Abstract
Researchers have recently renewed interest in bacteriophages. Being valuable models for the study of eukaryotic viruses, and more importantly, natural killers of bacteria, bacteriophages are being tapped for their potential role in multiple applications. Bacteriophages are also being increasingly sought for bacteriophage therapy due to rising antimicrobial resistance among pathogens. Reports show that there is an increasing trend in therapeutic application of natural bacteriophages, genetically engineered bacteriophages, and bacteriophage-encoded products as antimicrobial agents. In view of these applications, the isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from the environment has caught attention. In this review, various methods for isolation of bacteriophages from environmental sources like water, soil, and air are comprehensively described. The review also draws attention towards a handful on-field bacteriophage isolation techniques and the need for their further rapid development.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Payne S (2017) Viruses: from understanding to investigation. Academic Press
Tokarz-Deptuła B, Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej P, Czupryńska P, Deptuła W (2019) Protozoal giant viruses: agents potentially infectious to humans and animals. Virus Genes 55(5):574–591
Guttman B, Raya R, Kutter E (2005) Basic phage biology. Bacteriophages: Biology and Applications;4.
Sulakvelidze A, Kutter E (2004) Bacteriophage therapy in humans. Bacteriophages: biology and applications. 381.
Lin DM, Koskella B, Lin HC (2017) Phage therapy: an alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 8(3):162
Karimi M, Mirshekari H, Basri SM, Bahrami S, Moghoofei M, Hamblin MR (2016) Bacteriophages and phage-inspired nanocarriers for targeted delivery of therapeutic cargos. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 106:45–62
Jhamb S (2014) Biopreservation of food using bacteriocins, bacteriophages and endolysins. Bombay Technol 64(1):9–21
Sillankorva SM, Oliveira H, Azeredo J (2012) Bacteriophages and their role in food safety. Int J Microbiol.
Adriaenssens EM et al (2012) T4-related bacteriophage LIMEstone isolates for the control of soft rot on potato caused by ‘Dickeya solani.’ PloS One 7(3):e33227
Fujiwara A, Fujisawa M, Hamasaki R, Kawasaki T, Fujie M, Yamada T (2011) Biocontrol of Ralstonia solanacearum by treatment with lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(12):4155–4162
Hosseinidoust Z, Olsson AL, Tufenkji N (2014) Going viral: designing bioactive surfaces with bacteriophage. Colloids Surf, B 124:2–16
Benhar I (2001) Biotechnological applications of phage and cell display. Biotechnol Adv 19(1):1–33
Ronca R, Benzoni P, De Luca A, Crescini E, Dell’Era P (2012) Phage displayed peptides/antibodies recognizing growth factors and their tyrosine kinase receptors as tools for anti-cancer therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci 13(4):5254–5277
Zourob M, Ripp S (2010) Bacteriophage-based biosensors. Recognition receptors in biosensors. Springer, New York, pp 415–448
Ahmed A, Rushworth JV, Hirst NA, Millner PA (2014) Biosensors for whole-cell bacterial detection. Clin Microbiol Rev 27(3):631–646
Majewska J (2015) Oral application of T4 phage induces weak antibody production in the gut and in the blood. Viruses 7:4783–4799
Kaźmierczak Z, Górski A, Dąbrowska K (2014) Facing antibiotic resistance: Staphylococcus aureus phages as a medical tool. Viruses 6(7):2551–2570
Górski A, Międzybrodzki R, Weber-Dąbrowska B, Fortuna W, Letkiewicz S, Rogóż P, Jończyk-Matysiak E, Dąbrowska K, Majewska J, Borysowski J (2016) Phage therapy: combating infections with potential for evolving from merely a treatment for complications to targeting diseases. Front Microbiol 7:1515
Shlezinger M, Khalifa L, Houri-Haddad Y, Coppenhagen-Glazer S, Resch G, Que YA, Beyth S, Dorfman E, Hazan R, Beyth N (2017) Phage therapy: a new horizon in the antibacterial treatment of oral pathogens. Curr Top Med Chem 17(10):1199–1211
O’Flaherty S, Ross RP, Coffey A (2009) Bacteriophage and their lysins for elimination of infectious bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(4):801–819
Wittebole X, De Roock S, Opal SM (2014) A historical overview of bacteriophage therapy as an alternative to antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial pathogens. Virulence 5(1):226–235
Smith HW, Huggins MB (1983) Effectiveness of phages in treating experimental Escherichia coli diarrhoea in calves, piglets and lambs. Microbiology 129(8):2659–2675
Soothill JS (1992) Treatment of experimental infections of mice with bacteriophages. J Med Microbiol 37(4):258–261
Merril CR, Biswas B, Carlton R, Jensen NC, Creed GJ, Zullo S, Adhya S (1996) Long-circulating bacteriophage as antibacterial agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(8):3188–3192
Cooper CJ, Khan Mirzaei M, Nilsson AS (2016) Adapting drug approval pathways for bacteriophage-based therapeutics. Front Microbiol 7:1209
Schooley RT, Biswas B, Gill JJ, Hernandez-Morales A, Lancaster J, Lessor L, Barr JJ, Reed SL, Rohwer F, Benler S, Segall AM (2017) Development and use of personalized bacteriophage-based therapeutic cocktails to treat a patient with a disseminated resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(10).
Mostafa MF, Borhan A, Abdallah AF, Beheri AS, Abul-Hassan HS (1990) A retrospective study of 5505 burned patients admitted to Alexandria burns unit. Ann Mediterranean Burns Club 3:269–272
Markoishvili K, Tsitlanadze G, Katsarava R, Glenn J, Morris MD Jr, Sulakvelidze A (2002) A novel sustained-release matrix based on biodegradable poly (ester amide) s and impregnated with bacteriophages and an antibiotic shows promise in management of infected venous stasis ulcers and other poorly healing wounds. Int J Dermatol 41(7):453–458
Rhoads DD, Wolcott RD, Kuskowski MA, Wolcott BM, Ward LS, Sulakvelidze A (2009) Bacteriophage therapy of venous leg ulcers in humans: results of a phase I safety trial. J Wound Care 18(6):237–243
Kvachadze L et al (2011) Evaluation of lytic activity of staphylococcal bacteriophage Sb-1 against freshly isolated clinical pathogens. Microb Biotechnol 4(5):643–650
Rose T, Verbeken G, De Vos D, Merabishvili M, Vaneechoutte M, Lavigne R, Jennes S, Zizi M, Pirnay JP (2014) Experimental phage therapy of burn wound infection: difficult first steps. Int J Burns Trauma 4(2):66
Fish R, Kutter E, Wheat G, Blasdel B, Kutateladze M, Kuhl S (2016) Bacteriophage treatment of intransigent diabetic toe ulcers: a case series. J Wound Care 25(Sup7):S27-33
Jault P, Leclerc T, Jennes S, Pirnay JP, Que YA, Resch G, Rousseau AF, Ravat F, Carsin H, Le Floch R, Schaal JV (2019) Efficacy and tolerability of a cocktail of bacteriophages to treat burn wounds infected by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PhagoBurn): a randomised, controlled, double-blind phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 19(1):35–45
Jault P, Leclerc T, Jennes S, Pirnay JP, Que YA, Resch G, Rousseau AF, Ravat F, Carsin H, Le Floch R, Schaal JV (2019) Efficacy and tolerability of a cocktail of bacteriophages to treat burn wounds infected by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PhagoBurn): a randomised, controlled, double-blind phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 19(1):35–45
Morozova VV, Vlassov VV, Tikunova NV (2018) Applications of bacteriophages in the treatment of localized infections in humans. Front Microbiol 9:1696
Rohde C, Resch G, Pirnay JP, Blasdel BG, Debarbieux L, Gelman D, Górski A, Hazan R, Huys I, Kakabadze E, Łobocka M (2018) Expert opinion on three phage therapy related topics: bacterial phage resistance, phage training and prophages in bacterial production strains. Viruses 10(4):178
Summers WC (1993) Cholera and plague in India: the bacteriophage inquiry of 1927–1936. J Hist Med Allied Sci 48(3):275–301
Essoh C, Blouin Y, Loukou G, Cablanmian A, Lathro S, Kutter E, Thien HV, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C (2013) The susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from cystic fibrosis patients to bacteriophages. PLoS One 8(4):e60575
Kutateladze Á, Adamia R (2008) Phage therapy experience at the Eliava Institute. Med Mal Infect 38(8):426–430
Kutateladze M, Adamia R (2010) Bacteriophages as potential new therapeutics to replace or supplement antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol 28(12):591–595
Hoyle N, Zhvaniya P, Balarjishvili N, Bolkvadze D, Nadareishvili L, Nizharadze D, Wittmann J, Rohde C, Kutateladze M (2018) Phage therapy against Achromobacter xylosoxidans lung infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis: a case report. Res Microbiol 169(9):540–542
Wright A, Hawkins CH, Änggård EE, Harper DR (2009) A controlled clinical trial of a therapeutic bacteriophage preparation in chronic otitis due to antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; a preliminary report of efficacy. Clin Otolaryngol 34(4):349–357
Sarker SA et al (2016) Oral phage therapy of acute bacterial diarrhea with two coliphage preparations: a randomized trial in children from Bangladesh. EBioMedicine 4:124–137
Zhang H, Fouts DE, DePew J, Stevens RH (2013) Genetic modifications to temperate Enterococcus faecalis phage ϕEf11 that abolish the establishment of lysogeny and sensitivity to repressor, and increase host range and productivity of lytic infection. Microbiology 159(Pt 6):1023
Dedrick RM et al (2019) Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med 25(5):730–733
Wommack KE, Colwell RR (2000) Virioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(1):69–114
Abdelzaher AM, Solo-Gabriele HM, Wright ME, Palmer CJ (2008) Sequential concentration of bacteria and viruses from marine waters using a dual membrane system. J Environ Qual 37(4):1648–1655
Naghavi NS, Golgoljam M, Akbari M (2013) Effect of three sewage isolated bacteriophages on the multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria. J Biol Sci 13(5):422
Shukla KS, Hirpurkar SD, Singh SK, Rajoria R (2014) Isolation of phage from animal waste of different LSF and their utility in phage therapy. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3:205–210
Merabishvili M, Vervaet C, Pirnay JP, De Vos D, Verbeken G, Mast J, Chanishvili N, Vaneechoutte M (2013) Stability of Staphylococcus aureus phage ISP after freeze-drying (lyophilization). PloS One 8(7):e68797
Latz S, Wahida A, Arif A, Häfner H, Hoß M, Ritter K, Horz HP (2016) Preliminary survey of local bacteriophages with lytic activity against multi-drug resistant bacteria. J Basic Microbiol 56(10):1117–1123
Gill JJ, Young R (2011) Therapeutic applications of phage biology: history, practice and recommendations. In: Emerging Trends in Antibacterial Discovery: Answering the Call to Arms. 367, pp 410
Łobocka M, Hejnowicz MS, Gagała U, Weber-Dabrowska B, Wegrzyn G, Dadlez M (2014) The first step to bacteriophage therapy—how to choose the correct phage. In: Phage therapy: current research and applications. pp 23–69
Weber-Dąbrowska B, Żaczek M, Dziedzic B, Łusiak-Szelachowska M, Kiejzik M, Górski A, Gworek B, Wierzbicki K, Eymontt A (2014) Bacteriophages in green biotechnology–the utilization of drinking water. In: Industrial, medical and environmental applications of microorganisms: current status and trends. pp 500–4.
Vandersteegen K, Kropinski AM, Nash JH, Noben JP, Hermans K, Lavigne R (2013) Romulus and Remus, two phage isolates representing a distinct clade within the Twortlikevirus genus, display suitable properties for phage therapy applications. J Virol 87(6):3237–3247
Mattila S, Ruotsalainen P, Jalasvuori M (2015) On-demand isolation of bacteriophages against drug-resistant bacteria for personalized phage therapy. Front Microbiol 6:1271
Pires DP, Cleto S, Sillankorva S, Azeredo J, Lu TK (2016) Genetically engineered phages: a review of advances over the last decade. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80(3):523–543
Nair A, Khairnar K (2019) Genetically engineered phages for therapeutics: proceed with caution. Nat Med 25(7):1028
Weinbauer MG (2004) Ecology of prokaryotic viruses. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28(2):127–181
Drulis-Kawa Z, Majkowska-Skrobek G, Maciejewska B, Delattre AS, Lavigne R (2012) Learning from bacteriophages-advantages and limitations of phage and phage-encoded protein applications. Curr Protein Pept Sci 13(8):699–722
Hyman P (2019) Phages for phage therapy: isolation, characterization, and host range breadth. Pharmaceuticals 12(1):35
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. InterScience, New York
de Jonge PA, Nobrega FL, Brouns SJ, Dutilh BE (2019) Molecular and evolutionary determinants of bacteriophage host range. Trends Microbiol 27(1):51–63
Wooley JC, Ye Y (2010) Metagenomics: facts and artifacts, and computational challenges. J Comput Sci Technol 25(1):71–81
Clokie MR, Millard AD, Letarov AV, Heaphy S (2011) Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 1(1):31–45
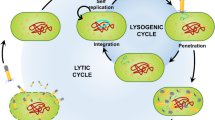
Howard-Varona C, Hargreaves KR, Abedon ST, Sullivan MB (2017) Lysogeny in nature: mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages. ISME J 11(7):1511–1520
Sekulovic O, Garneau JR, Néron A, Fortier LC (2014) Characterization of temperate phages infecting Clostridium difficile isolates of human and animal origins. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(8):2555–2563
Ra’l RR, H’bert EM (2009) Isolation of phage via induction of lysogens. In: Bacteriophages. Humana Press, pp 23–32
Otsuji N, Sekiguchi M, Iijima T, Takagi Y (1959) Induction of phage formation in the lysogenic Escherichia coli K-12 by mitomycin C. Nature 184(4692):1079–1080
Heinemann B, Howard AJ (1964) Induction of lambda-bacteriophage in Escherichia coli as a screening test for potential antitumor agents. Appl Microbiol 12(3):234–239
DeMarini DM, Lawrence BK (1992) Prophage induction by DNA topoisomerase II poisons and reactive-oxygen species: role of DNA breaks. Mut Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 267(1):1–7
Goerke C, Köller J, Wolz C (2006) Ciprofloxacin and trimethoprim cause phage induction and virulence modulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(1):171–177
López E, Domenech A, Ferrándiz MJ, Frias MJ, Ardanuy C, Ramirez M, García E, Liñares J, Adela G (2014) Induction of prophages by fluoroquinolones in Streptococcus pneumoniae: implications for emergence of resistance in genetically-related clones. Plos One 9(4):e94358
Łoś JM, Łoś M, Węgrzyn A, Węgrzyn G (2010) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated induction of the Shiga toxinconverting lambdoid prophage ST2-8624 in Escherichia coli O157: H7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 58(3):322–329
Hankin E (1896) The bactericidal action of the waters of the Jumna and the Ganges on Vibrio cholerae. Ann Inst Pasteur 10:511
Van Twest R, Kropinski AM (2009) Bacteriophage enrichment from water and soil. In: Bacteriophages. Humana Press, pp 15–21
Łobocka M, Hejnowicz MS, Gagała U, Weber-Dabrowska B, Wegrzyn G, Dadlez M (2014) The first step to bacteriophage therapy—how to choose the correct phage. Phage therapy: current research and applications. pp 23–69.
Sime-Ngando T (2014) Environmental bacteriophages: viruses of microbes in aquatic ecosystems. Front Microbiol 5:355
Suttle CA (2007) Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):801–812
Yooseph S et al (2010) Genomic and functional adaptation in surface ocean planktonic prokaryotes. Nature 468(7320):60
Brussaard CPD, Baudoux AC, and Rodriguez-Varela F (2016) Marine viruses. In: LJ Stal and SM Cretoiu (Eds) The marine microbiome–an untold resource of biodiversity and biotechnological potential. Springer International Publishing, pp 305–32
Tartera CA, Jofre JU (1987) Bacteriophages active against Bacteroides fragilis in sewage-polluted waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(7):1632–1637
Kfir R, Coubrough P, Grabow WO (1991) The occurrence of male-specific and somatic bacteriophages in polluted South African waters. Water Sci Technol 24(2):251–254
Goyal SM (1983) Indicators of viruses. Viral Pollut Environ 1:211–230
Hilton MC, Stotzky G (1973) Use of coliphages as indicators of water pollution. Can J Microbiol 19(6):747–751
Šimková A, Červenka J (1981) Coliphages as ecological indicators of enteroviruses in various water systems. Bull World Health Organ 59(4):611
Grabow WOK, Coubrough P, Nupen EM, Bateman BW (1984) Evaluation of coliphages as indicators of the virological quality of sewage-polluted water. Water SA 10(1):07–14
Shields PA, Farrah SR (1986) Concentration of viruses in beef extract by flocculation with ammonium sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol 51(1):211–213
Scheuerman PR, Farrah SR, Bitton G (1986) Reduction of microbial indicators and viruses in a cypress strand. Water Sci Technol 18(10):1–8
Araujo R, Lasobras J, Puig A, Lucena F, Jofre J (1997) Abundance of bacteriophages of enteric bacteria in different fresh water environments. Water Sci Technol 35(11–12):125–128
Primrose SB, Day M (1977) Rapid concentration of bacteriophages from aquatic habitats. J Appl Bacteriol 42(3):417–421
Seeley ND, Mallard G, Primrose SB (1979) A portable device for concentrating bacteriophages from large volumes of freshwater. J Appl Bacteriol 47(1):145–52
Bitton G, Chang LT, Farrah SR, Clifford K (1981) Recovery of coliphages from wastewater effluents and polluted lake water by the magnetite-organic flocculation method. Appl Environ Microbiol 41(1):93–96
Kennedy JE, Bitton G, Oblinger JL (1985) Comparison of selective media for assay of coliphages in sewage effluent and lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(1):33–36
Logan KB, Rees GE, Seeley ND, Primrose SB (1980) Rapid concentration of bacteriophages from large volumes of freshwater: evaluation of positively charged, microporous filters. J Virol Methods 1(2):87–97
Grabow WO, Holtzhausen CS, De Villiers JC (1993) Research on bacteriophages as indicators of water quality. Water Research Commission, Pretoria, South Africa. Project Report 321
Grabow WOK, Very A, Uys M, De Villiers JC (1998) Evaluation of the application of bacteriophages as indicators of water quality. WRC Report No 540/1/98. Water Research Commission.
Goyal SM, Gerba CP, Bitton G (1987) Phage ecology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p 321
Fleischer J, Schlafmann K, Otchwemah R, Botzenhart K (2000) Elimination of enteroviruses, other enteric viruses, F-specific coliphages, somatic coliphages and E. coli in four sewage treatment plants of southern Germany. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 49(3):127–38
Mocé-Llivina L, Muniesa M, Pimenta-Vale H, Lucena F, Jofre J (2003) Survival of bacterial indicator species and bacteriophages after thermal treatment of sludge and sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1452–1456
Muniesa M, Mocé-Llivina L, Katayama H, Jofre J (2003) Bacterial host strains that support replication of somatic coliphages. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83(4):305–315
Mandilara GD, Smeti EM, Mavridou AT, Lambiri MP, Vatopoulos AC, Rigas FP (2006) Correlation between bacterial indicators and bacteriophages in sewage and sludge. FEMS Microbiol Lett 263(1):119–126
Heinonen-Tanski H, Reponen T, Koivunen J (2009) Airborne enteric coliphages and bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Res 43(9):2558–2566
Blanch AR et al (2006) Integrated analysis of established and novel microbial and chemical methods for microbial source tracking. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(9):5915–5926
Imamovic L, Ballesté E, Jofre J, Muniesa M (2010) Quantification of Shiga toxin-converting bacteriophages in wastewater and in fecal samples by real-time quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(17):5693–5701
Breitbart M, Wegley L, Leeds S, Schoenfeld T, Rohwer F (2004) Phage community dynamics in hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(3):1633–1640
Schoenfeld T, Patterson M, Richardson PM, Wommack KE, Young M, Mead D (2008) Assembly of viral metagenomes from yellowstone hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(13):4164–4174
Bolduc B, Wirth JF, Mazurie A, Young MJ (2015) Viral assemblage composition in Yellowstone acidic hot springs assessed by network analysis. ISME J 9(10):2162–2177
Zablocki O, Van Zyl LJ, Kirby B, Trindade M (2017) Diversity of dsDNA viruses in a South African hot spring assessed by metagenomics and microscopy. Viruses 9(11):348
Sharma A, Schmidt M, Kiesel B, Mahato NK, Cralle L, Singh Y, Richnow HH, Gilbert JA, Arnold W, Lal R (2018) Bacterial and archaeal viruses of Himalayan hot springs at Manikaran modulate host genomes. Front Microbiol 9:3095
Munson-McGee JH, Snyder JC, Young MJ (2018) Archaeal viruses from high-temperature environments. Genes 9:E128
Zablocki O, van Zyl L, Trindade M (2018) Biogeography and taxonomic overview of terrestrial hot spring thermophilic phages. Extremophiles 22(6):827–837
Li M, Ji X, Wang B, Zhang Q, Lin L, Zhang B, Wei Y (2012) Isolation and characterization of a lytic bacteriophage from Mingyong glacier melt water. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 52(2):236–242
Bellas CM, Anesio AM (2013) High diversity and potential origins of T4-type bacteriophages on the surface of Arctic glaciers. Extremophiles 17(5):861–870
Luhtanen AM, Eronen-Rasimus E, Kaartokallio H, Rintala JM, Autio R, Roine E (2014) Isolation and characterization of phage–host systems from the Baltic Sea ice. Extremophiles 18(1):121–130
Senčilo A, Luhtanen AM, Saarijärvi M, Bamford DH, Roine E (2015) Cold-active bacteriophages from the Baltic Sea ice have diverse genomes and virus–host interactions. Environ Microbiol 17(10):3628–3641
Ji X, Zhang C, Kuang A, Li J, Cui Y, Qin K, Lin L, Cheng B, Zhang Q, Wei Y (2015) Morphological diversity of cultured cold-active lytic bacteriophages isolated from the Napahai plateau wetland in China. Virol Sin 30(6):457–459
Li M, Wang J, Zhang Q, Lin L, Kuang A, Materon LA, Ji X, Wei Y (2016) Isolation and characterization of the lytic cold-active bacteriophage MYSP06 from the Mingyong glacier in China. Curr Microbiol 72(2):120–127
Qin K, Cheng B, Zhang S, Wang N, Fang Y, Zhang Q, Kuang A, Lin L, Ji X, Wei Y (2016) Complete genome sequence of the cold-active bacteriophage VMY22 from Bacillus cereus. Virus Genes 52(3):432–435
Cabello-Yeves PJ, Zemskaya TI, Rosselli R, Coutinho FH, Zakharenko AS, Blinov VV, Rodriguez-Valera F (2018) Genomes of novel microbial lineages assembled from the sub-ice waters of Lake Baikal. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(1)
Luhtanen AM, Eronen-Rasimus E, Oksanen HM, Tison JL, Delille B, Dieckmann GS, Rintala JM, Bamford DH (2018) The first known virus isolates from Antarctic sea ice have complex infection patterns. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94(4):fiy028
Gencay YE, Birk T, Sørensen MC, Brøndsted L (2017) Methods for isolation, purification, and propagation of bacteriophages of Campylobacter jejuni. Campylobacter jejuni. Humana Press, New York, pp 19–28
Bhunchoth A et al (2015) Isolation of R alstonia solanacearum-infecting bacteriophages from tomato fields in C hiang M ai, T hailand, and their experimental use as biocontrol agents. J Appl Microbiol 118(4):1023–1033
Grabow WO (2001) Bacteriophages: update on application as models for viruses in water. Water SA 27(2):251–268
Tylenda CA, Calvert C, Kolenbrander PE, Tylenda A (1985) Isolation of Actinomyces bacteriophage from human dental plaque. Infect Immun 49(1):1–6
Debartolomeis J, Cabelli VJ (1991) Evaluation of an Escherichia coli host strain for enumeration of F male-specific bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(5):1301–1305
Bachrach G, Leizerovici-Zigmond M, Zlotkin A, Naor R, Steinberg D (2003) Bacteriophage isolation from human saliva. Lett Appl Microbiol 36(1):50–53
Chibani-Chennoufi S, Sidoti J, Bruttin A, Kutter E, Sarker S, Brüssow H (2004) In vitro and in vivo bacteriolytic activities of Escherichia coli phages: implications for phage therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(7):2558–2569
Grabow WO, Coubrough P (1986) Practical direct plaque assay for coliphages in 100-ml samples of drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol 52(3):430–433
Grabow WO, Vrey A, Uys M, De Villiers JC. Evaluation of the application of bacteriophages as indicators of water quality. WRC Report Nº 411/1/98. Water Research Commission, Pretoria.
Uys M (1999) Molecular characterisation of F-specific RNA phages in South Africa. Faculty of Medicine, University of Pretoria Department of Medical Virology, Pretoria
International Organization for Standardization (1995) Water quality-detection and enumeration of bacteriophages-Part 1: enumeration of F-specific RNA Bacteriophages. ISO
Sobsey MD, Schwab KJ, Handzel TR (1990) A simple membrane filter method to concentrate and enumerate male-specific RNA coliphages. J Am Water Works Assoc 82(9):52–59
Czajkowski R, Ozymko Z, Lojkowska E (2016) Application of zinc chloride precipitation method for rapid isolation and concentration of infectious Pectobacterium spp. and Dickeya spp. lytic bacteriophages from surface water and plant and soil extracts. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 61(1):29–33
Betz JV, Anderson KE (1964) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages active on Clostridium sporogenes. J Bacteriol 87(2):408–415
Poulos BT, John SG, Sullivan MB (2018) Iron chloride flocculation of bacteriophages from seawater. Bacteriophages. Humana Press, New York, pp 49–57
Strohmaier K (1967) A new procedure for quantitative measurements of virus particles in crude preparations. J Virol 1(5):1074–1081
Sweet BA, Ellender RD, Leong JK (1974) Recovery and removal of viruses from water utilizing membrane techniques. Dev Ind Microbiol 15:142–159
Jansons J, Bucens MR (1986) Virus detection in water by ultrafiltration. Water Res 20(12):1603–1606
Grabow WO, Holtzhausen CS, De Villiers JC (1993) Research on bacteriophages as indicators of water quality. Water Research Commission, Pretoria, South Africa. Project Report, 321
Berman DO, Rohr ME, Safferman RS (1980) Concentration of poliovirus in water by molecular filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol 40(2):426–428
Padan E, Shilo M, Kislev N (1967) Isolation of “cyanophages” from freshwater ponds and their interaction with Plectonema boryanum. Virology 32(2):234–246
Dahling DR, Phirke PM, Wright BA, Safferman RS (1985) Use of bituminous coal as an alternative technique for field concentration of waterborne viruses. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(5):1222–1225
Lakhe SB, Parhad NM (1988) Concentration of viruses from water on bituminous coal. Water Res 22(5):635–640
Borrego JJ, Cornax R, Preston DR, Farrah SR, McElhaney B, Bitton G (1991) Development and application of new positively charged filters for recovery of bacteriophages from water. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(4):1218–1222
(1998) Standard methods coliphage detection. In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE and Eaton AD (Eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th edn.) American Public Health Association, Washington DC, pp9–25
Goyal SM, Zerda KS, Gerba CP (1980) Concentration of coliphages from large volumes of water and wastewater. Appl Environ Microbiol 39(1):85–91
Sobsey MD, Glass JS (1980) Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters. Appl Environ Microbiol 40(2):201–210
Shields PA, Ling TF, Tjatha V, Shah DO, Farrah SR (1986) Comparison of positively charged membrane filters and their use in concentrating bacteriophages in water. Water Res 20(2):145–151
Wallis C, Henderson M, Melnick JL (1972) Enterovirus concentration on cellulose membranes. Appl Microbiol 23(3):476–480
Valentine RC, Allison AC, Virus particle adsorption I (1959) Theory of adsorption and experiments on the attachment of particles to non-biological surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta 34:10–23
Kessick MA, Wagner RA (1978) Electrophoretic mobilities of virus adsorbing filter materials. Water Res 12(4):263–8
ISO (1998a) Water quality - Detection and enumeration of bacteriophages. Part 2: Enumeration of Somatic Coliphages. ISO/DIS 10705–2.2. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. 17 pp
ISO (1998b) Water quality - Detection and enumeration of bacteriophages. Part 4: enumeration of bacteriophages infecting Bacteroides fragilis. ISO/CD 10705–4. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. 29 pp
Scott TM, Lukasik J, Farrah SR (2002) Improved method for recovery of bacteriophage from large volumes of water using negatively charged microporous filters. Can J Microbiol 48(4):305–310
Powell KL, Barrett MH, Pedley S, Tellam JH, Stagg KA (2000) Enteric virus detection in groundwater using a glass wool trap. In Groundwater: past achievements and future challenges, pp 813–816
Ruhanya V, Kabego L, Gichana JO (2016) Adsorption-elution techniques and molecular detection of enteric viruses from water. J Hum Virol Retrovirol 3.6(00112):64c
Haramoto E, Katayama H, Utagawa E, Ohgaki S (2009) Recovery of human norovirus from water by virus concentration methods. J Virol Methods 160(1–2):206–209
Seeley ND, Primrose SB (1982) A review: the isolation of bacteriophages from the environment. J Appl Bacteriol 53(1):1–7
Rose JB, Singh SN, Gerba CP, Kelley LM (1984) Comparison of microporous filters for concentration of viruses from wastewater. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(5):989–992
Primrose SB, Day M (1977) Rapid concentration of bacteriophages from aquatic habitats. J Appl Bacteriol 42(3):417–421
Seeley ND, Mallard G, Primrose SB (1979) A portable device for concentrating bacteriophages from large volumes of freshwater. J Appl Bacteriol 47(1):145–52
Singh SN, Gerba CP (1983) Concentration of coliphage from water and sewage with charge-modified filter aid. Appl Environ Microbiol 45(1):232–237
Goyal SM, Gerba CP, Bitton G (1987) Bacteriophage ecology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p 321
Sinton LW, Finlay RK, Reid AJ (1996) A simple membrane filtration-elution method for the enumeration of F-RNA, F-DNA and somatic coliphages in 100-ml water samples. J Microbiol Methods 25(3):257–269
Guelin A (1948) Quantitative study of bacteriophage of the sea. Ann Inst Pasteur 74(2):104–112
Kott Y (1966) Estimation of low numbers of Escherichia coli bacteriophage by use of the most probable number method. Appl Environ Microbiol 14(2):141–144
Hilton MC, Stotzky G (1973) Use of coliphages as indicators of water pollution. Can J Microbiol 19(6):747–751
Grabow WOK, Very A, Uys M, De Villiers JC (1998) Evaluation of the application of bacteriophages as indicators of water quality. WRC Report No 540/1/98. Water Research Commission
Ackermann HW, Nguyen TM (1983) Sewage coliphages studied by electron microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 45(3):1049–1059
International Organization for Standardization (2000) Water Quality – Detection and enumeration of bacteriophages, Part 2: enumeration of somatic coliphages. ISO 10705–2:2000(E) Geneva: International Organization for Standardization
Ghugare GS, Nair A, Nimkande V, Sarode P, Rangari P, Khairnar K (2017) Membrane filtration immobilization technique—a simple and novel method for primary isolation and enrichment of bacteriophages. J Appl Microbiol 122(2):531–539
Serwer P, Hayes SJ, Zaman S, Lieman K, Rolando M, Hardies SC (2004) Improved isolation of undersampled bacteriophages: finding of distant terminase genes. Virology 329(2):412–424
Serwer P, Hayes SJ, Thomas JA, Demeler B, Hardies SC (2009) Isolation of novel large and aggregating bacteriophages. In Bacteriophages. Humana Press, pp 55–66.
Abdelzaher AM, Solo-Gabriele HM, Wright ME, Palmer CJ (2008) Sequential concentration of bacteria and viruses from marine waters using a dual membrane system. J Environ Qual 37(4):1648–1655
Ashelford KE, Day MJ, Fry JC (2003) Elevated abundance of bacteriophage infecting bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(1):285–289
Srinivasiah S, Bhavsar J, Thapar K, Liles M, Schoenfeld T, Wommack KE (2008) Phages across the biosphere: contrasts of viruses in soil and aquatic environments. Res Microbiol 159(5):349–357
Pratama AA, van Elsas JD (2018) The ‘neglected’soil virome–potential role and impact. Trends Microbiol 26(8):649–662
Leroy M, Prigent M, Dutertre M, Confalonieri F, Dubow M (2008) Bacteriophage morphotype and genome diversity in Seine River sediment. Freshw Biol 53(6):1176–1185
Middelboe M, Jacquet S, Weinbauer M (2008) Viruses in freshwater ecosystems: an introduction to the exploration of viruses in new aquatic habitats. Freshw Biol 53(6):1069–1075
Skraber S, Schijven J, Italiaander R, Husman AM (2009) Accumulation of enteric bacteriophage in fresh water sediments J Water. Health 7(3):372–379
Calero-Cáceres W, Méndez J, Martín-Díaz J, Muniesa M (2017) The occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in a Mediterranean river and their persistence in the riverbed sediment. Environ Pollut 223:384–394
Wiebe WJ, Liston J (1968) Isolation and characterization of a marine bacteriophage. Mar Biol 1(3):244–249
Suttle CA (2005) Viruses in the sea. Nature 437(7057):356–361
Suttle CA (2007) Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):801–812
Azam F, Malfatti F (2007) Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):782–791
Børsheim KY (1993) Native marine bacteriophages. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 11(3–4):141–159
Breitbart M, Felts B, Kelley S, Mahaffy JM, Nulton J, Salamon P, Rohwer F (2004) Diversity and population structure of a near–shore marine–sediment viral community. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 271(1539):565–574
Sklarow SS, Colwell RR, Chapman GB, Zane SF (1973) Characteristics of a Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophage isolated from Atlantic coast sediment. Can J Microbiol 19(12):1519–1520
Lachnit T, Dafforn KA, Johnston EL, Steinberg P (2019) Contrasting distributions of bacteriophages and eukaryotic viruses from contaminated coastal sediments. Environ Microbiol 21(6):1929–1941
Batinovic S, Wassef F, Knowler SA, Rice DT, Stanton CR, Rose J, Tucci J, Nittami T, Vinh A, Drummond GR, Sobey CG (2019) Bacteriophages in natural and artificial environments. Pathogens 8(3):100
Danovaro R, Serresi M (2000) Viral density and virus-to-bacterium ratio in deep-sea sediments of the Eastern Mediterranean. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(5):1857–1861
Liu B, Wu S, Song Q, Zhang X, Xie L (2006) Two novel bacteriophages of thermophilic bacteria isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal fields. Curr Microbiol 53(2):163–166
Engelhardt T, Sahlberg M, Cypionka H, Engelen B (2013) Biogeography of Rhizobium radiobacter and distribution of associated temperate phages in deep subseafloor sediments. ISME J 7(1):199–209
Yoshida M, Takaki Y, Eitoku M, Nunoura T, Takai K (2013) Metagenomic analysis of viral communities in (hado) pelagic sediments. PloS One 8(2):e57271
Engelhardt T, Kallmeyer J, Cypionka H, Engelen B (2014) High virus-to-cell ratios indicate ongoing production of viruses in deep subsurface sediments. ISME J 8(7):1503–1509
Dell’Anno A, Corinaldesi C, Danovaro R (2015) Virus decomposition provides an important contribution to benthic deep-sea ecosystem functioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(16):E2014–E2019
Prigent M, Leroy M, Confalonieri F, Dutertre M, DuBow MS (2005) A diversity of bacteriophage forms and genomes can be isolated from the surface sands of the Sahara Desert. Extremophiles 9(4):289–296
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88(6):1354–1364
Prestel E, Salamitou S, DuBow MS (2008) An examination of the bacteriophages and bacteria of the Namib desert. J Microbiol 46(4):364–372
Andrew DR, Fitak RR, Munguia-Vega A, Racolta A, Martinson VG, Dontsova K (2012) Abiotic factors shape microbial diversity in Sonoran Desert soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(21):7527–7537
Prestel E, Regeard C, Salamitou S, Neveu J, DuBow MS (2013) The bacteria and bacteriophages from a Mesquite flats site of the Death Valley desert. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103(6):1329–1341
Fierer N et al (2012) Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(52):21390–21395
Reavy B, Swanson MM, Cock PJ, Dawson L, Freitag TE, Singh BK, Torrance L, Mushegian AR, Taliansky M (2015) Distinct circular single-stranded DNA viruses exist in different soil types. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(12):3934–3945
Makhalanyane TP, Valverde A, Gunnigle E, Frossard A, Ramond JB, Cowan DA (2015) Microbial ecology of hot desert edaphic systems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39(2):203–221
Zablocki O, Adriaenssens EM, Cowan D (2016) Diversity and ecology of viruses in hyperarid desert soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(3):770–777
Azua-Bustos A, González-Silva C, Arenas-Fajardo C, Vicuña R (2012) Extreme environments as potential drivers of convergent evolution by exaptation: the Atacama desert coastal range case. Front Microbiol 3:426
Meiring TL, Tuffin IM, Cary C, Cowan DA (2012) Genome sequence of temperate bacteriophage Psymv2 from Antarctic dry valley soil isolate Psychrobacter sp. MV2. Extremophiles 16(5):715–26
Trubl G, Solonenko N, Chittick L, Solonenko SA, Rich VI, Sullivan MB (2016) Optimization of viral resuspension methods for carbon-rich soils along a permafrost thaw gradient. PeerJ 4:e1999
Khairnar K (2016) Ganges: special at its origin. J Biol Res (Thessalon) 23(1):1–2
Adriaenssens EM, Kramer R, Van Goethem MW, Makhalanyane TP, Hogg I, Cowan DA (2017) Environmental drivers of viral community composition in Antarctic soils identified by viromics. Microbiome 5(1):1–4
Margesin R, Collins T (2019) Microbial ecology of the cryosphere (glacial and permafrost habitats): current knowledge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(6):2537–2549
Cowan DA, Makhalanyane TP, Dennis PG, Hopkins DW (2014) Microbial ecology and biogeochemistry of continental Antarctic soils. Front Microbiol 5:154
Khavina E (1954) Isolation of actinophages from soil. trudy. Mikrobiologijas Instituts (Latvijas PSR Zinatnu Akademija) 3:224–229
Welsch M, Minon A, Schönfeld JK (1955) Isolation of actinophages. Experientia 11(1):24–25
Reanney DC (1968) An assay for Bacillus stearothermophilus using thermophilic virus. N Z J Agric Res 11(4):763–770
Casida LE, Liu KC (1974) Arthrobacter globiformis and its bacteriophage in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 28(6):951–959
Tan JS, Reanney DC (1976) Interactions between bacteriophages and bacteria in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 8(2):145–150
Germida JJ, Casida LE (1981) Isolation of Arthrobacter bacteriophage from soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 41(6):1389–1393
Lanning S, Williams ST (1982) Methods for the direct isolation and enumeration of actinophages in soil. Microbiology 128(9):2063–2071
Dabbs ER (1998) Cloning of genes that have environmental and clinical importance from rhodococci and related bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 74(1):155–168
Ashelford KE, Norris SJ, Fry JC, Bailey MJ, Day MJ (2000) Seasonal population dynamics and interactions of competing bacteriophages and their host in the rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(10):4193–4199
Williamson KE, Wommack KE, Radosevich M (2003) Sampling natural viral communities from soil for culture-independent analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(11):6628–6633
Williamson KE, Radosevich M, Wommack KE (2005) Abundance and diversity of viruses in six Delaware soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(6):3119–3125
Swanson MM, Fraser G, Daniell TJ, Torrance L, Gregory PJ, Taliansky M (2009) Viruses in soils: morphological diversity and abundance in the rhizosphere. Ann Appl Biol 155(1):51–60
Van Twest R, Kropinski AM (2009) Bacteriophage enrichment from water and soil. In: Bacteriophages. Humana Press, pp 15–21
Williamson KE, Corzo KA, Drissi CL, Buckingham JM, Thompson CP, Helton RR (2013) Estimates of viral abundance in soils are strongly influenced by extraction and enumeration methods. Biol Fertil Soils 49(7):857–869
Ehrlich R, Miller S, Idoine LS (1964) Effects of environmental factors on the survival of airborne T-3 coliphage. Appl Microbiol 12(6):479–482
Harstad JB (1965) Sampling submicron T1 bacteriophage aerosols. Appl Microbiol 13(6):899–908
Benbough JE (1971) Some factors affecting the survival of airborne viruses. J Gen Virol 10(3):209–220
Warren JC, Akers TG, Dubovi EJ (1969) Effect of prehumidification on sampling of selected airborne viruses. Appl Environ Microbiol 18(5):893–896
Happ JW, Harstad JB, Buchanan LM (1966) Effect of air ions on submicron T1 bacteriophage aerosols. Appl Environ Microbiol 14(6):888–891
Neve H, Kemper U, Geis A, Heller KJ (1994) Monitoring and characterization of lactococcal bacteriophages in a dairy plant. Kieler Milchwirtschaftliche Forschungsberichte 46(2):167–178
Neve H, Berger A, Heller KJ (1995) A method for detecting and enumerating airborne virulent bacteriophages of dairy starter cultures. Kieler Milchwirtschaftliche Forschungsberichte 47(3):193–207
Neve H, Laborius A, Heller KJ (2003) Testing of the applicability of battery-powered portable microbial air samplers for detection and enumeration of airborne Lactococcus lactis dairy bacteriophages. Kieler Milchwirtschaftliche Forschungsberichte 55(4):301–315
Verreault D, Gendron L, Rousseau GM, Veillette M, Massé D, Lindsley WG, Moineau S, Duchaine C (2011) Detection of airborne lactococcal bacteriophages in cheese manufacturing plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(2):491–497
Verreault D, Moineau S, Duchaine C (2008) Methods for sampling of airborne viruses. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72(3):413–444
Fernández L, Escobedo S, Gutiérrez D, Portilla S, Martínez B, García P, Rodríguez A (2017) Bacteriophages in the dairy environment: from enemies to allies. Antibiotics 6(4):27
Espinosa IY, Pillai SD (2002) Impaction-based sampler for detecting male-specific coliphages in bioaerosols. J Rapid Methods Autom Microbiol 10(2):117–127
Fannin KF, Spendlove JC, Cochran KW, Gannon JJ (1976) Airborne coliphages from wastewater treatment facilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 31(5):705–710
Carducci A, Tozzi E, Rubulotta E, Casini B, Cantiani L, Rovini E, Muscillo M, Pacini R (2000) Assessing airborne biological hazard from urban wastewater treatment. Water Res 34(4):1173–1178
Magare B, Nair A, Khairnar K (2017) Isolation of bacteriophages from air using vacuum filtration technique: an improved and novel method. J Appl Microbiol 123(4):896–902
Hatch MT, Warren JC (1969) Enhanced recovery of airborne T3 coliphage and Pasteurella pestis bacteriophage by means of a presampling humidification technique. Appl Microbiol 17(5):685–689
Trouwborst T, De Jong JC, Winkler KC (1972) Mechanism of inactivation in aerosols of bacteriophage T1. J Gen Virol 15(3):235–242
Trouwborst T, De Jong JC (1973) Interaction of some factors in the mechanism of inactivation of bacteriophage MS2 in aerosols. Appl Microbiol 26(3):252–257
Trouwborst T, De Jong JC (1973) Surface inactivation, an important mechanism of aerosol inactivation for viruses, inactivated at high relative humidity. Airborne transmissionand airborne infection. Oosthoek Publishing Co., Utrecht, pp 137–140
Trouwborst T, Kuyper S (1974) Inactivation of baceriophage T3 in aerosols: effect of prehumidification on survival after spraying from solutions of salt, peptone, and saliva. Appl Microbiol 27(5):834–837
Tseng CC, Li CS (2005) Collection efficiencies of aerosol samplers for virus-containing aerosols. J Aerosol Sci 36(5–6):593–607
Hogan CJ Jr, Kettleson EM, Lee MH, Ramaswami B, Angenent LT, Biswas P (2005) Sampling methodologies and dosage assessment techniques for submicrometre and ultrafine virus aerosol particles. J Appl Microbiol 99(6):1422–1434
Burton NC, Grinshpun SA, Reponen T (2007) Physical collection efficiency of filter materials for bacteria and viruses. Ann Occup Hyg 51(2):143–151
Pasquarella C, Pitzurra O, Savino A (2000) The index of microbial air contamination. J Hosp Infect 46(4):241–256
Logan KB, Scott GE, Seeley ND, Primrose SB (1981) A portable device for the rapid concentration of viruses from large volumes of natural freshwater. J Virol Methods 3(4):241–249
Turgeon N, Toulouse MJ, Martel B, Moineau S, Duchaine C (2014) Comparison of five bacteriophages as models for viral aerosol studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(14):4242–4250
Moye ZD, Woolston J, Sulakvelidze A (2018) Bacteriophage applications for food production and processing. Viruses 10(4):205
Carlton RM, Noordman WH, Biswas B, De Meester ED, Loessner MJ (2005) Bacteriophage P100 for control of Listeria monocytogenes in foods: genome sequence, bioinformatic analyses, oral toxicity study, and application. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 43(3):301–312
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Camp MJ, Janisiewicz WJ, Abuladze T, Yang M, Saftner R, Sulakvelidze A (2003) Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes on fresh-cut produce by treatment with lytic bacteriophages and a bacteriocin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):4519–4526
Leverentz B, Conway WS, Janisiewicz W, Camp MJ (2004) Optimizing concentration and timing of a phage spray application to reduce Listeria monocytogenes on honeydew melon tissue. J Food Prot 67(8):1682–1686
Monk AB, Rees CD, Barrow P, Hagens S, Harper DR (2010) Bacteriophage applications: where are we now? Lett Appl Microbiol 51(4):363–369
Cross T, Schoff C, Chudoff D, Graves L, Broomell H, Terry K, Farina J, Correa A, Shade D, Dunbar D (2015) An optimized enrichment technique for the isolation of Arthrobacter bacteriophage species from soil sample isolates. JoVE J Vis Exp (98):e52781
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Director CSIR-NEERI, Nagpur for providing the research facility and infrastructure. We are grateful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for funding and supporting the research scholar. The manuscript has been checked for plagiarism using iThenticate Software and assigned KRC No.: CSIR-NEERI/KRC/2019/SEP/EVC/1
Funding
The research scholars Aparna Nair and Gaurav Ghugare were supported for fellowship by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AN wrote the manuscript and contributed to conceptualization of the review and its execution. GG contributed to acquisition of data and information relevant to the review. KK conceived and planned the review article and provided critical revision of the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, A., Ghugare, G.S. & Khairnar, K. An Appraisal of Bacteriophage Isolation Techniques from Environment. Microb Ecol 83, 519–535 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01782-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01782-z