Abstract
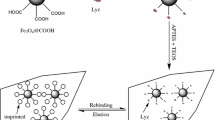
We describe the synthesis of molecularly imprinted core-shell microparticles via a metal chelating strategy that assists in the creation of selective recognition sites for albumin. Porcine serum albumin (PSA) was immobilized on silica beads via copper(II) chelation interaction. A solution containing 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and methacrylic acid as the monomers was mixed with the above particles, and free radical polymerization was performed at 25 °C. Copper ion and template were then removed to obtain PSA-imprinted core-shell particles (MIPs) with a typical diameter of 5 μm. The binding capacity of such MIP was 8.9 mg protein per gram of MIPs, and the adsorption equilibrium was established within <20 min. The imprinting factor for PSA reached 2.6 when the binding capacity was 7.7 mg protein per gram of MIPs. The use of such MIPs enabled PSA to be selectively recognized even in presence of the competitive proteins ribonuclease B, cytochrome c, and myoglobin. The results indicate that this imprinting strategy for protein may become a promising method to prepare MIPs for protein recognition.

Preparation and rebinding of surface imprinted particles for target protein recognition





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahon CS, Fulton DA (2014) Mimicking nature with synthetic macromolecules capable of recognition. Nat Chem 6(8):665–672. doi:10.1038/nchem.1994
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40(3):1547–1571. doi:10.1039/c0cs00049c
Pan G, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Li C, Zhang H (2011) Efficient one-pot synthesis of water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres by facile RAFT precipitation polymerization. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(49):11731–11734. doi:10.1002/anie.201104751
Yang KG, Liu ZB, Mao M, Zhang XH, Zhao CS, Nishi N (2005) Molecularly imprinted polyethersulfone microspheres for the binding and recognition of bisphenol A. Anal Chim Acta 546(1):30–36. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2005.05.008
Yang KG, Berg MM, Zhao CS, Ye L (2009) One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Macromolecules 42(22):8739–8746. doi:10.1021/Ma901761z
Shen XT, Ye L (2011) Molecular imprinting in Pickering emulsions: a new insight into molecular recognition in water. Chem Commun 47(37):10359–10361. doi:10.1039/c1cc13899e
Hao Y, Gao R, Shi L, Liu D, Tang Y, Guo Z (2015) Water-compatible magnetic imprinted nanoparticles served as solid-phase extraction sorbents for selective determination of trace 17beta-estradiol in environmental water samples by liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1396:7–16. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.083
Yang KG, Zhang LH, Liang Z, Zhang YK (2012) Protein-imprinted materials: rational design, application and challenges. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(8):2173–2183. doi:10.1007/s00216-012-5840-y
Fukazawa K, Ishihara K (2009) Fabrication of a cell-adhesive protein imprinting surface with an artificial cell membrane structure for cell capturing. Biosens Bioelectron 25(3):609–614. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.02.034
Zhou J, Gan N, Li T, Hu F, Li X, Wang L, Zheng L (2014) A cost-effective sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of HIV-1 antibody using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers as capture probes. Biosens Bioelectron 54:199–206. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.044
Zhang W, Liu W, Li P, Xiao H, Wang H, Tang B (2014) A fluorescence nanosensor for glycoproteins with activity based on the molecularly imprinted spatial structure of the target and boronate affinity. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(46):12489–12493. doi:10.1002/anie.201405634
Li Q, Yang K, Liang Y, Jiang B, Liu J, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2014) Surface protein imprinted core–shell particles for high selective lysozyme recognition prepared by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer strategy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(24):21954–21960. doi:10.1021/am5072783
Yang K, Liu J, Li S, Li Q, Wu Q, Zhou Y, Zhao Q, Deng N, Liang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2014) Epitope imprinted polyethersulfone beads by self-assembly for target protein capture from the plasma proteome. Chem Commun 50(67):9521–9524. doi:10.1039/c4cc03428g
Li QR, Yang KG, Liu JX, Zhang LH, Liang Z, Zhang YK (2013) Transferrin recognition based on a protein imprinted material prepared by hierarchical imprinting technique. Microchim Acta 180(15–16):1379–1386. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0994-7
Liu J, Yang K, Deng Q, Li Q, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2011) Preparation of a new type of affinity materials combining metal coordination with molecular imprinting. Chem Commun 47(13):3969–3971. doi:10.1039/c0cc05317a
Saridakis E, Khurshid S, Govada L, Phan Q, Hawkins D, Crichlow GV, Lolis E, Reddy SM, Chayen NE (2011) Protein crystallization facilitated by molecularly imprinted polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(27):11081–11086. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016539108
Saridakis E, Chayen NE (2013) Imprinted polymers assisting protein crystallization. Trends Biotechnol 31(9):515–520. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.05.003
Cutivet A, Schembri C, Kovensky J, Haupt K (2009) Molecularly imprinted microgels as enzyme inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 131(41):14699–14702. doi:10.1021/ja901600e
Liu J, Deng Q, Yang K, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2010) Macroporous molecularly imprinted monolithic polymer columns for protein recognition by liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci 33(17–18):2757–2761. doi:10.1002/jssc.201000350
Liu J, Deng Q, Tao D, Yang K, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2014) Preparation of protein imprinted materials by hierarchical imprinting techniques and application in selective depletion of albumin from human serum. Sci Rep 4:5487. doi:10.1038/srep05487
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2922–2942. doi:10.1039/c0cs00084a
Shen XT, Zhou TC, Ye L (2012) Molecular imprinting of protein in Pickering emulsion. Chem Commun 48(66):8198–8200. doi:10.1039/c2cc33572g
Gao RX, Kong X, Wang X, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2011) Preparation and characterization of uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized with core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for the recognition and enrichment of protein. J Mater Chem 21(44):17863–17871. doi:10.1039/c1jm12414e
Gao R, Mu X, Hao Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Tang Y (2014) Combination of surface imprinting and immobilized template techniques for preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers based on directly amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. J Mater Chem B 2(12):1733–1741. doi:10.1039/c3tb21684e
Liu J, Yang K, Qu Y, Li S, Wu Q, Liang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2015) An efficient approach to prepare boronate core-shell polymer nanoparticles for glycoprotein recognition via combined distillation precipitation polymerization and RAFT media precipitation polymerization. Chem Commun (Camb) 51(18):3896–3898. doi:10.1039/c4cc10004b
Lu Q, Chen X, Nie L, Luo J, Jiang H, Chen L, Hu Q, Du S, Zhang Z (2010) Tuning of the vinyl groups’ spacing at surface of modified silica in preparation of high density imprinted layer-coated silica nanoparticles: a dispersive solid-phase extraction materials for chlorpyrifos. Talanta 81(3):959–966. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.044
Hayden O, Lieberzeit PA, Blaas D, Dickert FL (2006) Artificial antibodies for bioanalyte detection-sensing viruses and proteins. Adv Funct Mater 16(10):1269–1278. doi:10.1002/adfm.200500626
Dechtrirat D, Jetzschmann KJ, Stocklein WFM, Scheller FW, Gajovic-Eichelmann N (2012) Protein rebinding to a surface-confined imprint. Adv Funct Mater 22(24):5231–5237. doi:10.1002/adfm.201201328
Hoshino Y, Urakami T, Kodama T, Koide H, Oku N, Okahata Y, Shea KJ (2009) Design of synthetic polymer nanoparticles that capture and neutralize a toxic peptide. Small 5(13):1562–1568. doi:10.1002/smll.200900186
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB910601 and 2013CB911202), National Nature Science Foundation (21375128 and 21190043), the Creative Research Group Project of the NSFC (21321064), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA020202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 2154 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Yang, K., Li, S. et al. Preparation of surface imprinted core-shell particles via a metal chelating strategy: specific recognition of porcine serum albumin. Microchim Acta 183, 345–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1640-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1640-3