Abstract
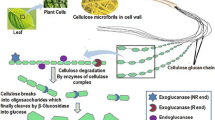
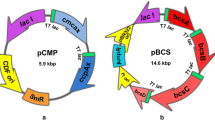
To explore the potential of Ashbya gossypii as a host for the expression of recombinant proteins and to assess whether protein secretion would be more similar to the closely related Saccharomyces cerevisiae or to other filamentous fungi, endoglucanase I (EGI) and cellobiohydrolase I (CBHI) from the fungus Trichoderma reesei were successfully expressed in A. gossypii from plasmids containing the two micron sequences from S. cerevisiae, under the S. cerevisiae PGK1 promoter. The native signal sequences of EGI and CBHI were able to direct the secretion of EGI and CBHI into the culture medium in A. gossypii. Although CBHI activity was not detected using 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-d-lactoside as substrate, the protein was detected by Western blot using monoclonal antibodies. EGI activity was detectable, the specific activity being comparable to that produced by a similar EGI producing S. cerevisiae construct. More EGI was secreted than CBHI, or more active protein was produced. Partial characterization of CBHI and EGI expressed in A. gossypii revealed overglycosylation when compared with the native T. reesei proteins, but the glycosylation was less extensive than on cellulases expressed in S. cerevisiae.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho S, Olkkonen V, Jalava T, Paloheimo M, Bühler R, Niku-Paavola ML, Bamford DH, Korhola M (1991) Monoclonal antibodies against core and cellulose-binding domains of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolases I and II and endoglucanase I. Eur J Biochem 200:643–649
Althöefer H, Pompeus M, Revuelta JL, Santos M, Jiminez A, Benito R, Santamaria R, Fernandez J (2001) Protein production using Ashbya gossypii. Patent WO/2001/023576
Archer DB, Mckenzie DA, Jeenes DJ, Roberts IN (1992) Proteolytic degradation of heterologous protein expressed in Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Lett 14:357–362
Ashby SF, Nowell W (1926) The fungi of stigmatomycosis. Ann Bot 40:69–84
Boer H, Teeri T, Koiivula A (2000) Characterization of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel7A secreted from Pichia pastoris using two different promoters. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:486–494
Broekhuijsen MP, Mattern IE, Contreras R, Kinghorn JR, van den Hondel CAMJJ (1993) Secretion of heterologous proteins by Aspergillus niger: production of active human interleukin-6 in a protease-deficient mutant by KEX2-like processing of a glucoamylase-HIL6 fusion protein. J Biotechnol 31:135–145
Clarke AJ (1997) Biodegradation of cellulose: enzymology and biotechnology. Technomic Publishing, Lancaster
Dean N (1999) Asparagine-linked glycosylation in the yeast Golgi. Biochem Biophys Acta 1426:309–322
Demain AL (1972) Riboflavin oversynthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol 26:369–388
Deshpande N, Wilkins MR, Packer N, Nevalainen H (2008) Protein glycosylation pathways in filamentous fungi. Glycobiology 18:626–637
Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pöhlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P (2004) The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Science 304:304–307
Dünkler A, Wendland J (2007) Use of MET3 promoters for regulated gene expression in Ashbya gossypii. Curr Genet 52:1–10
Flint HJ, Zhang J-X, Martin J (1994) Multiplicity and expression of xylanases in the rumen cellulolytic bacterium Ruminococcus flavefaciens. Curr Microbiol 29:139–143
Gemmill TR, Trimble RB (1999) Overview of N- and O-linked oligosaccharide structures found in various yeast species. Biochem Biophys Acta 1426:227–237
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11:355–360
Godbole S, Decker SR, Nieves RA, Adney WS, Vinzant TB, Baker JO, Thomas SR, Himmel ME (1999) Cloning and expression of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Prog 15:828–833
Güldener U, Heck S, Fielder T, Beinhauer J, Hegemann JH (1996) A new efficient gene disruption cassette for repeated use in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 24:2519–2524
Jeoh T, Michener W, Himmel ME, Decker SR, Adney WS (2008) Implications of cellobiohydrolase glycosylation for use in biomass conversion. Biotechnol Biofuels 1:1–10
Jiménez A, Santos MA, Pompejus M, Revuelta JL (2005) Metabolic engineering of the purine pathway for riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5743–5751
Jimenez A, Davies J (1980) Expression of a transposable antibiotic resistance element in Saccharomyces. Nature 287:869–871
Kanamasa S, Tajima S, Park EY (2007) Isocitrate dehydrogenase and isocitrate lyase are essential enzymes for riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 12:92–99
Karos M, Vilarino C, Bollschweiler C, Revuelta JL (2004) A genome-wide transcription analysis of a fungal riboflavin overproducer. J Biotechnol 113:69–76
Kato T, Park EY (2005) Expression of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:46–52
Kubicek CP (1992) The cellulase proteins of Trichoderma reesei: structure, multiplicity, mode of action and regulation of formation. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 45:1–25
Kubicek CP, Messner R, Gruber F, Mach RL, Kubicek-Pranz EM (1993) The Trichoderma cellulase regulatory puzzle: from the interior life of a secretory fungus. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:90–99
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laymon RA, Adney WS, Mohagheghi A, Himmel ME, Thomas SR (1996) Cloning and expression of full-length Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I cDNAs in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotech 57(58):389–400
Li Z, Xiong F, Lin Q, d'Anjou M, Daugulis AJ, Yang DS, Hew CL (2001) Low-temperature increases the yield of biologically active herring antifreeze protein in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 21:438–445
Maley F, Trimble RB, Tarentino AL, Plummer TH Jr (1989) Characterization of glycoproteins and their associated oligosaccharides through the use of endoglycosidases. Anal Biochem 180:195–204
Maras M, De Bruyn A, Schraml J, Herdewijn P, Claeyssens M, Fiers W, Contreras R (1997) Structural characterization of N-linked oligosaccharides from cellobiohydrolase I secreted by the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei RUTC 30. Eur J Biochem 245:617–625
Maras M, van Die I, Contreras R, van den Hondel CA (1999) Filamentous fungi as production organisms for glycoproteins of bio-medical interest. Glycoconj J 16:99–107
Park CS, Chang CC, Ryu DD (2000) Expression and high-level secretion of Trichoderma reesei endoglucanase I in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 87:1–15
Penttilä M, Nevalainen H, Rättö M, Salminen E, Knowles J (1987a) A versatile transformation system for the cellulolytic filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Gene 61:155–164
Penttilä ME, André L, Saloheimo M, Lehtovaara P, Knowles JK (1987b) Expression of two Trichoderma reesei endoglucanases in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 3:175–185
Penttilä ME, Andre L, Lehtovaara P, Bailey M, Teeri TT, Knowles JKC (1988) Efficient secretion of two fungal cellobiohydrolases by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 63:103–112
Plummer TH Jr, Tarentino AL (1991) Purification of the oligosaccharide-cleaving enzymes of Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Glycobiology 1:257–263
Reinikainen T, Rouhonen L, Nevanen T, Laaksonen L, Kraulis P, Jones TA, Knowles J, Teeri T (1992) Investigation of the function of mutated cellulose-binding domains of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 14:475–482
Roberts IN, Jeenes DJ, MacKenzie DA, Wilkinson AP, Sumner IG, Archer DB (1992) Heterologous gene expression in A. niger: a glucoamylase-porcine pancreatic prophospholipase A2 fusion protein is secreted and processed to yield mature enzyme. Gene 122:155–161
Royer JC, Moyer DL, Reiwitch SG, Madden MS, Jensen EB, Brown SH, Yonker CC, Johnston JA, Golightly EJ, Yoder WT, Shuster JR (1995) Fusarium graminearum A 3/5 as a novel host for heterologous protein production. Biotechnology (NY) 13:1479–1483
Ruohonen L, Aalto MK, Keränen S (1995) Modifications to the ADH1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient production of heterologous proteins. J Biotechnol 39:193–203
Saloheimo A, Henrissat B, Hoffrén AM, Teleman O, Penttilä M (1994) A novel, small endoglucanase gene, egl5, from Trichoderma reesei isolated by expression in yeast. Mol Microbiol 13:219–228
Sherman F, Fink GR, Hicks JB (1986) Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor LabPress, Plainview
Shi X, Karkut T, Chamankhah M, Alting-Mees M, Hemmingsen SM, Hegedus D (2003) Optimal conditions for the expression of a single-chain antibody (scFv) gene in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 28:321–330
Srisodsuk M, Reinikainen T, Penttilä M, Teeri TT (1993) Role of the interdomain linker peptide of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I in its interaction with crystalline cellulose. J Biol Chem 268:20756–20761
Stahmann KP, Böddecker T, Sahm H (1997) Regulation and properties of a fungal lipase showing interfacial inactivation by gas bubbles, or droplets of lipid or fatty acid. Eur J Biochem 244:220–225
Stals I, Sandra K, Geysens S, Contreras R, Van Beeumen J, Claeyssens M (2004) Factors influencing glycosylation of Trichoderma reesei cellulases. I: postsecretorial changes of the O- and N-glycosylation pattern of Cel7A. Glycobiology 14:713–724
Steiner S, Wendland J, Wright MC, Philippsen P (1995) Homologous recombination as the main mechanism for DNA integration and cause of rearrangements in the filamentous ascomycete Ashbya gossypii. Genetics 140:973–987
Takashima S, Iikura H, Nakamura A, Hidaka M, Masaki H, Uozumi T (1998) Overproduction of recombinant Trichoderma reesei cellulases by Aspergillus oryzae and their enzymatic properties. J Biotechnol 65:163–171
Teather RM, Wood PJ (1982) Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterisation of cellulolytic bacteria from bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:777–780
Teeri TT (1987) The cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma reesei. Dissertation, University of Helsinki, VTT Publication No. 38
Teeri TT, Kumar V, Lehtovaara P, Knowles J (1987) Construction of cDNA libraries by blunt-end ligation: high-frequency cloning of long cDNAs from filamentous fungi. Anal Biochem 164:60–67
Trimble RB, Maley F (1984) Optimizing hydrolysis of N-linked high-mannose oligosaccharides by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. Anal Biochem 141:515–522
Van Arsdell JN, Kwokl S, Schweickart VL, Ladner MB, Gelfandl DH, Innisl MA (1987) Cloning, characterization and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae endoglucanase I from Trichoderma reesei. Bio/technology 5:60–64
van den Hombergh JP, van de Vondervoort PJ, Fraissinet TL, Visser J (1997) Aspergillus as a host for heterologous protein production: the problem of proteases. Trends Biotechnol 15:256–263
von Ossowski I, Teeri T, Kalkkinen N, Oker-Blom C (1997) Expression of a fungal cellobiohydrolase in insect cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 233:25–29
Wach A, Brachat A, Pöhlmann R, Philippsen P (1994) New heterologous modules for classical or PCR-based gene disruptions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 10:1793–1808
Webster TD, Dickson RC (1983) Direct selection of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the antibiotic G418 following transformation with a DNA vector carrying the kanamycin-resistance gene of Tn903. Gene 26:243–252
Wendland J, Pohlmann R, Dietrich F, Steiner S, Mohr C, Philippsen P (1999) Compact organization of rRNA genes in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. Curr Genet 35:618–625
Wendland J, Ayad-Durieux Y, Knechtle P, Rebischung C, Philippsen P (2000) PCR-based gene targeting in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. Gene 242:381–391
Wickerham L, Flickinger MH, Johnston RM (1946) The production of riboflavin by Ashbya gossypii. Arch Biochem 9:95–98
Wright MC, Philippsen P (1991) Replicative transformation of the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii with plasmids containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARS elements. Gene 109:99–105
Acknowledgements
The financial support of Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, is acknowledged: project AshByofactory PTDC/EBB-EBI/101985/2008 and grant SFRH/BD/30229/2006 to Orquidea Ribeiro.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, O., Wiebe, M., Ilmén, M. et al. Expression of Trichoderma reesei cellulases CBHI and EGI in Ashbya gossypii . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87, 1437–1446 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2610-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2610-7