Abstract.
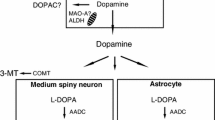
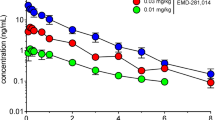
Rationale:L-Dopa induces dyskinesias during the treatment of Parkinson's disease and also in primates with nigrostriatal lesions produced by MPTP, but it is claimed that L-dopa does not provoke dyskinesia in humans or monkeys with an intact or mildly damaged nigrostriatal system. Objectives: This study assessed the behavioural and pharmacokinetic effects of chronic oral administration of L-dopa plus carbidopa alone, or with co-administration of the peripheral COMT inhibitor entacapone, to normal macaque monkeys. Repeated high dose L-dopa administration was shown to induce marked dyskinesias in monkeys with an intact nigrostriatal system, and the threshold for dyskinesia expression was increased by peripheral catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition with entacapone. Methods: Six groups of normal macaque monkeys (n=8 per group; Macaca fascicularis) were treated with L-dopa (20, 40 or 80 mg/kg) plus carbidopa (5, 10 or 20 mg/kg) with or without the catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor entacapone (20, 40 or 80 mg/kg), or with entacapone alone (80 mg/kg), by oral administration once daily for 13 weeks. Results: Eleven of 16 animals receiving high dose L-dopa (80 mg/kg plus carbidopa 20 mg/kg PO with or without entacapone 80 mg/kg PO for 13 weeks) gradually developed reproducible and idiosyncratic combinations of chorea, athetosis and dystonia maximal at 60–100 min after L-dopa administration, which progressively intensified over the course of the study. The dyskinesias observed were similar in type and distribution to L-dopa-induced dyskinesia observed in patients with Parkinson's disease and in MPTP-treated primates. The occurrence of dyskinesia correlated with plasma concentrations of L-dopa, with animals displaying the most severe dyskinesias having significantly higher plasma concentrations of L-dopa one hour after dosing than animals with mild or moderate dyskinesia or no dyskinesia. Co-administration of entacapone with L-dopa plus carbidopa significantly lowered peak plasma concentrations of L-dopa and this was reflected by a decrease in the severity of dyskinesias, with only one animal receiving entacapone and high dose L-dopa plus carbidopa showing severe dyskinesia, while four receiving high dose L-dopa plus carbidopa alone did so. Conclusions: These results show for the first time that chronic oral L-dopa administration can provoke dyskinesias in primates independently of nigrostriatal damage, and that this effect is dose related.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearce, .R., Heikkilä, .M., Lindén, .IB. et al. L-Dopa induces dyskinesia in normal monkeys: behavioural and pharmacokinetic observations. Psychopharmacology 156, 402–409 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100733
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100733