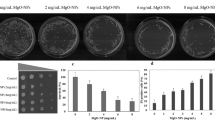
Abstract
As well-known antibiotic-producing and filamentous bacteria, streptomycetes can be an ideal model to study the effects of microgravity on microbial development and antibiotic production. In this study, the model organism Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) was exposed to simulated microgravity (SMG) on a rotating clinostat and microgravity (μg) on the Shenzhou-8 spacecraft. The strain exhibited some similar responses under both conditions. Compared with the controls, its life cycle in agar medium was shortened relatively, and the sporulation process was accelerated with higher accumulation of the gray spore pigment; the liquid cultures yielded more cell biomass, coupled with thicker, more fragmented, and well-dispersed hyphae of the μg spaceflight samples. Global transcriptional analysis verified that most of the differentially expressed genes involved in morphological differentiation of S. coelicolor were upregulated during days 4–6 under SMG conditions, notably the whi genes (whiD, sigF, and whiE). Production of actinorhodin (ACT) in agar cultures decreased under both conditions while undecylprodigiosin (RED) was produced earlier, which were consistent with the transcriptional levels of act and red gene clusters. Meanwhile, expression of the gene clusters for calcium-dependent antibiotic (CDA), methylenomycin (MMY), and a cryptic polyketide (CPK) was unchanged, downregulated, and upregulated, respectively, the latter of which might contribute to the enhanced activity of S. coelicolor against Bacillus subtilis under microgravity. Our study provides new insights into the morphological and secondary metabolic responses of streptomycetes to microgravity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aínsa JA, Parry HD, Chater KF (1999) A response regulator-like protein that functions at an intermediate stage of sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 34:607–619. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01630.x
Benoit MR, Klaus DM (2007) Microgravity, bacteria, and the influence of motility. Adv Space Res 39:1225–1232. doi:10.1089/ast.2010.0536
Benoit MR, Li W, Stodieck LS, Lam KS, Winther CL, Roane TM, Klaus DM (2006) Microbial antibiotic production aboard the International Space Station. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:403–411. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0098-3
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147. doi:10.1038/417141a
Bibb MJ (2005) Regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:208–215. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2005.02.016
Brungs S, Hauslage J, Hilbig R, Hemmersbach R, Anken R (2011) Effects of simulated weightlessness on fish otolith growth: clinostat versus rotating-wall vessel. Adv Space Res 48:792–798. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2011.04.014
Chater KF (1998) Taking a genetic scalpel to the Streptomyces colony. Microbiol-SGM 144:1465–1478. doi:10.1099/00221287-144-6-1465
Crabbé A, De Boever P, Van Houdt R, Moors H, Mergeay M, Cornelis P (2008) Use of the rotating wall vessel technology to study the effect of shear stress on growth behaviour of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Environ Microbiol 10:2098–2110. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01631.x
Crabbé A, Pycke B, Van Houdt R, Monsieurs P, Nickerson C, Leys N, Cornelis P (2010) Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to low shear modelled microgravity involves AlgU regulation. Environ Microbiol 12:1545–1564. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02184.x
Crabbé A, Schurr MJ, Monsieurs P, Morici L, Schurr J, Wilson JW, Ott CM, Tsaprailis G, Pierson DL, Stefanyshyn-Piper H, Nickerson CA (2011) Transcriptional and proteomic responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to spaceflight conditions involve Hfq regulation and reveal a role for oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1221–1230. doi:10.1128/Aem. 01582-10
Davis NK, Chater KF (1990) Spore color in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) involves the developmentally regulated synthesis of a compound biosynthetically related to polyketide antibiotics. Mol Microbiol 4:1679–1691. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00545.x
Demain AL, Fang A (2001) Secondary metabolism in simulated microgravity. Chem Rec 1:333–346. doi:10.1002/Tcr.1018
Eiermann P, Kopp S, Hauslage J, Hemmersbach R, Gerzer R, Ivanova K (2013) Adaptation of a 2-D clinostat for simulated microgravity experiments with adherent cells. Microgravity Sci Technol 25:153–159. doi:10.1007/s12217-013-9341-1
Fang A, Pierson DL, Mishra SK, Koenig DW, Demain AL (1997) Secondary metabolism in simulated microgravity: β-lactam production by Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 18:22–25. doi:10.1038/sj.jim.2900345
Fang A, Pierson DL, Mishra SK, Demain AL (2000) Growth of Streptomyces hygroscopicus in rotating-wall bioreactor under simulated microgravity inhibits rapamycin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:33–36. doi:10.1007/s002539900303
Flardh K, Buttner MJ (2009) Streptomyces morphogenetics: dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:36–49. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro1968
Gao C, Hindra MD, Yin C, Elliot MA (2012) Crp is a global regulator of antibiotic production in Streptomyces. MBio 3:e00407–e00412. doi:10.1128/mBio. 00407-12
Gottelt M, Kol S, Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb M, Takano E (2010) Deletion of a regulatory gene within the cpk gene cluster reveals novel antibacterial activity in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiol-SGM 156:2343–2353. doi:10.1099/Mic. 0.038281-0
Haneishi T, Kitahara N, Takiguch Y, Arai M, Sugawara S (1974) New antibiotics, methylenomycins A and B. I. Producing organism, fermentation and isolation, biological-activities and physical and chemical properties. J Antibiot 27:386–392. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.27.386
Hemmersbach R, Strauch SM, Seibt D, Schuber M (2006) Comparative studies on gravisensitive protists on ground (2D and 3D clinostats) and in microgravity. Microgravity Sci Technol 18:257–259. doi:10.1007/Bf02870423
Herranz R, Anken R, Boonstra J, Braun M, Christianen PC, de Geest M, Hauslage J, Hilbig R, Hill RJ, Lebert M, Medina FJ, Vagt N, Ullrich O, van Loon JJ, Hemmersbach R (2013) Ground-based facilities for simulation of microgravity: organism-specific recommendations for their use, and recommended terminology. Astrobiology 13:1–17. doi:10.1089/ast.2012.0876
Kacena MA, Todd P (1997) Growth characteristics of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis cultured on an agar substrate in microgravity. Microgravity Sci Technol 10:58–62
Kacena MA, Leonard PE, Todd P, Luttges MW (1997) Low gravity and inertial effects on the growth of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis in semi-solid media. Aviat Space Environ Med 68:1104–1108
Kacena MA, Merrell GA, Manfredi B, Smith EE, Klaus DM, Todd P (1999) Bacterial growth in space flight: logistic growth curve parameters for Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:229–234. doi:10.1007/s002530051386
Kang SG, Jin W, Bibb M, Lee KJ (1998) Actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin production in wild-type and relA mutant strains of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) grown in continuous culture. FEMS Microbiol Lett 168:221–226. doi:10.1016/S0378-1097(98)00446-7
Kelemen GH, Brown GL, Kormanec J, Potuckova L, Chater KF, Buttner MJ (1996) The positions of the sigma-factor genes, whiG and sigF, in the hierarchy controlling the development of spore chains in the aerial hyphae of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 21:593–603. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02567.x
Kelemen GH, Brian P, Flärdh K, Chamberlin L, Chater KF, Buttner MJ (1998) Developmental regulation of transcription of whiE, a locus specifying the polyketide spore pigment in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 180:2515–2521
Kirby R, Herron P, Hoskisson P (2011) Analysis of developmental gene conservation in the Actinomycetales using DNA/DNA microarray comparisons. Anton Leeuw Int J G 99:159–177. doi:10.1007/s10482-010-9473-x
Klaus DM (2001) Clinostats and Bioreactors. Gravit Space Biol Bull 14(2):55–64
Klaus D, Simske S, Todd P, Stodieck L (1997) Investigation of space flight effects on Escherichia coli and a proposed model of underlying physical mechanisms. Microbiol-SGM 143:449–455. doi:10.1099/00221287-143-2-449
Lakey JH, Lea EJA, Rudd BAM, Wright HM, Hopwood DA (1983) A new channel-forming antibiotic from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) which requires calcium for its activity. J Gen Microbiol 129:3565–3573. doi:10.1099/00221287-129-12-3565
Lam KS, Mamber SW, Pack EJ, Forenza S, Fernandes PB, Klaus DM (1998) The effects of space flight on the production of monorden by Humicola fuscoatra WC5157 in solid-state fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:579–583. doi:10.1007/s002530051216
Lam KS, Gustavson DR, Pirnik DL, Pack E, Bulanhagui C, Mamber SW, Forenza S, Stodieck LS, Klaus DM (2002) The effect of space flight on the production of actinomycin D by Streptomyces plicatus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 29:299–302. doi:10.1038/sj.jim.7000312
Lawal A, Jejelowo OA, Rosenzweig JA (2010) The effects of low-shear mechanical stress on Yersinia pestis virulence. Astrobiology 10:881–888. doi:10.1089/ast.2010.0493
Lawal A, Kirtley ML, van Lier CJ, Erova TE, Kozlova EV, Sha J, Chopra AK, Rosenzweig JA (2013) The effects of modeled microgravity on growth kinetics, antibiotic susceptibility, cold growth, and the virulence potential of a Yersinia pestis ymoA-deficient mutant and its isogenic parental strain. Astrobiology 13:821–832. doi:10.1089/ast.2013.0968
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu GQ, Tan HR (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:112–143. doi:10.1128/Mmbr. 00054-12
Lynch SV, Brodie EL, Matin A (2004) Role and regulation of σS in general resistance conferred by low-shear simulated microgravity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 186:8207–8212. doi:10.1128/Jb.186.24.8207-8212.2004
Lynch SV, Mukundakrishnan K, Benoit MR, Ayyaswamy PS, Matin A (2006) Escherichia coli biofilms formed under low-shear modeled microgravity in a ground-based system. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7701–7710. doi:10.1128/Aem. 01294-06
Mennigmann HD, Lange M (1986) Growth and differentiation of Bacillus subtilis under microgravity. Naturwissenschaften 73:415–417. doi:10.1007/Bf00367283
Molle V, Palframan WJ, Findlay KC, Buttner MJ (2000) WhiD and WhiB, homologous proteins required for different stages of sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 182:1286–1295. doi:10.1128/Jb.182.5.1286-1295.2000
Nasir A, Strauch SM, Becker I, Sperling A, Schuster M, Richter PR, Weisskopf M, Ntefidou M, Daiker V, An YA, Li XY, Liu YD, Lebert M (2014) The influence of microgravity on Euglena gracilis as studied on Shenzhou 8. Plant Biol 16:113–119. doi:10.1111/plb.12067
Paulsen K, Tauber S, Goelz N, Simmet DM, Engeli S, Birlem M, Dumrese C, Karer A, Hunziker S, Biskup J, Konopasek S, Suh D, Hurlimann E, Signer C, Wang A, Sang C, Grote KH, Zhuang FY, Ullrich O (2014) Severe disruption of the cytoskeleton and immunologically relevant surface molecules in a human macrophageal cell line in microgravity-Results of an in vitro experiment on board of the Shenzhou-8 space mission. Acta Astronaut 94:277–292. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2013.06.007
Pawlik K, Kotowska M, Chater KF, Kuczek K, Takano E (2007) A cryptic type I polyketide synthase (cpk) gene cluster in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Arch Microbiol 187:87–99. doi:10.1007/s00203-006-0176-7
Pietsch J, Ma X, Wehland M, Aleshcheva G, Schwarzwalder A, Segerer J, Birlem M, Horn A, Bauer J, Infanger M, Grimm D (2013) Spheroid formation of human thyroid cancer cells in an automated culturing system during the Shenzhou-8 Space mission. Biomaterials 34:7694–7705. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.06.054
Prasad G, Jayaram S, Ward J, Gupta P (2004) SimBOX: a scalable architecture for aggregate distributed command and control of spaceport and service constellation. Proc SPIE Enabling Technol Simul Sci 5423(VIII):437–446. doi:10.1117/12.543058
Preu P, Braun M (2014) German SIMBOX on Chinese mission Shenzhou-8: Europe's first bilateral cooperation utilizing China's Shenzhou programme. Acta Astronaut 94:584–591. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2013.08.022
Ryding NJ, Kelemen GH, Whatling CA, Flardh K, Buttner MJ, Chater KF (1998) A developmentally regulated gene encoding a repressor-like protein is essential for sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 29:343–357. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00939.x
Shu D, Chen L, Wang WH, Yu ZY, Ren C, Zhang WW, Yang S, Lu YH, Jiang WH (2009) afsQ1-Q2-sigQ is a pleiotropic but conditionally required signal transduction system for both secondary metabolism and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1149–1160. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1738-1
Thiel CS, Paulsen K, Bradacs G, Lust K, Tauber S, Dumrese C, Hilliger A, Schoppmann K, Biskup J, Golz N, Sang C, Ziegler U, Grote KH, Zipp F, Zhuang FY, Engelmann F, Hemmersbach R, Cogoli A, Ullrich O (2012) Rapid alterations of cell cycle control proteins in human T lymphocytes in microgravity. Cell Commun Signal 10:1–16. doi:10.1186/1478-811x-10-1
van Loon JJWA (2007) Some history and use of the random positioning machine, RPM, in gravity related research. Adv Space Res 39:1161–1165. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.02.016
Van Mulders SE, Stassen C, Daenen L, Devreese B, Siewers V, van Eijsden RG, Nielsen J, Delvaux FR, Willaert R (2011) The influence of microgravity on invasive growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Astrobiology 11:45–55. doi:10.1089/ast.2010.0518
Viollier PH, Kelemen GH, Dale GE, Nguyen KT, Buttner MJ, Thompson CJ (2003) Specialized osmotic stress response systems involve multiple SigB-like sigma factors in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 47:699–714. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03302.x
Wang WH, Shu D, Chen L, Jiang WH, Lu YH (2009) Cross-talk between an orphan response regulator and a noncognate histidine kinase in Streptomyces coelicolor. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294:150–156. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01563.x
Wilson JW, Ott CM, Ramamurthy R, Porwollik S, McClelland M, Pierson DL, Nickerson CA (2002a) Low-shear modeled microgravity alters the Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium stress response in an RpoS-independent manner. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5408–5416. doi:10.1128/Aem. 68.11.5408-5416.2002
Wilson JW, Ramamurthy R, Porwollik S, McClelland M, Hammond T, Allen P, Ott CM, Pierson DL, Nickerson CA (2002b) Microarray analysis identifies Salmonella genes belonging to the low-shear modeled microgravity regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13807–13812. doi:10.1073/pnas.212387899
Wilson JW, Ott CM, Bentrup KHZ, Ramamurthy R, Quick L, Porwollik S, Cheng P, McClelland M, Tsaprailis G, Radabaugh T, Hunt A, Fernandez D, Richter E, Shah M, Kilcoyne M, Joshi L, Neiman-Gonzalez M, Hing S, Parra M, Dumars P, Norwood K, Bober R, Devich J, Ruggles A, Goulart C, Rupert M, Stodieck L, Stafford P, Catella L, Schurr MJ, Buchanan K, Morici L, McCracken J, Allen P, Baker-Coleman C, Hammond T, Vogel J, Nelson R, Pierson DL, Stefanyshyn-Piper HM, Nickerson CA (2007) Space flight alters bacterial gene expression and virulence and reveals a role for global regulator Hfq. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:16299–16304. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707155104
Wright LF, Hopwood DA (1976) Actinorhodin is a chromosomally-determined antibiotic in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol 96:289–297. doi:10.1099/00221287-96-2-289
Yu TW, Hopwood DA (1995) Ectopic expression of the Streptomyces coelicolor whiE genes for polyketide spore pigment synthesis and their interaction with the act genes for actinorhodin biosynthesis. Microbiol-SGM 141:2779–2791. doi:10.1099/13500872-141-11-2779
Yu TW, Shen YM, McDaniel R, Floss HG, Khosla C, Hopwood DA, Moore BS (1998) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides from Streptomyces spore pigment polyketide synthases. J Am Chem Soc 120:7749–7759. doi:10.1021/Ja9803658
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Manned Space Engineering Program (CMSE, 921-2). We thank Prof. Hua-Rong Tan (Institute of Microbiology, CAS) for kindly providing S. coelicolor A3(2) and M145, and Chunli Li and Jingnan Liang (Institute of Microbiology, CAS) for their help in SEM analyses. We are also grateful to German Aerospace Center’s (DLR) Space Administration, EADS (Astrium), the China Manned Space Engineering Office (CMSEO; now CMSA, China Manned Space Agency) and the General Establishment of Space Science and Application, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GESSA, CAS) for technical and logistical support to the SIMBOX-Shenzhou-8 space mission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 489 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Liu, N., Rong, X. et al. Effects of simulated microgravity and spaceflight on morphological differentiation and secondary metabolism of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4409–4422 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6386-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6386-7