Abstract
Purpose
Fluoroquinolones are popular and widely used in primary care and hospital settings. Premarketing studies showed a favourable side-effect profile. However, significant morbidity and the need for liver transplantation for acute liver failure have been reported. We reviewed the available data on liver damage linked to fluoroquinolones.
Methods
A systematic search of case reports on the MEDLINE database encompassing the years 2000–2011 was carried out. Additional references were found by a manual search of the retrieved paper. We also describe three new cases of hepatotoxicity attributable to fluoroquinolones seen at our Unit.
Results
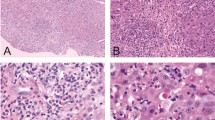
Thirty-five cases were retrieved from MEDLINE (51.4% male). According to the RUCAM scale, liver injury was classified as hepatocellular (51.4%), cholestatic (28.6%) or mixed (20.0%). Older age (≥ 65 years) was present in 42.8%. The time between initiation of treatment and hepatic injury ranged from 1 to 39 days (median 8 days). According to the RUCAM score, our cases were classified to be “highly probable” or “probable”. Only one patient underwent liver biopsy, which showed the features of liver damage linked to drug exposure. Liver enzymes from all patients return to normal range within 4 weeks of withdrawal. Only one patient showed a renal failure, associated with liver injury, with a need for haemodialysis for 3 weeks.
Conclusions
Fluoroquinolones are substantially safe antibiotics. Although fluoroquinolone-related hepatic injury occurs infrequently, its consequences can be severe. Patients should also be cautioned to avoid re-exposure to other members of the fluoroquinolone class.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desarro A, Desarro G (2001) Adverse reactions to fluoroquinolones. An overview on mechanistic aspects. Curr Med Chem 8:371–384
Lapi F, Tuccori M, Motola D et al (2010) Safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Analysis of adverse drug reactions in relation to prescription data using four regional pharmacovigilance databases in Italy. Drug Saf 33:789–799
Mehlhorn AJ, Brown DA (2007) Safety concerns with fluoroquinolones. Ann Pharmacother 41:1859–1866
Gruppo di lavoro OsMed (2010) L’uso dei farmaci in Italia. Rapporto Nazionale. Roma: Il pensiero scientifico editore 2011
Polson JE (2007) Hepatotoxicity due to antibiotics. Clin Liver Dis 11:549–561
Andrade RJ, Tulkens PM (2011) Hepatic safety of antibiotics used in primary care. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:1431–1446
George DK, Crawford DH (1996) Antibacterial-induced hepatotoxicity. Incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf 15:79–85
Andrade RJ, Lucena MI, Fernandez MC et al (2005) Drug-induced liver injury: an analysis of 461 incidences submitted to the Spanish registry over a 10-year period. Gastroenterology 129:512–521
Nori S, Nebesio C, Brashear R et al (2004) Moxifloxacin-associated drug hypersensitivity syndrome with toxic epidermal necrolysis and fulminant hepatic failure. Arch Dermatol 140:1537–1538
Grassmick BK, Lehr VT, Sundareson AS (1992) Fulminant hepatic failure possibly related to ciprofloxacin. Ann Pharmacother 26:636–639
Fuchs S, Simon Z, Brezis M (1994) Fatal hepatic failure associated with ciprofloxacin. Lancet 343:738–739
Spahr L, Rubbia-Brandt L, Marinescu O et al (2001) Acute fatal hepatitis related to levofloxacin. J Hepatol 35:308–309
Thiim M, Friedman LS (2003) Hepatotoxicity of antibiotics and antifungals. Clin Liver Dis 7:381–399
Danan G, Benichou C (1993) Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs. I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol 46:1323–1330
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM et al (1981) A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther 30:239–245
García-Cortés M, Lucena MI, Pachkoria K, for the Spanish Group for the Study of Drug-induced Liver Disease (grupo de Estudio para las Hepatopatias Asociadas a Medicamentos, Geham) et al (2008) Evaluation of Naranjo adverse drug reactions probability scale in causality assessment of drug-induced liver injury. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27:780–789
Orman ES, Conjeevaram HS, Vuppalanchi R et al (2011) Clinical and histopathologic features of fluoroquinolone-induced liver injury. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:517–523
Alan C, Koçoğlu H, Ersay AR et al (2011) Unexpected severe hepatotoxicity of ciprofloxacine: two case reports. Drug Chem Toxicol 34:189–191
Titos-Arcos JC, Hallal H, Robles M et al (2011) Acute cholestatic hepatitis associated with levofloxacin. Gastroenterol Hepatol 34:369–370
Figueira-Coelho J, Pereira O, Picado B et al (2010) Acute hepatitis associated with the use of levofloxacin. Clin Ther 32:1733–1737
Cholongitas E, Georgousaki C, Spyrou S et al (2009) Ciprofloxacin-induced acute cholestatic hepatitis. Ann Hepatol 8:400–401
Carrascosa MF, Lucena MI, Andrade RJ et al (2009) Fatal acute hepatitis after sequential treatment with levofloxacin, doxycycline, and naproxen in a patient presenting with acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Ther 31:1014–1019
García-Aparicio J, Herrero-Herrero JI (2010) Toxic hepatitis following sequential treatment with cotrimoxazol, levofloxacin, doxycycline and sertraline in a patient with a respiratory infection. Farm Hosp 34:152–154
Verma R, Dhamija R, Batts DH et al (2009) Moxifloxacin induced fatal hepatotoxicity in a 72-year-old man: a case report. Cases J 2:8063
Dichiara AJ, Atkinson M, Goodman Z et al (2008) Ciprofloxacin-induced acute cholestatic liver injury and associated renal failure. Case report and review. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 54:307–315
Bhagirath KM (2008) A case report of highly suspected ciprofloxacin-induced hepatotoxicity. Turk J Gastroenterol 19:204–206
Okan G, Yaylaci S, Peker O et al (2008) Vanishing bile duct and Stevens-Johnson syndrome associated with ciprofloxacin treated with tacrolimus. World J Gastroenterol 14:4697–4700
Coban S, Ceydilek B, Ekiz F et al (2005) Levofloxacin-induced acute fulminant hepatic failure in a patient with chronic hepatitis B infection. Ann Pharmacother 39:1737–1740
Zimpfer A, Propst A, Mikuz G et al (2004) Ciprofloxacin-induced acute liver injury: case report and review of literature. Virchows Arch 444:87–89
Goetz M, Galle PR, Schwarting A (2003) Non-fatal acute liver injury possibly related to high-dose ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22:294–296
Schwalm JD, Lee CH (2003) Acute hepatitis associated with oral levofloxacin therapy in a hemodialysis patient. CMAJ 168:847–848
Airey KJ, Koller E (2003) Acute hepatitis associated with levaquin in a patient with renal insufficiency taking amiodarone. CMAJ 14:169
Bataille L, Rahier J, Geubel A (2002) Delayed and prolonged cholestatic hepatitis with ductopenia after long-term ciprofloxacin therapy for Crohn's disease. J Hepatol 37:696–699
Soto S, López-Rosés L, Avila S et al (2002) Moxifloxacin-induced acute liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol 97:1853–1854
Contreras MA, Luna R, Mulero J et al (2001) Severe ciprofloxacin-induced acute hepatitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 20:434–435
Karim A, Ahmed S, Rossoff LJ (2001) Possible levofloxacin-induced acute hepatocellular injury in a patient with chronic obstructive lung disease. Clin Infect Dis 33:2088–2090
Nakamae H, Hino M, Yamane T (2000) A case of rhabdomyolysis due to levofloxacin. Clin Drug Invest 20:203–205
Björnsson E, Olsson R (2000) Norfloxacin-induced eosinophilic necrotizing granulomatous hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 95:3662–3663
Iannini PB (2007) The safety profile of moxifloxacin and other fluoroquinolones in special patient populations. Curr Med Res Opin 23:1403–1413
O’Donnell JA, Gelone SP (2000) Fluoroquinolones. Infect Dis Clin North Am 14:489–513
De Valle MB, Av Klinteberg V, Alem N et al (2006) Drug induced liver injury in a Swedish university hospital out-patient hepatology clinic. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 24:1187–1195
Van Bambeke F, Tulkens PM (2009) Safety profile of the respiratory fluoroquinolone moxifloxacin: comparison with other fluoroquinolones and other antibacterial classes. Drug Saf 32:359–378
Chalasani N, Björnsson E (2010) Risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology 138:2246–2259
Aithal GP, Day CP (2007) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 11:563–575
Larson AM (2007) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 11:525–548
Elouni B, Ben Salem C, Zamy M (2010) Cytolytic hepatitis possibly related to levonorgestrel/ethinylestradiol oral contraceptive use: 2 case reports. Ann Pharmacother 44:2035–2037
Wolfson JS, Hooper DC (1991) Overview of fluoroquinolone safety. Am J Med 91:153–161
Liu HH (2010) Safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Focus on levofloxacin. Drug Saf 33:353–369
Owens RC, Ambrose PG (2005) Antimicrobial safety: focus on fluoroquinolones. Clin Infect Dis 41 [Suppl 2]:S144–S157
Jones SE, Smith RH (1997) Quinolones may induce hepatitis. BMJ 314:869
Hautekeete ML, Kockx MM, Naegels S et al (1995) Cholestatic hepatitis related to quinolones: a report of two cases. J Hepatol 23:759–760
Blum A (1991) Ofloxacin-induced acute severe hepatitis. South Med J 84:1158
EMEA/CHMP (issued 24/07/08) European Medicines Agency recommends restricting the use of oral moxifloxacin-containing medicines. http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/press/pr/38292708en.pdf
Lopez-Navidad A, Domingo P, Cadafalch J et al (1990) Norfloxacin-induced hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol 11:277–278
Davoren P, Mainstone K (1993) Norfloxacin-induced hepatitis. Med J Aust 159:423–426
Lucena MI, Andrade RJ, Sánchez-Martinez H et al (1998) Norfloxacin-induced cholestatic jaundice. Am J Gastroenterol 93:2309–2311
Romero-Gómez M, Suárez García E, Fernández MC (1999) Norfloxacin-induced acute cholestatic hepatitis in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2324–2325
Henann NE, Zambie MF (2001) Gatifloxacin-associated acute hepatitis. Pharmacotherapy 21:157–182
Ball P, Mandell L, Niki Y et al (1999) Comparative tolerability of the newer fluoroquinolone antibacterials. Drug Saf 21:407–421
Bertino J Jr, Fish D (2000) The safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Clin Ther 22:798–817
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Licata, A., Randazzo, C., Morreale, I. et al. Fluoroquinolone-induced liver injury: three new cases and a review of the literature. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68, 525–532 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1201-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1201-6