Abstract
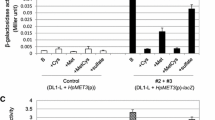
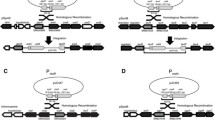
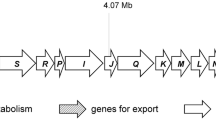
A central tool for gene function analysis is the construction mutant strains. This can be done conveniently in A. gossypii using PCR-based tools. The deletion of essential genes can be performed since initial transformants are sheltered in a heterokaryotic mycelium, which contains nuclei with both wild type and mutant alleles. The analysis of mutant phenotypes in A. gossypii is regularly started by germinating spores, which contain only one nucleus. Thus, selection can be used to identify mutant germ cells and germlings. However, such an analysis yields only mutant mycelia if the deleted gene is not essential. We describe the use of the regulatable Saccharomyces cerevisiae and A. gossypii MET3 promoters as novel tools to regulate gene expression in A. gossypii. Conditional expression was tested using GFP and lacZ-reporter genes. Regulation of MET3 promoters was found to be dependent on methionine but not on cysteine and down-regulation to about 1/10 of the initial expression levels was achieved. We used the A. gossypii WAL1 and CYK1 genes as models to demonstrate that MET3 promoters could regulate the expression of these genes and reveal their mutant phenotypes depending on the presence or absence of methionine. Finally, we show that the AgMET3 promoter contains two Cpf1-binding sites and that AgCPF1 can complement the S. cerevisiae cpf1 methionine auxotrophy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswas K, Rieger KJ, Morschhauser J (2003) Functional characterization of CaCBF1, the Candida albicans homolog of centromere binding factor 1. Gene 323:43–55
Care RS, Trevethick J, Binley KM, Sudbery PE (1999) The MET3 promoter: a new tool for Candida albicans molecular genetics. Mol Microbiol 34:792–798
Cherest H, Nguyen NT, Surdin-Kerjan Y (1985) Transcriptional regulation of the MET3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 34:269–281
Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pohlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P (2004) The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Science 304:304–307
Dünkler A, Wendland J (2007) Candida albicans Rho-type GTPase encoding genes required for polarized cell growth and cell separation. Eukaryot. Cell, in press
Eck R, Stoyan T, Kunkel W (2001) The centromere-binding factor Cbf1p from Candida albicans complements the methionine auxotrophic phenotype of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 18:1047–1052
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11:355–360
Kent NA, Eibert SM, Mellor J (2004) Cbf1p is required for chromatin remodeling at promoter-proximal CACGTG motifs in yeast. J biol chem 279:27116–27123
Kuras L, Thomas D (1995) Identification of the yeast methionine biosynthetic genes that require the centromere binding factor 1 for their transcriptional activation. FEBS Lett 367:15–18
Liu M, Healy MD, Dougherty BA, Esposito KM, Maurice TC, Mazzucco CE, Bruccoleri RE, Davison DB, Frosco M, Barrett JF, Wang YK (2006) Conserved fungal genes as potential targets for broad-spectrum antifungal drug discovery. Eukaryot Cell 5:638–649
Marzluf GA (1997) Molecular genetics of sulfur assimilation in filamentous fungi and yeast. Ann Rev Microbiol 51:73–96
Mountain HA, Bystrom AS, Larsen JT, Korch C (1991) Four major transcriptional responses in the methionine/threonine biosynthetic pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast (Chichester, England) 7:781–803
Sikorski RS, Hieter P (1989) A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122:19–27
Thomas D, Cherest H, Surdin-Kerjan Y (1989) Elements involved in S-adenosylmethionine-mediated regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae MET25 gene. Mol Cell Biol 9:3292–3298
Uhl MA, Johnson AD (2001) Development of Streptococcus thermophilus lacZ as a reporter gene for Candida albicans. Microbiol (Reading, England) 147:1189–1195
Wach A, Brachat A, Pöhlmann R, Philippsen P (2004). New heterologous modules for classical or PCR-based gene disruptions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 10:179–1808
Walther A, Wendland J (2004) Apical localization of actin patches and vacuolar dynamics in Ashbya gossypii depend on the WASP homolog Wal1p. J Cell Sci 117:4947–4958
Wendland J (2003) PCR-based methods facilitate targeted gene manipulations and cloning procedures. Curr Genet 44:115–123
Wendland J, Philippsen P (2001) Cell polarity and hyphal morphogenesis are controlled by multiple rho-protein modules in the filamentous ascomycete Ashbya gossypii. Genetics 157:601–610
Wendland J, Philippsen P (2002) An IQGAP-related protein, encoded by AgCYK1, is required for septation in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. Fungal Genet Biol 37:81–88
Wendland J, Ayad-Durieux Y, Knechtle P, Rebischung C, Philippsen P (2000) PCR-based gene targeting in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. Gene 242:381–391
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the Friedrich-Schiller University and the Leibniz-Institute for Natural Products Research and Infection Biology—Hans-Knöll Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Cormack.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dünkler, A., Wendland, J. Use of MET3 promoters for regulated gene expression in Ashbya gossypii . Curr Genet 52, 1–10 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-007-0134-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-007-0134-1