Abstract
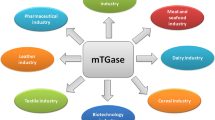
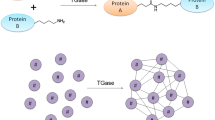
Some properties and applications of the transglutaminase (TGase) referred to as microbial TGase (MTGase), derived from a variant of Streptomyces mobaraensis (formerly classified as Streptoverticillium mobaraense), are described. MTGase cross-linked most food proteins, such as caseins, soybean globulins, gluten, actin, myosins, and egg proteins, as efficiently as mammalian TGases by forming an ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine bond. However, unlike many other TGases, MTGase is calcium-independent and has a relatively low molecular weight. Both of these properties are of advantage in industrial applications; a number of studies have illustrated the potential of MTGase in food processing and other areas. The crystal structure of MTGase has been solved. It provides basic structural information on the MTGase and accounts well for its characteristics. Moreover, an efficient method for producing extracellular MTGase has been established using Corynebacterium glutamicum. MTGase may be expected to find many uses in both food and non-food applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschlimann D, Paulsson M (1994) Transglutaminases: protein cross-linking enzymes in tissues and body fluids. Thromb Haemost 71:402–415
Ando H, Adachi M, Umeda K, Matsuura A, Nonaka M, Uchio R, Tanaka H, Motoki M (1989) Purification and characteristics of a novel transglutaminase derived from microorganism. Agric Biol Chem 53:2613–2617
Bishop PD, Teller DC, Smith RA, Lasser GW, Gilbert T, Seale RL (1990) Expression, purification, and characterization of human factor XIII in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 29:1861–1869
Chung SI, Lewis MS, Folk JE (1974) Relationships of the catalytic properties of human plasma and platelet transglutaminases (activated blood coagulation factor XIII) to their subunit structures. J Biol Chem 249:940–950
Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2003) Production of native-type Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3011–3014
Enzyme Nomenclature (1992) Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (eds) Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.
Fink ML, Chung SI, Folk JE (1980) γ-Glutamine cyclotransferase: specificity toward ε-(γ-glutamyl)-l-lysine and related compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:4564–4568
Finot PA, Mottu F, Bujard E, Mauron J (1978) In: Friedman M (ed) Nutritional improvement of food and foods proteins. Plenum Press, London, pp 549–570
Friedman M, Finot PA (1990) Nutritional improvement of bread with lysine and γ-glutamyllysine. J Agric Food Chem 38:2011–2020
Hornyak TJ, Bishop PD, Shafer JA (1989) α-Thrombin-catalyzed activation of human platelet factor XIII: relationship between proteolysis and factor XIIIa activity. Biochemistry 28:7326–7332
Ikeda M, Nakagawa S (2003) The Corynebacterium glutamicum genome: features and impacts on biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:99–109
Ikura K, Sasaki R, Motoki M (1992) Use of transglutaminase in quality-improvement and processing of food proteins. Comments Agric Food Chem 2:389–407
Ikura K, Nasu T, Yokota H, Tsuchiya Y, Sasaki R, Chiba H (1998) Amino acid sequence of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. Biochemistry 27:2898–2905
Iwami K, Yasumoto K (1986) Amine-binding capacities of food proteins in transglutaminase reaction and digestibility of wheat gliadin with ε-attached lysine. J Sci Food Agric 37:495–503
Kanaji T, Ozaki H, Takao T, Kawajiri H, Ide H, Motoki M, Shimonishi Y (1993) Primary structure of microbial transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium sp. strain s-8112. J Biol Chem 268:11565–11572
Kang IJ, Matsumura Y, Ikura K, Motoki M, Sakamoto H, Mori T (1994) Gelation and properties of soybean glycinin in a transglutaminase-catalyzed system. J Agric Food Chem 42:159–165
Kashiwagi T, Yokoyama K, Ishikawa K, Ono K, Ejima D, Matui H, Suzuki E (2002) Crystal structure of microbial transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium mobaraense. J Biol Chem 277 46:44252–44260
Kato A, Wada T, Kobayashi K, Seguro K, Motoki M (1991) Ovomucin-food protein conjugates prepared through the transglutaminase reaction. Agric Biol Chem 55:1027–1031
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Umezawa Y, Yokoyama K, Heima H, Matsui H (2002) Method for the secretion and production protein. International Patent Cooperation Treaty patent WO02/081694
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H (2003) Secretion of active-form Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase by Corynebacterium glutamicum: processing of the pro-domain by a co-secreted subtilisin-like protease from Streptomyces albogriseolus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:358–366
Krämer R (1994) Secretion of amino acids by bacteria: physiology and mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Rev 12:75–94
Kumazawa Y, Sakamoto H, Kawajiri H, Seguro K, Motoki M (1996a) Determination of ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine in several fish eggs and muscle proteins. Fish Sci 62:331–332
Kumazawa Y, Nakanishi K, Yasueda H, Motoki M (1996b) Purification and characterization of transglutaminase from walleye pollack liver. Fish Sci 62:959–964
Kuraishi C, Sakamoto J, Soeda T (1996) The usefulness of transglutaminase for food processing. biotechnology for improved foods and flavors. In: Takeoka GR, Teranishi R, Williams PJ, Kobayashi A (eds) Biotechnology for improved foods and flavors. ACS symposium series 637 pp 29–38
Kurth L, Rogers PJ (1984) Transglutaminase catalyzed crosslinking of myosin to soya protein, casein, and gluten. J Food Sci 49:573–576
Liebl W (1991) The genus Corynebacterium—nonmedical. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1157–1171
Malumbres M, Gil JA, Martin JF (1993) Codon preference in Corynebacteria. Gene 134:15–24
Meister A, Tate SS, Griffith OW (1981) γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase. Methods Enzymol 77:237–253
Motoki M, Nio N (1983) Crosslinking between different food proteins by transglutaminase. J Food Sci 48:561–566
Motoki M, Nio N, Takinami K (1984) Functional properties of food proteins polymerized by transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 48:1257–1261
Motoki M, Seguro K, Nio N, Takinami K (1986) Glutamine-specific deamidation of transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 50:3025–3030
Motoki M, Aso H, Seguro K, Nio N (1987a) αS1-Casein film prepared using transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 51:993–996
Motoki M, Nio N, Takinami K (1987b) Functional properties of heterologous polymer prepared by transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 51:237–238
Neilsen PM (1995) Reactions and potential industrial applications of transglutaminase. Review of literature and patents. Food Biotechol 9:119–156
Nio N, Motoki M (1986) Gelation of protein emulsion by transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 50:1409–1412
Nio N, Motoki M, Takinami K (1985) Gelation of casein and soybean globulins by transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 49:851–855
Nio N, Motoki M, Takinami K (1986) Gelation mechanism of protein solutions by transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 48:851–855
Noguchi K, Ishikawa K, Yokoyama K, Ohtsuka T, Nio N, Suzuki E (2001) Crystal structure of red sea bream transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 276 15:12055–12059
Nonaka M, Tanaka H, Okiyama A, Motoki M, Ando H, Umeda K, Matsuura A (1989) Polymerization of several proteins by Ca2+-independent transglutaminase derived from microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 53:2619–2623
Nonaka M, Sakamoto H, Toiguchi S, Kawajiri H, Soeda T, Motoki M (1992) Sodium caseinate and skim milk gels formed by incubation with microbial transglutaminase. J Food Sci 57:1214–1218
Nonaka M, Matsuura Y, Nakano K, Motoki M (1997) Improvement of the pH-solubility profile of sodium caseinate by using Ca2+-independent microbial transglutaminase with gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids 11:347–349
Pasternack R, Dorsch S, Otterbach JT, Robenek IR, Wolf S, Fuchsbauer HL (1998) Bacterial pro-transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium mobaraense: purification, characterization and sequence of zymogen. Eur J Biochem 257:570–576
Sakamoto H, Kumazawa Y, Kawajiri H, Motoki M (1995) ε-(γ-Glutamyl)lysine crosslink distribution in foods as determined by improved method. J Food Sci 60:416–419
Sakamoto H, Yamazaki K, Kaga C, Yamamoto Y, Ito R, Kurosawa Y (1996) Strength enhancement by addition of microbial transglutaminase during Chinese noodle processing. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kaishi 43:598–602
Seguro K, Kumazawa Y, Kuraishi C, Sakamoto H, Motoki M (1994) Trends Jpn Soy Protein Res Inform 5:308–313
Seguro K, Kumazawa Y, Ohtsuka T, Toiguchi S, Motoki M (1995a) Microbial transglutaminase and ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine crosslink effects on elastic properties of kamaboko gel. J Food Sci 60:305–311
Seguro K, Kumazawa Y, Ohtsuka T, Ide H, Nio N, Motoki M, Kubota K (1995b) ε-(γ-Glutamyl)lysine: hydrolysis by γ-glutamyl transferase of different origins, when free or protein bound. J Agric Food Chem 43:1977–1981
Seki N, Uno H, Lee NH, Kimura I, Toyoda K, Fujita T, Arai K (1990) Transglutaminase activity in Alaska pollack muscle and surimi, and its reaction with myosin b. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 56:125–132
Shimba N, Yokoyama K, Suzuki E (2002) NMR-based screening method for transglutaminase: rapid analysis of their substrate specificities and reaction rates. J Agric Food Chem 50:1330–1334
Suzuki M, Taguchi S, Yamada S, Kojima S, Miura K, Momose H (1997) A novel member of the subtilisin-like protease family from Streptomyces albogriseolus. J Bacteriol 179:430–438
Takehana S, Washizu K, Ando K, Koikeda S, Takeuchi K, Matsui H, Motoki M, Takagi H (1994) Chemical synthesis of the gene for microbial transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium and its expression in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:88–92
Washizu K, Ando K, Koikeda S, Hirose S, Matsuura A, Akagi H, Motoki M, Takeuchi K (1994) Molecular cloning of the gene for microbial transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium and its expression in Streptomyces lividans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:82–87
Whitaker JR (1977) In: Feeney RE, Whitaker JR (eds) Food proteins-improvement through chemical and enzymatic modification. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C., pp 95–105
Wilson SA (1992) Modifying meat proteins via enzymatic crosslinking, proceedings of the 27th meat industry research conference, Hamilton, Meal Industry Research Institutes of New Zealand, Mirinz, pp 247–277
Yasueda H, Nakanishi K, Kumazawa Y, Nagase K, Motoki M, Matsui H (1995) Tissue-type transglutaminase from red sea bream (Pagrus major) sequence analysis of the cDNA and functional expression in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biol 232:411–419
Yee VC, Pedersen LC, Trong IL, Bishop PD, Stenkamp RE, Teller DC (1994) Tree-dimensional structure of a transglutaminase: human blood coagulation factor XIII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7296–7300
Yokoyama K, Nakamura N, Saguaro K, Kubota K (2000) Overproduction of microbial transglutaminase in Escherichia coli, in vitro refolding, and characterization of the refolded form. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1263–1270
Zhu Y, Rinzema A, Tramper J, Bol J (1995) Microbial transglutaminase—a review of its production and application in food processing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:277–282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoyama, K., Nio, N. & Kikuchi, Y. Properties and applications of microbial transglutaminase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64, 447–454 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1539-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1539-5