Abstract
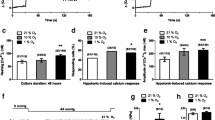
Transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels are nonselective cation channels pertinent to diverse physiological functions. Multiple TRPV channel subtypes have been identified in different tissues and cloned. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of TRPV channels in hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and its possible signal pathway. Reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction, real-time polymerase chain reaction, and Western blot analysis were used to detect the expression of TRPV in human PASMCs. Cell number was determined with a hemocytometer. Cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) was measured with a dynamic digital Ca2+ imaging system. The mRNA of TRPV1-4 was detected in human PASMCs and chronic hypoxia up-regulated expression levels of the TRPV1 gene and protein. The ability to proliferate, the resting [Ca2+]cyt, and cyclopiazonic acid–induced capacitative Ca2+ entry in human PASMCs were enhanced significantly by chronic hypoxia compared with the control, and these effects were inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by capsazepine, a TRPV1 channel inhibitor. These results suggest that TRPV1 may be a critical pathway or mediator in chronic hypoxia-induced proliferation of human PASMCs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevan S, Hothi S, Hughes G, James IF, Rang HP, Shah K, Walpole CS, Yeats JC (1992) Capsazepine: a competitive antagonist of the sensory neurone excitant capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol 107:544–552
Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strubing C (2001) The TRP ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:387–396
Earley S, Heppner TJ, Nelson MT, Brayden JE (2005) TRPV4 forms a novel Ca2+ signaling complex with ryanodine receptors and BKCa channels. Circ Res 97:1270–1279
Fantozzi I, Zhang S, Platoshyn O, Remillard CV, Cowling RT, Yuan JX (2003) Hypoxia increases AP-1 binding activity by enhancing capacitative Ca2+ entry in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285:L1233–L1245
Firth AL, Remillard CV, Yuan JX (2007) TRP channels in hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:895–906
Gauden V, Hu DE, Kurokawa T, Sarker MH, Fraser PA (2007) Novel technique for estimating cerebrovascular permeability demonstrates capsazepine protection following ischemia–reperfusion. Microcirculation 14:1–12
Golovina VA (1999) Cell proliferation is associated with enhanced capacitative Ca(2+) entry in human arterial myocytes. Am J Physiol 277:C343–C349
Inoue R, Jensen LJ, Shi J, Morita H, Nishida M, Honda A, Ito Y (2006) Transient receptor potential channels in cardiovascular function and disease. Circ Res 99:119–131
Jia Y, Lee LY (2007) Role of TRPV receptors in respiratory diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:915–927
Jordt SE, Ehrlich BE (2007) TRP channels in disease. Subcell Biochem 45:253–271
Kunichika N, Landsberg JW, Yu Y, Kunichika H, Thistlethwaite PA, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004a) Bosentan inhibits transient receptor potential channel expression in pulmonary vascular myocytes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1101–1107
Kunichika N, Yu Y, Remillard CV, Platoshyn O, Zhang S, Yuan JX (2004b) Overexpression of TRPC1 enhances pulmonary vasoconstriction induced by capacitative Ca2+ entry. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L962–L969
Landsberg JW, Yuan JX (2004) Calcium and TRP channels in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. News Physiol Sci 19:44–50
Lin MJ, Leung GP, Zhang WM, Yang XR, Yip KP, Tse CM, Sham JS (2004) Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 95:496–505
Minke B (2006) TRP channels and Ca2+ signaling. Cell Calcium 40:261–275
Muraki K, Iwata Y, Katanosaka Y, Ito T, Ohya S, Shigekawa M, Imaizumi Y (2003) TRPV2 is a component of osmotically sensitive cation channels in murine aortic myocytes. Circ Res 93:829–838
Patel HH, Zhang S, Murray F, Suda RY, Head BP, Yokoyama U, Swaney JS, Niesman IR, Schermuly RT, Pullamsetti SS, Thistlethwaite PA, Miyanohara A, Farquhar MG, Yuan JX, Insel PA (2007) Increased smooth muscle cell expression of caveolin-1 and caveolae contribute to the pathophysiology of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. FASEB J 21:2970–2979
Remillard CV, Yuan JX (2006) TRP channels, CCE, and the pulmonary vascular smooth muscle. Microcirculation 13:671–692
Skogvall S, Dalence-Guzman MF, Berglund M, Svensson K, Mesic A, Jonsson P, Persson CG, Sterner O (2008) Discovery of a potent and long-acting bronchorelaxing capsazepinoid, RESPIR 4–95. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21:125–133
Takahashi Y, Watanabe H, Murakami M, Ohba T, Radovanovic M, Ono K, Iijima T, Ito H (2007) Involvement of transient receptor potential canonical 1 (TRPC1) in angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy. Atherosclerosis 195:287–296
Wang J, Weigand L, Lu W, Sylvester JT, Semenza GL, Shimoda LA (2006) Hypoxia inducible factor 1 mediates hypoxia-induced TRPC expression and elevated intracellular Ca2+ in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 98:1528–1537
Waning J, Vriens J, Owsianik G, Stuwe L, Mally S, Fabian A, Frippiat C, Nilius B, Schwab A (2007) A novel function of capsaicin-sensitive TRPV1 channels: involvement in cell migration. Cell Calcium 42:17–25
Yang XR, Lin MJ, McIntosh LS, Sham JSK (2006) Functional expression of transient receptor potential melastatin- and vanilloid-related channels in pulmonary arterial and aortic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L1267–L1276
Yu Y, Fantozzi I, Remillard CV, Landsberg JW, Kunichika N, Platoshyn O, Tigno DD, Thistlethwaite PA, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004) Enhanced expression of transient receptor potential channels in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13861–13866
Zhang Y, Xiang B, Li YM, Wang Y, Wang X, Wang YN, Wu LL, Yu GY (2006) Expression and characteristics of vanilloid receptor 1 in the rabbit submandibular gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:467–473
Zhang S, Patel HH, Murray F, Remillard CV, Schach C, Thistlethwaite PA, Insel PA, Yuan JX (2007) Pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from normal subjects and IPAH patients show divergent cAMP-mediated effects on TRPC expression and capacitative Ca2+ entry. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L1202–L1210
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program in the Eleventh Five-year Plan Period (grant 2006BAI01A06), the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (grant 7082012), the Scientific Research Common Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (grant KM200710025002), the Key Project of Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (grant 208002), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant 2009CB522107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.X., Wang, J., Wang, C. et al. Functional Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-Related Channels in Chronically Hypoxic Human Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. J Membrane Biol 223, 151–159 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-008-9121-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-008-9121-9