Abstract
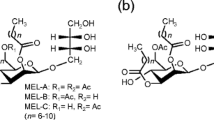
The producers of glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid-B (MEL-B), were isolated from leaves of Perilla frutescens on Ibaraki in Japan. Four isolates, 1D9, 1D10, 1D11, and 1E5, were identified as basidiomycetous yeast Pseudozyma tsukubaensis by rDNA sequence and biochemical properties. The structure of MEL-B produced by these strains was analyzed by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry methods, and was determined to be the same as the diastereomer MEL-B produced by P. tsukubaensis NBRC 1940. Of these isolates, P. tsukubaensis 1E5 (JCM 16987) is capable of producing the largest amount of the diastereomer MEL-B from vegetable oils. In order to progress the diastereomer MEL-B production by strain 1E5, factors affecting the production, such as carbon and organic nutrient sources, were further examined. Olive oil and yeast extract were the best carbon and nutrient sources, respectively. Under the optimal conditions, a maximum yield, productivity, and yield coefficient of 73.1 g/L, 10.4 g L−1 day−1, and 43.5 g/g were achieved by feeding of olive oil in a 5-L jar-fermenter culture using strain 1E5.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Banat IM, Makkar RS, Cameotra SS (2000) Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:495–508
Begerow D, Bauer R, Boekhout T (2000) Phylogenetic placements of ustilaginomycetous anamorphs as deduced from nuclear LSU rDNA sequences. Mycol Res 104:53–60
Boekhout T, Fell JW (1998) Pseudozyma Bandoni emend. Boekhout and a comparison with the yeast state of Ustilago maydis (De Candolle) Corda. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 790–797
Boekhout T, Fell JW, O'Donnell K (1995) Molecular systematics of some yeast-like anamorphs belonging to the Ustilaginales and Tilletiales. Stud Mycol 38:175–183
Boekhout T, Gildemacher P, Theelen B, Muller WH, Heijne B, Lutz M (2006) Extensive colonization of apples by smut anamorphs causes a new postharvest disorder. FEMS Yeast Res 6:63–76
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolutioni 39:783–791
Fukuoka T, Morita T, Konishi M, Imura T, Sakai H, Kitamoto D (2007a) Structural characterization and surface-active properties of a new glycolipid biosurfactant, mono-acylated mannosylerythritol lipid, produced from glucose by Pseudozyma antarctica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:801–810
Fukuoka T, Morita T, Konishi M, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007b) Characterization of new glycolipid biosurfactants, tri-acylated mannosylerythritol lipids, produced by Pseudozyma yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 29:1111–1118
Fukuoka T, Morita T, Konishi M, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007c) Characterization of new types of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants produced from soybean oil by a basidiomycetous yeast, Pseudozyma shanxiensis. J Oleo Sci 56:435–442
Fukuoka T, Morita T, Konishi M, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2008) A basidiomycetous yeast, Pseudozyma tsukubaensis, efficiently produces a novel glycolipid biosurfactant. The identification of a new diastereomer of mannosylerythritol lipid-B. Carbohydr Res 343:555–560
Hewald S, Linne U, Scherer M, Marahiel MA, Kämper J, Bölker M (2006) Identification of a gene cluster for biosynthesis of mannosylerythritol lipids in the basidiomycetous fungus Ustilago maydis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5469–5477
Imura T, Yanagishita H, Kitamoto D (2004) Coacervate formation from natural glycolipid: one acetyl group on the headgroup triggers coacervate-to-vesicle transition. J Am Chem Soc 126:10804–10805
Imura T, Ohta N, Inoue K, Yagi H, Negishi H, Yanagishita H, Kitamoto D (2006) Naturally engineered glycolipid biosurfactants leading to distinctive self-assembled structures. Chem Eur J 12:2434–2440
Imura T, Ito S, Azumi R, Yanagishita H, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2007) Monolayers assembled from a glycolipid biosurfactant from Pseudozyma (Candida) antarctica serve as a high-affinity ligand system for immunoglobulin G and M. Biotechnol Lett 29:865–870
Isoda H, Kitamoto D, Shinomoto H, Matsumura M, Nakahara T (1997) Microbial extracellular glycolipid induction of differentiation and inhibition of the protein kinase C activity of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line activity of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:609–614
Ito S, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Morita T, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2007) Kinetic studies on the interactions between glycolipid biosurfactants assembled monolayers and various classes of immunoglobulins using surface phasmon resonance. Colloid Surf B 58:165–171
Kitamoto D, Akiba S, Hioki C, Tabuchi T (1990) Extracellular accumulation of mannosylerythritol lipids by a atrain of Candida antarctica. Agric Biol Chem 54:31–36
Kitamoto D, Nemoto T, Yanagishita H, Nakane T, Kitmoto HK, Nakahara T (1993) Fatty-acid metabolism of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica. J Jpn Oil Chem Soc 42:346–358
Kitamoto D, Ikegami T, Suzuki T, Sasaki A, Takeyama Y, Idemoto Y, Koura N, Yanagishita H (2001) Microbial conversion of n-alkanes into glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by Pseudozyma antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 23:1709–1714
Kitamoto D, Isoda H, Nakahara T (2002) Functional and potential applications of glycolipid biosurfactants. J Biosci Bioeng 94:187–201
Kitamoto D, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Konishi M, Imura T (2009) Self-assembling properties of glycolipid biosurfactants and their potential applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14:315–328
Konishi M, Imura T, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D (2007a) A yeast glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosyl-erythritol lipid, shows high binding affinity towards lectins on a self-assembled monolayer system. Biotechnol Lett 29:473–480
Konishi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kakugawa K, Kitamoto D (2007b) Production of different types of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants by the newly isolated yeast strains belonging to the genus Pseudozyma. Appl Microbial Biotechnol 75:521–531
Konishi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kakugawa K, Kitamoto D (2008) Efficient production of mannosylerythritol lipids with high hydrophilicity by Pseudozyma hubeiensis KM-59. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:37–46
Lang S (2002) Biological amphiphiles (microbial biosurfactants). Curr Opin Coll Int Sci 7:12–20
Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2006) Discovery of Pseudozyma rugulosa NBRC 10877 as a novel producer of the glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, based on rDNA sequence. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:305–315
Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007a) Characterization of the genus Pseudozyma by the formation of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids. FEMS Yeast Res 7:286–292
Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007b) Physiological differences in the formation of the glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, between Pseudozyma antarctica and Pseudozyma aphidis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:305–315
Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Yamamoto S, Kitagawa M, Sogabe A, Kitamoto D (2008a) Identification of Pseudozyma graminicola CBS 10092 as a producer of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids. J Oleo Sci 57:123–131
Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2008b) Production of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by Pseudozyma siamensis CBS 9960 and their interfacial properties. J Biosci Bioeng 105:493–502
Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2009a) Production of glycolipid biosurfactants by basidiomycetous yeasts. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 53:39–49
Morita T, Kitagawa M, Suzuki M, Yamamoto S, Sogabe A, Yanagidani S, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D (2009b) Yeast glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, shows potential moisturizing activity toward cultured human skin cells: the recovery effect of MEL-A on the SDS-damaged human skin cells. J Oleo Sci 58:639–642
Morita T, Fukuoka T, Konishi M, Imura T, Yamamoto S, Kitagawa M, Sogabe A, Kitamoto D (2009c) Production of a novel glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylmannitol lipid, by Pseudozyma parantarctica and its interfacial properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:1017–1025
Morita T, Ishibashi Y, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2009d) Production of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by a smut fungus, Ustilago scitaminea NBRC 32730. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:788–792
Morita T, Kitagawa M, Yamamoto S, Sogabe A, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D (2010) Glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, repair the damaged hair. J Oleo Sci 59:267–272
Rau U, Nguyen LA, Schulz S, Wary V, Nimtz M, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S (2005a) Formation and analysis of mannosylerythritol lipids secreted by Pseudozyma aphidis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:551–559
Rau U, Nguyen LA, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S (2005b) Fed-batch bioreactor production of mannosylerythritol lipids secreted by Pseudozyma aphidis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:607–613
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Stoll M, Begerow D, Oberwinkler F (2005) Molecular phylogeny of Ustilago, Sporisorium, and related taxa based on combined analysis of rDNA sequences. Mycol Res 109:342–356
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wakamatsu Y, Zhao X, Jin C, Day N, Shibahara M, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Murata T, Yokoyama KK (2001) Mannosylerythritol lipid induces characteristics of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells through an ERK-related signal cascade. Eur J Biochem 268:374–383
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Worakitkanchanakul W, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Morita T, Sakai H, Abe M, Rujiravanit R, Chavadej S, Minamikawa H, Kitamoto D (2008) Aqueous-phase behavior and vesicle formation of natural glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid-B. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 65:106–112
Yarrow D (1998) Methods for the isolation, maintenance and identification of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 77–100
Zhao XX, Murata T, Ohno S, Day N, Song J, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Yokoyama KK (2001) Protein kinase C alpha plays a critical role in mannosylerythritol lipid-induced differentiation of melanoma B16 cells. J Biol Chem 276:39903–39910
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. Shun Azami and Dr. Shunichi Miyakoshi for their technical assistance. This study was supported by the Industrial Technology Research Grant Program in 06A17501c from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morita, T., Takashima, M., Fukuoka, T. et al. Isolation of basidiomycetous yeast Pseudozyma tsukubaensis and production of glycolipid biosurfactant, a diastereomer type of mannosylerythritol lipid-B. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 679–688 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2762-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2762-5