–97
Youk H, van Oudenaarden A (2009) Growth landscape formed by perception and import of glucose in yeast. Nature 462:875–879
Yuan T, Ren Y, Meng K, Feng Y, Yang P, Wang S, Shi P, Wang L, Xie D, Yao B (2011) RNA-Seq of the xylose-fermenting yeast Scheffersomyces stipitis cultivated in glucose or xylose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:1237–1249
Zhou H, Cheng JS, Wang BL, Fink GR, Stephanopoulos G (2012) Xylose isomerase overexpression along with engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway and evolutionary engineering enable rapid xylose utilization and ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:611–622
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Stefan Bruder for his help in the wet-lab work of the gene expression analysis and Sami Holmström for his help in the analysis of cultivation samples. We thank Dr. Marilyn Wiebe for the valuable comments on the study. Heidi Turkia is thanked for measuring the minor acid concentrations. Additionally, Dr. Maurizio Bettiga from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, is thanked for curing VTT C-10880 for its uracil auxotrophy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research did not involve any human participants or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
The research has received funding from the European Commission, the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under the project NEMO (grant agreement no. 222699). PJ acknowledges funding from the Academy of Finland for a Postdoctoral research (grant 140380).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alff-Tuomala, S., Salusjärvi, L., Barth, D. et al. Xylose-induced dynamic effects on metabolism and gene expression in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae in anaerobic glucose-xylose cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 969–985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7038-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7038-7