Abstract
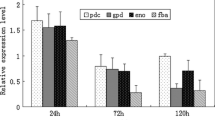
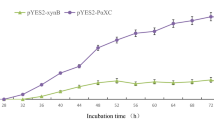
The fodder yeast Candida utilis is able to use xylose mono- and oligomers as sources of carbon but not the abundant polymer xylan. C. utilis transformants producing the Penicillium simplicissimum xylanase XynA were constructed using expression vectors encoding fusions of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mfα1 pre-pro secretion leader to XynA. The Mfα1-XynA fusion was efficiently processed in transformants and XynA was secreted almost quantitatively into the culture medium. Secreted XynA was enzymatically active and allowed transformants to grow on xylan as the sole carbon source. Addition of a second expression unit for the heterologous green fluorescent protein (GFP) generated C. utilis transformants, which showed intracellular GFP fluorescence during growth on xylan. The results suggest that xylanase-producing C. utilis is suited as a cost-effective host organism for heterologous protein production and for other biotechnical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekatorou A, Psaríanos C, Koutinas AA (2006) Production of food grade yeasts. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:407–415
Biely P (1985) Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends Biotechnol 3:286–290
Buerth C, Heilmann CJ, Klis FM, de Koster CG, Ernst JF, Tielker D (2011) Growth-dependent secretome of Candida utilis. Microbiology 157:2493–2503
Caplan S, Green R, Rocco J, Kurjan J (1991) Glycosylation and structure of the yeast MFα1-factor precursor is important for efficient transport through the secretory pathway. J Bacteriol 173:627–635
Delic M, Valli M, Graf AB, Pfeffer M, Mattanovich D, Gasser B (2013) The secretory pathway: exploring yeast diversity. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:872–914
Demeke MM, Dietz H, Li Y, Foulquie-Moreno MR, Mutturi S, Deprez S, Den Abt T, Bonini BM, Lidén G, Dumortier F, Verplaetse A, Boles E, Thevelein JM (2013) Development of a D-xylose fermenting and inhibitor tolerant industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high performance in lignocellulose hydrolysates using metabolic and evolutionary engineering. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:89
Dodd D, Cann IK (2009) Enzymatic deconstruction of xylan for biofuel production. Glob Change Biol Bioenergy 1:2–17
Gübitz GM, Haltrich D, Latal B, Steiner W (1997) Mode of depolymerisation of hemicellulose by various mannanases and xylanases in relation to their ability to bleach softwood pulp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 4:658–662
Harris AD, Ramalingam C (2010) Xylanases and its application in food industry: a review. J Exp Sci 1:1-11
Hong YR, Chen YL, Farh L, Yang WJ, Liao CH, Shiuan D (2006) Recombinant Candida utilis for the production of biotin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:211–221
Idiris A, Tohda H, Kumagai H, Takegawa K (2010) Engineering of protein secretion in yeast: strategies and impact on protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:403–417
Ikushima S, Fujii T, Kobayashi O (2009) Efficient gene disruption in the high-ploidy yeast Candida utilis using the Cre-loxP system. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:879–884
Jeffries TW, Jin YS (2004) Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:495–509
Katahira S, Fujita Y, Mizuike, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2004) Construction of a xylan-fermenting strain through codisplay of xylanolytic enzymes on the surface of xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5407–5414
Kim B, Du J, Eriksen DT, Zhao H (2013) Combinatorial design of a highly efficient xylose-utilizing pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of cellulosic biofuels. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:931-941
Kondo K, Miura Y, Sone H, Kobayashi K, Iijima H (1997) High-level expression of a sweet protein, monellin, in the food yeast Candida utilis. Nat Biotechnol 15:453–457
Kunigo M, Buerth C, Tielker D, Ernst JF (2013) Heterologous protein secretion by Candida utilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7357–7368
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011) The yeasts—a taxonomic study. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Lee H, Biely P, Latta RK, Barbosa M, Schneider H (1986) Utilization of xylan by yeasts and its conversion to ethanol by Pichia stipitis strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:320–324
Matsushika A, Inoue H, Kodaki T, Sawayama S (2009) Ethanol production from xylose in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:37–53
Minter DW (2009) Cyberlindnera, a replacement name for Lindnera Kurtzman et al. nom. illegit. Mycotaxon 110:473–476
Obrdlik P, El-Bakkoury M, Hamacher T, Cappellaro C, Vilarino C, Fleischer C, Ellerbrok H, Kamuzinzi R, Ledent V, Blaudez D, Sanders D, Revuelta JL, Boles E, André B, Frommer WB (2004) K+ channel interactions detected by a genetic system optimized for systematic studies of membrane protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12242–12247
Öczan S, Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1991) Xylan hydrolysing enzymes of the yeast Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:190–195
Polizeli ML, Rizzatti AC, Monti R, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Amorim DS (2005) Xylanases from fungi: properties and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:577–591
Schmidt A, Schlacher A, Steiner W, Schwab H, Kratky C (1998) Structure of the xylanase from Penicillium simplicissimum. Protein Sci 7:2081–2088
Schmidt A, Gübitz GM, Kratky C (1999) Xylan binding subsite mapping in the xylanase from Penicillium simplicissimum using xylooligosaccharides as cryo-protectant. Biochemistry 38:2403–2412
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Sherman F, Fink G, Hicks J (1986) Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Tamakawa H, Ikushima S, Yoshida S (2011) Ethanol production from xylose by a recombinant Candida utilis strain expressing protein-engineered xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1994–2000
Tamakawa H, Ikushima S, Yoshida S (2012) Efficient production of L-lactic acid from xylose by a recombinant Candida utilis strain. J Biosci Bioeng 113:73–75
Toivola A, Yarrow D, van den Bosch E, van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1984) Alcoholic fermentation of D-xylose by yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:1221–1223
Tomita Y, Ikeo K, Tamakawa H, Gojobori T, Ikushima S (2012) Genome and transcriptome analysis of the food-yeast Candida utilis. PLoS One 7:e37226
Weber C, Farwick A, Benisch F, Brat D, Dietz H, Subtil T, Boles E (2010) Trends and challenges in the microbial production of lignocellulosic bioalcohol fuels. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1303–1315
Wilson RB, Davis D, Mitchell AP (1999) Rapid hypothesis testing with Candida albicans through gene disruption with short homology regions. J Bacteriol 181:1868–1874
Wohlbach DJ, Kuo A, Sato TK, Potts KM, Salamov AA, LaButti KM, Sun H, Clum A, Pangilinan JL, Lindquist EA, Lucas S, Lapidus A, Jin M, Gunawan C, Balan V, Dale BE, Jeffries TW, Zinkel R, Barry KW, Grigoriev IV, Gasch AP (2011) Comparative genomics of xylose-fermenting fungi for enhanced biofuel production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:13212–13217
Yanai T, Sato M (2001) Purification and characterization of an β-D-xylosidase from Candida utilis IFO 0639. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:527–533
Yu S, Jeppsson H, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1995) Xylulose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and xylose-fermenting yeast strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:314–320
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Cluster of Industrial Biotechnology NRW CLIB2021.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 127 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunigo, M., Buerth, C. & Ernst, J.F. Secreted xylanase XynA mediates utilization of xylan as sole carbon source in Candida utilis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 8055–8064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6703-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6703-1