Abstract
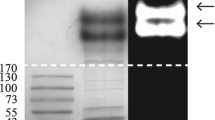
A fungal strain, Penicillium chrysogenum A096, was isolated from an Arctic sediment sample. Its culture supernatant inhibited mycelial growth of some plant pathogenic fungi. After saturation of P. chrysogenum A096 culture supernatant with ammonium sulfate and ion exchange chromatography, a novel antifungal protein (Pc-Arctin) was purified and identified by matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight-time of flight-mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS). The gene encoding for Pc-Arctin consisting of 195 nucleotides was cloned from P. chrysogenum A096 to confirm the mass spectrometry result. Pc-Arctin displays antifungal activity against Paecilomyces variotii, Alternaria longipes, and Trichoderma viride at minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of 24, 48, and 192 ng/disc, respectively. Pc-Arctin was most sensitive to proteinase K and then to trypsin but insensitive to papain. Pc-Arctin possesses high thermostability and cannot be antagonized by common surfactants, except for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Divalent ions, such as Mn2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+, inhibited the antifungal activity of Pc-Arctin. Hemagglutination assays showed that Pc-Arctin had no hemagglutinating or hemolytic activity against red blood cells (RBC) from rabbits, rats, and guinea pigs. Therefore, Pc-Arctin from Arctic P. chrysogenum may represent a novel antifungal protein with potential for application in controlling plant pathogenic fungal infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batta G, Barna T, Gáspári Z, Sándor S, Kövér KE, Binder U, Sarg B, Kaiserer L, Chhillar AK, Eigentler A, Leiter E, Hegedüs N, Pócsi I, Lindner H, Marx F (2009) Functional aspects of the solution structure and dynamics of PAF—a highly-stable antifungal protein from Penicillium chrysogenum. FEBS J 276(10):2875–2890
Binder U, Chu M, Read ND, Marx F (2010) The antifungal activity of the Penicillium chrysogenum protein PAF disrupts calcium homeostasis in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot Cell 9(9):1374–1382
Chen SC, Sorrell TC (2007) Antifungal agents. Med J Aust 187(7):404–409
Coca M, Bortolotti C, Rufat M, Penas G, Eritja R, Tharreau D, del Pozo AM, Messeguer J, San Segundo B (2004) Transgenic rice plants expressing the antifungal AFP protein from Aspergillus giganteus show enhanced resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Mol Biol 54(2):245–259
Denning DW (2003) Echinocandin antifungal drugs. Lancet 362(9390):1142–1151
Gun Lee D, Shin SY, Maeng CY, Jin ZZ, Kim KL, Hahm KS (1999) Isolation and characterization of a novel antifungal peptide from Aspergillus niger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263(3):646–651
Gupte M, Kulkarni P, Ganguli BN (2002) Antifungal antibiotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(1):46–57
Kaiserer L, Oberparleiter C, Weiler-Gorz R, Burgstaller W, Leiter E, Marx F (2003) Characterization of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF. Arch Microbiol 180(3):204–210
Lay FT, Anderson MA (2005) Defensins—components of the innate immune system in plants. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6(1):85–101
Lehrer RI, Ganz T (1999) Antimicrobial peptides in mammalian and insect host defence. Curr Opin Immunol 11(1):23–27
Lemke A, Kiderlen AF, Kayser O (2005) Amphotericin B. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(2):151–162
Marx F (2004) Small, basic antifungal proteins secreted from filamentous ascomycetes: a comparative study regarding expression, structure, function and potential application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65(2):133–142
Marx F, Haas H, Reindl M, Stoffler G, Lottspeich F, Redl B (1995) Cloning, structural organization and regulation of expression of the Penicillium chrysogenum paf gene encoding an abundantly secreted protein with antifungal activity. Gene 167(1–2):167–171
Marx F, Binder U, Leiter E, Pocsi I (2008) The Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF, a promising tool for the development of new antifungal therapies and fungal cell biology studies. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(3):445–454
Meyer V (2008) A small protein that fights fungi: AFP as a new promising antifungal agent of biotechnological value. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(1):17–28
Mitsuhara I, Matsufuru H, Ohshima M, Kaku H, Nakajima Y, Murai N, Natori S, Ohashi Y (2000) Induced expression of sarcotoxin IA enhanced host resistance against both bacterial and fungal pathogens in transgenic tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13(8):860–868
Moreno AB, Peñas G, Rufat M, Bravo JM, Estopà M, Messeguer J, San Segundo B (2005) Pathogen-induced production of the antifungal AFP protein from Aspergillus giganteus confers resistance to the blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18(9):960–972
Ouedraogo JP, Hagen S, Spielvogel A, Engelhardt S, Meyer V (2011) Survival strategies of yeast and filamentous fungi against the antifungal protein AFP. J Biol Chem 286(16):13859–13868
Rodriguez-Martin A, Acosta R, Liddell S, Nunez F, Benito MJ, Asensio MA (2010) Characterization of the novel antifungal protein PgAFP and the encoding gene of Penicillium chrysogenum. Peptides 31(4):541–547
Sharma A, Sharma R, Imamura M, Yamakawa M, Machii H (2000) Transgenic expression of cecropin B, an antibacterial peptide from Bombyx mori, confers enhanced resistance to bacterial leaf blight in rice. FEBS Lett 484(1):7–11
Skouri-Gargouri H, Gargouri A (2008) First isolation of a novel thermostable antifungal peptide secreted by Aspergillus clavatus. Peptides 29(11):1871–1877
Skouri-Gargouri H, Jellouli-Chaker N, Gargouri A (2010) Factors affecting production and stability of the AcAFP antifungal peptide secreted by Aspergillus clavatus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86(2):535–543
Theis T, Stahl U (2004) Antifungal proteins: targets, mechanisms and prospective applications. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(4):437–455
Theis T, Wedde M, Meyer V, Stahl U (2003) The antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus causes membrane permeabilization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(2):588–593
van den Berg MA, Albang R, Albermann K, Badger JH, Daran JM, Driessen AJ, Garcia-Estrada C, Fedorova ND, Harris DM, Heijne WH, Joardar V, Kiel JA, Kovalchuk A, Martin JF, Nierman WC, Nijland JG, Pronk JT, Roubos JA, van der Klei IJ, van Peij NN, Veenhuis M, von Dohren H, Wagner C, Wortman J, Bovenberg RA (2008) Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat Biotechnol 26(10):1161–1168
van’t Hof W, Veerman EC, Helmerhorst EJ, Amerongen AV (2001) Antimicrobial peptides: properties and applicability. Biol Chem 382(4):597–619
White TF, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky FS, White TT (eds) PCR protocol: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Wnendt S, Ulbrich N, Stahl U (1994) Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the gene encoding an antifungal-protein from Aspergillus giganteus. Curr Genet 25(6):519–523
Wong JH, Ng TB (2003) Gymnin, a potent defensin-like antifungal peptide from the Yunnan bean (Gymnocladus chinensis Baill). Peptides 24(7):963–968
Wong JH, Hao J, Cao Z, Qiao M, Xu H, Bai Y, Ng TB (2008) An antifungal protein from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Appl Microbiol 105(6):1888–1898
Woo JH, Kitamura E, Myouga H, Kamei Y (2002) An antifungal protein from the marine bacterium Streptomyces sp. strain AP77 is specific for Pythium porphyrae, a causative agent of red rot disease in Porphyra spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(6):2666–2675
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415(6870):389–395
Zhang B, Xie C, Yang X (2008) A novel small antifungal peptide from Bacillus strain B-TL2 isolated from tobacco stems. Peptides 29(3):350–355
Acknowledgments
We thank Xingzhong Qiao and Tianhua Zhong for their assistance with the experiments. The work was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Project of the Marine Public Welfare Industry of China (201005032, 201205020), the Nature Science Foundation of China (40930847), and China Polar Environment Comprehensive investigation and Assessment Program (CHINARE2013-01-06 and CHINARE2013-04-03).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Ao, J., Yang, W. et al. Purification and characterization of a novel antifungal protein secreted by Penicillium chrysogenum from an Arctic sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 10381–10390 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4800-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4800-6