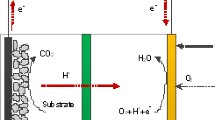
Abstract
As the microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology is getting nearer to practical applications such as wastewater treatment, it is crucial to consider the different aspects that will make this technology viable in the future. In this paper, we provide information about the specifications of an energy self-sufficient MFC system as a basis to extrapolate on the potential benefits and limits of a future MFC-based wastewater treatment plant. We particularly emphasize on the importance of two crucial parameters that characterize an MFC: its electromotive force (E emf) and its internal resistance (R int). A numerical projection using state-of-art values (E emf = 0.8 V and R int = 5 Ω) emphasized on the difficulty at this moment to reach self-sufficiency using a reasonable number of MFCs at the laboratory scale. We found that a realistic number of MFCs to provide enough voltage (=5 V) at a sufficient current (=0.8 A) to power a pump requiring 4 W would be of 13 MFCs in series and 10 stacks of MFCs in parallel, resulting in a total number of 130 MFCs. That would result in a treatment capacity of 144 L of domestic wastewater (0.5 g-COD L−1) per day. The total MFC system would be characterized by an internal resistance of 6.5 Ω.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Pham HT, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40(10):3388–3394
Ahn Y, Logan BE (2010) Effectiveness of domestic wastewater treatment using microbial fuel cells at ambient and mesophilic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 101(2):469–475. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.039
Bergel A, Feron D, Mollica A (2005) Catalysis of oxygen reduction in pem fuel cell by seawater biofilm. Electrochem Commun 7(9):900–904
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity production by geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1548–1555
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2005) Evidence for involvement of an electron shuttle in electricity generation by geothrix fermentans. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(4):2186–2189
Cao XX, Huang X, Liang P, Xiao K, Zhou YJ, Zhang XY, Logan BE (2009) A new method for water desalination using microbial desalination cells. Environ Sci Technol 43(18):7148–7152. doi:10.1021/es901950j
Chang IS, Jang JK, Gil GC, Kim M, Kim HJ, Cho BW, Kim BH (2004) Continuous determination of biochemical oxygen demand using microbial fuel cell type biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 19(6):607–613
Chang IS, Moon H, Jang JK, Kim BH (2005) Improvement of a microbial fuel cell performance as a bod sensor using respiratory inhibitors. Biosens Bioelectron 20(9):1856–1859
Cheng S, Logan BE (2007a) Sustainable and efficient biohydrogen production via electrohydrogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(47):18871–18873
Cheng SA, Logan BE (2007b) Ammonia treatment of carbon cloth anodes to enhance power generation of microbial fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 9(3):492–496
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006a) Increased power generation in a continuous flow mfc with advective flow through the porous anode and reduced electrode spacing. Environ Sci Technol 40(7):2426–2432
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006b) Power densities using different cathode catalysts (pt and cotmpp) and polymer binders (nafion and ptfe) in single chamber microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40(1):364–369
Cheng SA, Xing DF, Call DF, Logan BE (2009) Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3953–3958. doi:10.1021/es803531g
Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Pham TH, De Schamphelaire L, Carballa M, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2008) Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: the road to applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(6):901–913. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1522-2
Clauwaert P, Mulenga S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2009) Litre-scale microbial fuel cells operated in a complete loop. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(2):241–247. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-1876-0
Deng Q, Li XY, Zuo JE, Ling A, Logan BE (2010) Power generation using an activated carbon fiber felt cathode in an upflow microbial fuel cell. J Power Sources 195(4):1130–1135. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.092
Du ZW, Li HR, Gu TY (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: a promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol Adv 25(5):464–482
Fan YZ, Hu HQ, Liu H (2007) Enhanced coulombic efficiency and power density of air-cathode microbial fuel cells with an improved cell configuration. J Power Sources 171(2):348–354
Fan YZ, Sharbrough E, Liu H (2008) Quantification of the internal resistance distribution of microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):8101–8107. doi:10.1021/es801229j
Feng YJ, Lee H, Wang X, Liu YL, He WH (2010) Continuous electricity generation by a graphite granule baffled air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 101(2):632–638. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.046
Fornero JJ, Rosenbaum M, Cotta MA, Angenent LT (2009) Ion exchange membrane influence on ohmic resistance. Paper presented at the The 2nd Microbial Fuel Cell Conference, Gwangju
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2007) Non-catalyzed cathodic oxygen reduction at graphite granules in microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 53(2):598–603
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan ZG, Keller J (2008) Sequential anode-cathode configuration improves cathodic oxygen reduction and effluent quality of microbial fuel cells. Water Res 42(6–7):1387–1396. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.007
Fricke K, Harnisch F, Schroder U (2008) On the use of cyclic voltammetry for the study of anodic electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 1(1):144–147. doi:10.1039/b802363h
Gorby YA, Yanina S, McLean JS, Rosso KM, Moyles D, Dohnalkova A, Beveridge TJ, Chang IS, Kim BH, Kim KS, Culley DE, Reed SB, Romine MF, Saffarini DA, Hill EA, Shi L, Elias DA, Kennedy DW, Pinchuk G, Watanabe K, Ishii S, Logan B, Nealson KH, Fredrickson JK (2006) Electrically conductive bacterial nanowires produced by Shewanella oneidensis strain mr-1 and other microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(30):11358–11363
Harnisch F, Wirth S, Schroder U (2009) Effects of substrate and metabolite crossover on the cathodic oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells: platinum vs. iron(II) phthalocyanine based electrodes. Electrochem Commun 11(11):2253–2256. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2009.10.002
He Z, Minteer SD, Angenent LT (2005) Electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5262–5267
Ieropoulos I, Greenman J, Melhuish C (2008) Microbial fuel cells based on carbon veil electrodes: stack configuration and scalability. Int J Energy Res 32(13):1228–1240. doi:10.1002/er.1419
Jiang JQ, Zhao QL, Zhang JN, Zhang GD, Lee DJ (2009) Electricity generation from bio-treatment of sewage sludge with microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 100(23):5808–5812. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.076
Kelly I (2003) The design of a robotic predator: the slugbot. Robotica 21:399–406
Kim BH, Kim HJ, Hyun MS, Park DH (1999) Direct electrode reaction of Fe(III)-reducing bacterium, shewanella putrefaciens. J Microbiol Biotechnol 9(2):127–131
Kim BH, Chang IS, Gil GC, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Novel bod (biological oxygen demand) sensor using mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol Lett 25(7):541–545
Kim JR, Premier GC, Hawkes FR, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ (2009) Development of a tubular microbial fuel cell (mfc) employing a membrane electrode assembly cathode. J Power Sources 187(2):393–399. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.11.020
Lefebvre O, Al-Mamun A, Ooi WK, Tang Z, Chua DHC, Ng HY (2008) An insight into cathode options for microbial fuel cells. Water Sci Technol 57(12):2031–2037
Lefebvre O, Ooi WK, Tang Z, Abdullah-Al-Mamun M, Chua DHC, Ng HY (2009) Optimization of a pt-free cathode suitable for practical applications of microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 100(20):4907–4910. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.04.061
Lefebvre O, Nguyen TTH, Abdullah-Al-Mamun M, Chang IS, Ng HY (2010) T-RFLP reveals high β-proteobacteria diversity in microbial fuel cells enriched with domestic wastewater. J Appl Microbiol 109(3):839–850. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04735.x
Lettinga G, Deman A, Vanderlast ARM, Wiegant W, Vanknippenberg K, Frijns J, Vanbuuren JCL (1993) Anaerobic treatment of domestic sewage and waste-water. Water Sci Technol 27(9):67–73
Li ZJ, Zhang XW, Zeng YX, Lei LC (2009) Electricity production by an overflow-type wetted-wall microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 100(9):2551–2555. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.018
Liu H, Logan BE (2004) Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ Sci Technol 38(14):4040–4046
Liu H, Ramnarayanan R, Logan BE (2004) Production of electricity during wastewater treatment using a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(7):2281–2285
Logan BE (2005) Simultaneous wastewater treatment and biological electricity generation. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):31–37
Logan B (2008) Microbial fuel cells. Wiley, New York
Logan BE (2010) Scaling up microbial fuel cells and other bioelectrochemical systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(6):1665–1671. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2378-9
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol 14(12):512–518
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schrorder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5181–5192
Logan B, Cheng S, Watson V, Estadt G (2007) Graphite fiber brush anodes for increased power production in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41(9):3341–3346
Logan BE, Call D, Cheng S, Hamelers HVM, Sleutels T, Jeremiasse AW, Rozendal RA (2008) Microbial electrolysis cells for high yield hydrogen gas production from organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8630–8640. doi:10.1021/es801553z
Lovley DR (2008) The microbe electric: conversion of organic matter to electricity. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(6):564–571. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.10.005
Marcus AK, Torres CI, Rittmann BE (2007) Conduction-based modeling of the biofilm anode of a microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol Bioeng 98(6):1171–1182
Melhuish C, Ieropoulos I, Greenman J, Horsfield I (2006) Energetically autonomous robots: food for thought. Auton Robot 21(3):187–198
Min B, Logan BE (2004) Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(21):5809–5814
Moon H, Chang IS, Kang KH, Jang JK, Kim BH (2004) Improving the dynamic response of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell as a biochemical oxygen demand (bod) sensor. Biotechnol Lett 26(22):1717–1721
Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2000) Lack of production of electron-shuttling compounds or solubilization of Fe(III) during reduction of insoluble Fe(III) oxide by geobacter metallireducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(5):2248–2251
Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2002a) Mechanisms for accessing insoluble Fe(III) oxide during dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction by geothrix fermentans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(5):2294–2299. doi:10.1128/aem.68.5.2294-2299.2002|issn0099-2240
Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2002b) Mechanisms for Fe(III) oxide reduction in sedimentary environments. Geomicrobiol J 19(2):141–159
Newman DK, Kolter R (2000) A role for excreted quinones in extracellular electron transfer. Nature 405(6782):94–97
Park DH, Zeikus JG (2003) Improved fuel cell and electrode designs for producing electricity from microbial degradation. Biotechnol Bioeng 81(3):348–355
Pham TH, Jang JK, Moon HS, Chang IS, Kim BH (2005) Improved performance of microbial fuel cell using membrane-electrode assembly. J Microbiol Biotechnol 15(2):438–441
Pham TH, Rabaey K, Aelterman P, Clauwaert P, De Schamphelaire L, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Microbial fuel cells in relation to conventional anaerobic digestion technology. Eng Life Sci 6(3):285–292
Qian F, Baum M, Gu Q, Morse DE (2009) A 1.5 mu l microbial fuel cell for on-chip bioelectricity generation. Lab Chip 9(21):3076–3081. doi:10.1039/b910586g
Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol 23(6):291–298
Rabaey K, Lissens G, Siciliano SD, Verstraete W (2003) A microbial fuel cell capable of converting glucose to electricity at high rate and efficiency. Biotechnol Lett 25(18):1531–1535
Rabaey K, Boon N, Siciliano SD, Verhaege M, Verstraete W (2004) Biofuel cells select for microbial consortia that self-mediate electron transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5373–5382
Rabaey K, Boon N, Hofte M, Verstraete W (2005a) Microbial phenazine production enhances electron transfer in biofuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 39(9):3401–3408
Rabaey K, Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2005b) Tubular microbial fuel cells for efficient electricity generation. Environ Sci Technol 39(20):8077–8082
Rabaey K, Rodriguez J, Blackall LL, Keller J, Gross P, Batstone D, Verstraete W, Nealson KH (2007) Microbial ecology meets electrochemistry: electricity-driven and driving communities. ISME J 1(1):9–18
Rabaey K, Read ST, Clauwaert P, Freguia S, Bond PL, Blackall LL, Keller J (2008) Cathodic oxygen reduction catalyzed by bacteria in microbial fuel cells. ISME J 2(5):519–527. doi:10.1038/ismej.2008.1
Reimers CE, Tender LM, Fertig S, Wang W (2001) Harvesting energy from the marine sediment–water interface. Environ Sci Technol 35(1):192–195
Ringeisen BR, Henderson E, Wu PK, Pietron J, Ray R, Little B, Biffinger JC, Jones-Meehan JM (2006) High power density from a miniature microbial fuel cell using Shewanella oneidensis dsp10. Environ Sci Technol 40(8):2629–2634
Rozendal RA, Hamelers HVM, Euverink GJW, Metz SJ, Buisman CJN (2006) Principle and perspectives of hydrogen production through biocatalyzed electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 31(12):1632–1640
Rozendal RA, Hamelers HV, Rabaey K, Keller J, Buisman CJ (2008) Towards practical implementation of bioelectrochemical wastewater treatment. Trends Biotechnol 26(8):450–459. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.04.008
Schaetzle O, Barriere F, Schroder U (2009) An improved microbial fuel cell with laccase as the oxygen reduction catalyst. Energy Environ Sci 2(1):96–99. doi:10.1039/b815331k
Shimoyama T, Komukai S, Yamazawa A, Ueno Y, Logan BE, Watanabe K (2008) Electricity generation from model organic wastewater in a cassette-electrode microbial fuel cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80(2):325–330. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1516-0
Sun J, Hu YY, Bi Z, Cao YQ (2009) Improved performance of air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment using microfiltration membranes and multiple sludge inoculation. J Power Sources 187(2):471–479. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.11.022
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse, 4th edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Tender LM, Reimers CE, Stecher HA, Holmes DE, Bond DR, Lowy DA, Pilobello K, Fertig SJ, Lovley DR (2002) Harnessing microbially generated power on the seafloor. Nat Biotechnol 20(8):821–825. doi:10.1038/nbt716|ISSN1087-0156
Tender LM, Gray SA, Groveman E, Lowy DA, Kauffman P, Melhado J, Tyce RC, Flynn D, Petrecca R, Dobarro J (2008) The first demonstration of a microbial fuel cell as a viable power supply: powering a meteorological buoy. J Power Sources 179(2):571–575. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.12.123
Wang B, Han JI (2009) A single chamber stackable microbial fuel cell with air cathode. Biotechnol Lett 31(3):387–393. doi:10.1007/s10529-008-9877-0
Wang YF, Tsujimura S, Cheng SS, Kano K (2007) Self-excreted mediator from escherichia coli k-12 for electron transfer to carbon electrodes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(6):1439–1446
Wang X, Cheng SA, Feng YJ, Merrill MD, Saito T, Logan BE (2009) Use of carbon mesh anodes and the effect of different pretreatment methods on power production in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 43(17):6870–6874. doi:10.1021/es900997w
Wilkinson S (2000) “Gastrobots”—benefits and challenges of microbial fuel cells in food powered robot applications. Auton Robot 9(2):99–111
Wilkinson S, Klar J, Applegarth S (2006) Optimizing biofuel cell performance using a targeted mixed mediator combination. Electroanalysis 18(19–20):2001–2007
Zhang BG, Zhao HZ, Zhou SG, Shi CH, Wang C, Ni JR (2009) A novel uasb-mfc-baf integrated system for high strength molasses wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation. Bioresour Technol 100(23):5687–5693. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.045
Zhao F, Harnisch F, Schroder U, Scholz F, Bogdanoff P, Herrmann I (2005) Application of pyrolysed iron(II) phthalocyanine and cotmpp based oxygen reduction catalysts as cathode materials in microbial fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 7(12):1405–1410
Zhuang L, Zhou SG, Wang YQ, Liu CS, Geng S (2009) Membrane-less cloth cathode assembly (cca) for scalable microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 24(12):3652–3656. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.05.032
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by a grant from the Environment & Water and Industry Development Council, Singapore (MEWR 651/06/159) and partly from a grant from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) NRL Program (R0A-2008-000-20088-0) by the Korean government (MEST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lefebvre, O., Uzabiaga, A., Chang, I.S. et al. Microbial fuel cells for energy self-sufficient domestic wastewater treatment—a review and discussion from energetic consideration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 259–270 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2881-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2881-z