Abstract
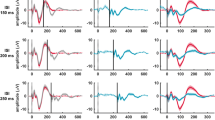
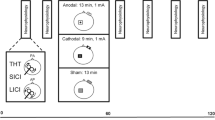
We investigated whether human attentional processes influence the activity of intracortical inhibitory and excitatory circuits—short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI), long-interval intracortical inhibition (LICI), and the intracortical facilitation (ICF)—elicited by paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in healthy subjects. In eight healthy subjects we tested SICI, LICI and ICF under different attention-demanding conditions: “relaxed”, “target hand” and “non-target hand”. To compare the effects of attentional levels on SICI, LICI and ICF with those produced on the MEPs elicited by repetitive TMS (rTMS), in the same subjects we also delivered supra-threshold 5-Hz rTMS under the same three experimental conditions. To disclose whether attentional processes act selectively on circuits engaged by TMS delivered at 5 Hz frequency and at an interstimulus interval (ISI) of 200 ms, we also investigated the effects of different attention levels on paired-pulse TMS delivered at the 200 ms ISI and on the MEP size during 1-Hz rTMS. Attentional levels had no influence on SICI, ICF and LICI activated by paired-pulse TMS, but increased the MEP facilitation elicited by 5-Hz rTMS. Varying the attention level left the findings from 1-Hz rTMS unchanged. The finding that attention leaves the activity of intracortical inhibitory and excitatory circuits elicited by paired-pulse TMS unchanged but influences the MEP facilitation elicited by 5-Hz rTMS suggests that attention operates only when the stimulation entrains neural circuits made up of a large number of cortical cells with plasticity properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese G, Assini A, Buccolieri A, Marchese R, Trompetto C (1999) Changes of intracortical inhibition during motor imagery in human subjects. Neurosci Lett 263:113–116
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Buccolieri A, Abbruzzese G, Rothwell JC (2004) Relaxation from a voluntary contraction is preceded by increased excitability of motor cortical inhibitory circuits. J Physiol 558:685–695
Castro-Alamancos MA, Connors BW (1996) Short-term synaptic enhancement and long-term potentiation in neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1335–1339
Chen R, Tam A, Bütefisch CM, Corwell B, Ziemann U, Rothwell JC, Cohen LG (1998) Intracortical inhibition and facilitation in different representations of the human motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 80:2870–2881
Conte A, Gilio F, Iezzi E, Frasca V, Inghilleri M, Berardelli A (2007) Attention influences the excitability of cortical motor areas in healthy humans. Exp Brain Res 182:109–117
Di Lazzaro V, Restuccia D, Oliviero A, Profice P, Ferrara L, Insola A, Mazzone P, Tonali P, Rothwell JC (1998) Magnetic transcranial stimulation at intensities below active motor threshold activates intracortical inhibitory circuits. Exp Brain Res 119:265–268
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Meglio M, Cioni B, Tamburrini G, Tonali P, Rothwell JC (2000) Direct demonstration of the effect of lorazepam on the excitability of the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 111:794–799
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Mazzone P, Pilato F, Saturno E, Insola A, Visocchi M, Colosimo C, Tonali PA, Rothwell JC (2002) Direct demonstration of long latency cortico-cortical inhibition in normal subjects and in a patient with vascular parkinsonism. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1673–1679
Eysenck HJ, Thompson W (1966) The effects of distraction on pursuit rotor learning, performance and reminiscence. Br J Psychol 57:99–106
Gilio F, Currà A, Inghilleri M, Lorenzano C, Suppa A, Manfredi M, Berardelli A (2003) Abnormalities of motor cortex excitability preceding movement in patients with dystonia. Brain 126:1745–1754
Hammond G, Faulkner D, Byrnes M, Mastaglia F, Thickbroom G (2004) Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals asymmetrical efficacy of intracortical circuits in primary motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 155:19–23
Hanajima R, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Sakai K, Furubayashi T, Machii K, Kanazawa I (1998) Paired-pulse magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex: differences among I waves. J Physiol 509:607–618
Hazeltine E, Grafton ST, Ivry R (1997) Attention and stimulus characteristics determine the locus of motor-sequence encoding. A PET study. Brain 120:123–140
Hess A, Kunesch E, Classen J, Hoeppner J, Stefan K, Benecke R (1999) Task-dependent modulation of inhibitory actions within the primary motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 124:321–330
Jueptner M, Stephan KM, Frith CD, Brooks DJ, Frackowiak RS, Passingham RE (1997) Anatomy of motor learning. I. Frontal cortex and attention to action. J Neurophysiol 77:1313–1324
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Liepert J, Schwenkreis P, Tegenthoff M, Malin JP (1997) The glutamate antagonist riluzole suppresses intracortical facilitation. J Neural Transm 104:1207–1214
Liepert J, Classen J, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1998) Task-dependent changes of intracortical inhibition. Exp Brain Res 118:421–426
Lorenzano C, Gilio F, Inghilleri M, Conte A, Fofi L, Manfredi M, Berardelli A (2002) Spread of electrical activity at cortical level after repetitive magnetic stimulation in normal subjects. Exp Brain Res 147:186–192
Passingham RE (1996) Attention to action. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351:1473–1479
Reynolds C, Ashby P (1999) Inhibition in the human motor cortex is reduced just before a voluntary contraction. Neurology 53:730–735
Ridding MC, Taylor JL, Rothwell JC (1995a) The effect of voluntary contraction on cortico-cortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 487:541–548
Ridding MC, Sheean G, Rothwell JC, Inzelberg R, Kujirai T (1995b) Changes in the balance between motor cortical excitation and inhibition in focal, task specific dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:493–498
Roick H, von Giesen HJ, Benecke R (1993) On the origin of the postexcitatory inhibition seen after transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in awake human subjects. Exp Brain Res 94:489–498
Rosenkranz K, Rothwell JC (2004) The effect of sensory input and attention on the sensorimotor organization of the hand area of the human motor cortex. J Physiol 561:307–320
Rowe J, Friston K, Frackowiak R, Passingham R (2002) Attention to action: specific modulation of corticocortical interactions in humans. Neuroimage 17:988–998
Sanger TD, Garg RR, Chen R (2001) Interactions between two different inhibitory systems in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 530:307–317
Stefan K, Wycislo M, Classen J (2004) Modulation of associative human motor cortical plasticity by attention. J Neurophysiol 92:66–72
Stinear CM, Byblow WD (2003) Role of intracortical inhibition in selective hand muscle activation. J Neurophysiol 89:2014–2020
Valls-Sole´ J, Pascual-Leone A, Wassermann EM, Hallett M (1992) Human motor evoked responses to paired transcranial magnetic stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:355–364
Werhahn KJ, Kunesch E, Noachtar S, Benecke R, Classen J (1999) Differential effects on motorcortical inhibition induced by blockade of GABA uptake in humans. J Physiol 517:591–597
Ziemann U, Lonnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W (1996a) The effect of lorazepam on the motor cortical excitability in man. Exp Brain Res 109:127–135
Ziemann U, Rothwell JC, Ridding MC (1996b) Interaction between intracortical inhibition and facilitation in human motor cortex. J Physiol 496:873–881
Ziemann U, Tergau F, Wassermann EM, Wischer S, Hildebrandt J, Paulus W (1998) Demonstration of facilitatory I wave interaction in the human motor cortex by paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Physiol 511:181–190
Zoghi M, Pearce SL, Nordstrom MS (2003) Differential modulation of intracortical inhibition in human motor cortex during selective activation of an intrinsic hand muscle. J Physiol 550: 933–946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conte, A., Belvisi, D., Iezzi, E. et al. Effects of attention on inhibitory and facilitatory phenomena elicited by paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res 186, 393–399 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1244-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1244-1