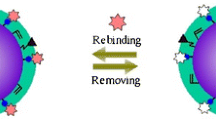
Abstract
Synthetic materials capable of recognizing proteins are important in separation, biosensors and biomaterials. In this study, bovine serum albumin-imprinted soft-wet polyacrylamide gel beads were prepared via inverse-phase suspension polymerization, using acrylamide and N,N′-methylene diacrylamide as polymeric matrix components and methacrylic acid as functional monomer. The adsorption study showed, through the imprinting process, that the imprinted gel beads had much higher adsorption capacity than the nonimprinted gel beads, and that the matching of the surface zeta-potential between the templates and the imprinted gel beads can enhance the imprinting effect. Adsorption kinetics indicated that the adsorption process could be described as an apparent first-order kinetic process for the gel beads. From the adsorption isotherm curve, we found that the adsorption of the imprinted gel beads was in agreement with the Langmuir adsorption model. Moreover, selectivity testing of the imprinted gel beads showed that imprinted gel beads exhibited good recognition for BSA as compared to the control protein. We speculate that the formation of complementary shapes and multiple-point electrostatic interactions between the imprinting cavities and the template proteins are the two factors that lead to the imprinting effect.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cormack PAG, Mosbach K (1999) React Funct Polym 41:115–124
Wulff G (1995) Angew Chem Int Edit 31:1812–1832
Ansell RJ, Mosbach KJ (1997) J Chromatogr A 787:55–66
Chen W, Liu F, Xu Y, Li KA (2001) Anal Chim Acta 432: 277–282
Cheong SH, Mcniven S, Uezu K, Goto M, Furusaki S (1997) Macromolecules 30: 1317–1322
Lu SL, Cheng GX, Pang XS (2003) J Appl Polym Sci 89:3790–3796
Zhang LY, Cheng GX, Fu C (2003) React Funct Polym 56:167–173
Kempe M, Glad M, Mosbach K (1995) J Mol Recognit 8:35
Hjerten S, Liao J-L, Nakazato K, Wang Y, Zamaratskaina G, Zhang H-Y (1997) Chromatographia 44: 227–234
Hirayama K, Burow M, Morikawa K, Minoura N (1998) Chem Lett 731
Shi HQ, Tsai W, Garrison MD, Ferrari S, Ratner BD (1999) Nature 398:593–597
Ou SH, Wu MC, Chou TC, Liu CC (2004) Anal Chim Acta 504:163–166
Pang XS, Cheng GX, Li RS, Lu SL, Zhang YH (2005) Anal Chim Acta 550:13–17
Piletsky SA, Andersson HS, Nicholls IA (1999) Macromolecules 32:633–636
Yin G, Liu Z, Zhan J, Ding FX, Yuan NJ (2002) Chem Eng J 87:181–186
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 50373032) and the Teaching and Research Award Program for Outstanding Young Teachers in Higher Education Institutions of MOE, P.R.C. (2002–123) for supporting this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, X., Cheng, G., Lu, S. et al. Synthesis of polyacrylamide gel beads with electrostatic functional groups for the molecular imprinting of bovine serum albumin. Anal Bioanal Chem 384, 225–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0147-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0147-x