Abstract
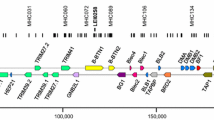
The swine is an important animal model for allo- and xeno-transplantation donor studies, which necessitates an extensive characterization of the expression and sequence variations within the highly polygenic and polymorphic swine leukocyte antigen (SLA) region. Massively parallel pyrosequencing is potentially an effective new 2ndGen method for simultaneous high-throughput genotyping and detection of SLA class I gene expression levels. In this study, we compared the 2ndGen method using the Roche Genome Sequencer 454 FLX with the conventional method using sub-cloning and Sanger sequencing to genotype SLA class I genes in five pigs of the Clawn breed and four pigs of the Landrace breed. We obtained an average of 10.4 SLA class I sequences per pig by the 2ndGen method, consistent with the inheritance data, and an average of only 6.0 sequences by the conventional method. We also performed a correlation analysis between the sequence read numbers obtained by the 2ndGen method and the relative expression values obtained by quantitative real-time PCR analysis at the allele level. A significant correlation coefficient (r = 0.899, P < 0.01) was observed between the sequence read numbers and the relative quantitative values for the expressed classical SLA class I genes SLA-1, SLA-2, and SLA-3, suggesting that the sequence read numbers closely reflect the gene expression levels in white blood cells. Overall, five novel class I sequences, different haplotype-specific expression patterns and a splice variant for one of the SLA class I genes were identified by the 2ndGen method at greater efficiency and sensitivity than the conventional method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando A, Chardon P (2006) Gene organization and polymorphism of the swine major histocompatibility complex. Anim Sci J 77:127–137
Ando A, Kawata H, Shigenari A, Anzai T, Ota M, Katsuyama Y, Sada M, Goto R, Takeshima SN, Aida Y, Iwanaga T, Fujimura N, Suzuki Y, Gojobori T, Inoko H (2003) Genetic polymorphism of the swine major histocompatibility complex ( SLA) class I genes, SLA-1, -2 and -3. Immunogenetics 55:583–593
Ando A, Ota M, Sada M, Katsuyama Y, Goto R, Shigenari A, Kawata H, Anzai T, Iwanaga T, Miyoshi Y, Fujimura N, Inoko H (2005) Rapid assignment of the swine major histocompatibility complex (SLA) class I and II genotypes in Clawn miniature swine using PCR-SSP and PCR-RFLP methods. Xenotransplantation 12:121–126
Babik W, Taberlet P, Ejsmond MJ, Radwan J (2009) New generation sequencers as a tool for genotyping of highly polymorphic multilocus MHC system. Mol Ecol Resour 9:713–719
Budde ML, Wiseman RW, Karl JA, Hanczaruk B, Simen BB, O’Connor DH (2010) Characterization of Mauritian cynomolgus macaque major histocompatibility complex class I haplotypes by high-resolution pyrosequencing. Immunogenetics 62:773–780
Chen FX, Tang J, Li NL, Shen BH, Zhou Y, Xie J, Chou KY (2003) Novel SLA class I alleles of Chinese pig strains and their significance in xenotransplantation. Cell Res 13:285–294
Crew MD, Phanavanh B, Garcia-Borges CN (2004) Sequence and mRNA expression of nonclassical SLA class I genes SLA-7 and SLA-8. Immunogenetics 56:111–114
Ehrlich R, Lifshitz R, Pescovitz MD, Rudikoff S, Singer DS (1987) Tissue-specific expression and structure of a divergent member of a class I MHC gene family. J Immunol 139:593–602
Ekblom R, Balakrishnan CN, Burke T, Slate J (2010) Digital gene expression analysis of the zebra finch genome. BMC Genomics 11:219
Gabriel C, Danzer M, Hackl C, Kopal G, Hufnagl P, Hofer K, Polin H, Stabentheiner S, Proll J (2009) Rapid high-throughput human leukocyte antigen typing by massively parallel pyrosequencing for high-resolution allele identification. Hum Immunol 70:960–964
Galan M, Guivier E, Caraux G, Charbonnel N, Cosson JF (2010) A 454 multiplex sequencing method for rapid and reliable genotyping of highly polymorphic genes in large-scale studies. BMC Genomics 11:296
Garcia-Ruano AB, Mendez R, Romero JM, Cabrera T, Ruiz-Cabello F, Garrido F (2010) Analysis of HLA-ABC locus-specific transcription in normal tissues. Immunogenetics 62:711–719
Ho CS, Rochelle ES, Martens GW, Schook LB, Smith DM (2006) Characterization of swine leukocyte antigen polymorphism by sequence-based and PCR-SSP methods in Meishan pigs. Immunogenetics 58:873–882
Ho CS, Lunney JK, Ando A, Rogel-Gaillard C, Lee JH, Schook LB, Smith DM (2009) Nomenclature for factors of the SLA system, update 2008. Tissue Antigens 73:307–315
Holcomb CL, Hoglund B, Anderson MW, Blake LA, Bohme I, Egholm M, Ferriola D, Gabriel C, Gelber SE, Goodridge D, Hawbecker S, Klein R, Ladner M, Lind C, Monos D, Pando MJ, Proll J, Sayer DC, Schmitz-Agheguian G, Simen BB, Thiele B, Trachtenberg EA, Tyan DB, Wassmuth R, White S, Erlich HA (2011) A multi-site study using high-resolution HLA genotyping by next generation sequencing. Tissue Antigens 77:206–217
Kloch A, Babik W, Bajer A, Sinski E, Radwan J (2010) Effects of an MHC-DRB genotype and allele number on the load of gut parasites in the bank vole Myodes glareolus. Mol Ecol 19(Suppl 1):255–265
Lank SM, Wiseman RW, Dudley DM, O’Connor DH (2010) A novel single cDNA amplicon pyrosequencing method for high-throughput, cost-effective sequence-based HLA class I genotyping. Hum Immunol 71:1011–1017
Lee JH, Simond D, Hawthorne WJ, Walters SN, Patel AT, Smith DM, O'Connell PJ, Moran C (2005) Characterization of the swine major histocompatibility complex alleles at eight loci in Westran pigs. Xenotransplantation 12:303–307
Lee YJ, Cho KH, Kim MJ, Smith DM, Ho CS, Jung KC, Jin DI, Park CS, Jeon JT, Lee JH (2008) Sequence-based characterization of the eight SLA loci in Korean native pigs. Int J Immunogenet 35:333–334
Lind C, Ferriola D, Mackiewicz K, Heron S, Rogers M, Slavich L, Walker R, Hsiao T, McLaughlin L, D'Arcy M, Gai X, Goodridge D, Sayer D, Monos D (2010) Next-generation sequencing: the solution for high-resolution, unambiguous human leukocyte antigen typing. Hum Immunol 71:1033–1042
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Lunney JK, Ho CS, Wysocki M, Smith DM (2009) Molecular genetics of the swine major histocompatibility complex, the SLA complex. Dev Comp Immunol 33:362–374
Martens GW, Lunney JK, Baker JE, Smith DM (2003) Rapid assignment of swine leukocyte antigen haplotypes in pedigreed herds using a polymerase chain reaction-based assay. Immunogenetics 55:395–401
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7799–7806
O’Leary CE, Wiseman RW, Karl JA, Bimber BN, Lank SM, Tuscher JJ, O'Connor DH (2009) Identification of novel MHC class I sequences in pig-tailed macaques by amplicon pyrosequencing and full-length cDNA cloning and sequencing. Immunogenetics 61:689–701
Renard C, Vaiman M, Chiannilkulchai N, Cattolico L, Robert C, Chardon P (2001) Sequence of the pig major histocompatibility region containing the classical class I genes. Immunogenetics 53:490–500
Renard C, Hart E, Sehra H, Beasley H, Coggill P, Howe K, Harrow J, Gilbert J, Sims S, Rogers J, Ando A, Shigenari A, Shiina T, Inoko H, Chardon P, Beck S (2006) The genomic sequence and analysis of the swine major histocompatibility complex. Genomics 88:96–110
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Shiina T, Inoko H, Kulski JK (2004) An update of the HLA genomic region, locus information and disease associations: 2004. Tissue Antigens 64:631–649
Shiina T, Hosomichi K, Inoko H, Kulski JK (2009) The HLA genomic loci map: expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J Hum Genet 54:15–39
Smith DM, Lunney JK, Ho CS, Martens GW, Ando A, Lee JH, Schook L, Renard C, Chardon P (2005a) Nomenclature for factors of the swine leukocyte antigen class II system, 2005. Tissue Antigens 66:623–639
Smith DM, Lunney JK, Martens GW, Ando A, Lee JH, Ho CS, Schook L, Renard C, Chardon P (2005b) Nomenclature for factors of the SLA class-I system, 2004. Tissue Antigens 65:136–149
Smith DM, Martens GW, Ho CS, Asbury JM (2005c) DNA sequence based typing of swine leukocyte antigens in Yucatan miniature pigs. Xenotransplantation 12:481–488
Soe OK, Ohba Y, Imaeda N, Nishii N, Takasu M, Yoshioka G, Kawata H, Shigenari A, Uenishi H, Inoko H, Ando A, Kitagawa H (2008) Assignment of the SLA alleles and reproductive potential of selective breeding Duroc pig lines. Xenotransplantation 15:390–397
Sullivan JA, Oettinger HF, Sachs DH, Edge AS (1997) Analysis of polymorphism in porcine MHC class I genes: alterations in signals recognized by human cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Immunol 159:2318–2326
Tanaka-Matsuda M, Ando A, Rogel-Gaillard C, Chardon P, Uenishi H (2009) Difference in number of loci of swine leukocyte antigen classical class I genes among haplotypes. Genomics 93:261–273
Wegner KM (2009) Massive parallel MHC genotyping: titanium that shines. Mol Ecol 18:1818–1820
Wiseman RW, Karl JA, Bimber BN, O’Leary CE, Lank SM, Tuscher JJ, Detmer AM, Bouffard P, Levenkova N, Turcotte CL, Szekeres E Jr, Wright C, Harkins T, O'Connor DH (2009) Major histocompatibility complex genotyping with massively parallel pyrosequencing. Nat Med 15:1322–1326
Zagalska-Neubauer M, Babik W, Stuglik M, Gustafsson L, Cichon M, Radwan J (2010) 454 Sequencing reveals extreme complexity of the class II major histocompatibility complex in the collared flycatcher. BMC Evol Biol 10:395
Acknowledgments
We thank the Japan Farm CLAWN Institute (Kagoshima, Japan) and the National Institute of Livestock and Grassland Sciences (Tsukuba, Japan) for providing the swine blood samples. We thank Masayuki Tanaka, Hideki Hayashi, and Hiroshi Kamiguchi in Education and Research Support Center in the Tokai University School of Medicine for technical assistance. The work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (22133002) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (21300155) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) and the Animal Genome Research Project of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to the DDBJ, EMBL, and GenBank nucleotide sequence databases and have been assigned accession numbers AB599993 to AB599997.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Genotyping of SLA class I genes by the 2ndGen method using perfectly matched reads of the SLA class I sequences (PDF 54 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Expression levels and normalized read numbers of classical SLA class I genes SLA-1, SLA-2, and SLA-3 (PDF 12 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Results of an ANOVA testing on the pyrosequencing read numbers and the expression levels (PDF 5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kita, Y.F., Ando, A., Tanaka, K. et al. Application of high-resolution, massively parallel pyrosequencing for estimation of haplotypes and gene expression levels of swine leukocyte antigen (SLA) class I genes. Immunogenetics 64, 187–199 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0572-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0572-2