Abstract
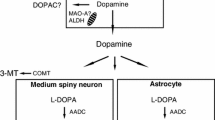
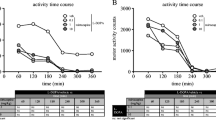
Whereas monoamine oxidase (MAO) type B inhibitors are used as adjunct to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the enzyme MAO type A (MAO-A) also participates in the metabolism of dopamine in the human and primate striatum. Here, we sought to assess the effect of the selective reversible MAO-A inhibitor moclobemide on L-DOPA anti-parkinsonian in the gold standard animal model of PD, the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned primate. We also assessed the effect of moclobemide on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and psychosis-like behaviours (PLBs). Experiments were performed in six MPTP-lesioned marmosets chronically treated with L-DOPA and exhibiting stable dyskinesia and PLBs upon each administration. In a randomised within-subject design, animals were administered a therapeutic dose of L-DOPA in combination with moclobemide (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg) or its vehicle, after which the severity of parkinsonism, dyskinesia, and PLBs was rated by an experienced blinded rater. Moclobemide significantly reduced the global parkinsonian disability (− 36% with 0.1 mg/kg, P < 0.05; − 38% with 1 mg/kg, P < 0.01; − 47% with 10 mg/kg, P < 0.01), when compared with its vehicle. This reduction of parkinsonism was not accompanied by an exacerbation of dyskinesia or PLBs. Reversible MAO-A inhibition with moclobemide appears as an effective way to increase the anti-parkinsonian action of L-DOPA, without negatively affecting dyskinesia or dopaminergic psychosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrein R, Stabl M, Henauer S, Affolter E, Jonkanski I (1997) Efficacy and tolerability of moclobemide in comparison with placebo, tricyclic antidepressants, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in elderly depressed patients: a clinical overview. Can J Psychiatr 42(10):1043–1050. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674379704201005
Bandelow B (2020) Current and novel psychopharmacological drugs for anxiety disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol 1191:347–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_19
Bonnet U (2002) Moclobemide: evolution, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties. CNS Drug Rev 8(3):283–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00229.x
Chiuccariello L, Cooke RG, Miler L, Levitan RD, Baker GB, Kish SJ, Kolla NJ, Rusjan PM, Houle S, Wilson AA, Meyer JH (2015) Monoamine oxidase-a occupancy by moclobemide and phenelzine: implications for the development of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 19(1):pyv078. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyv078
Colzi A, D’Agostini F, Cesura AM, Borroni E, Da Prada M (1993) Monoamine oxidase-A inhibitors and dopamine metabolism in rat caudatus: evidence that an increased cytosolic level of dopamine displaces reversible monoamine oxidase-A inhibitors in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265(1):103–111
Fenelon G, Gimenez-Roldan S, Montastruc JL, Bermejo F, Durif F, Bourdeix I, Pere JJ, Galiano L, Schadrack J (2003) Efficacy and tolerability of entacapone in patients with Parkinson’s disease treated with levodopa plus a dopamine agonist and experiencing wearing-off motor fluctuations. A randomized, double-blind, multicentre study. J Neural Transm 110(3):239–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-002-0799-z
Fowler CJ, Benedetti MS (1983) The metabolism of dopamine by both forms of monoamine oxidase in the rat brain and its inhibition by cimoxatone. J Neurochem 40(6):1534–1541. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08123.x
Fox SH, Visanji N, Reyes G, Huot P, Gomez-Ramirez J, Johnston T, Brotchie JM (2010) Neuropsychiatric behaviors in the MPTP marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 37(1):86–95
Frouni I, Hamadjida A, Kwan C, Bedard D, Nafade V, Gaudette F, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Beaudry F, Huot P (2019) Activation of mGlu2/3 receptors, a novel therapeutic approach to alleviate dyskinesia and psychosis in experimental parkinsonism. Neuropharmacology 158:107725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107725
Gimenez-Roldan S, Dobato JL, Mateo D (1997) Treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease with moclobemide: a pilot open-label study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 3(4):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1353-8020(97)00028-x
Haefely W, Burkard WP, Cesura AM, Kettler R, Lorez HP, Martin JR, Richards JG, Scherschlicht R, Da Prada M (1992) Biochemistry and pharmacology of moclobemide, a prototype RIMA. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106(Suppl):S6–S14. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02246225
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Veyres N, Frouni I, Kwan C, Sid-Otmane L, Harraka MJ, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2017) The effect of mirtazapine on dopaminergic psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Psychopharmacology 234(6):905–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4530-z
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Bedard D, Frouni I, Kwan C, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018a) Nefazodone reduces dyskinesia, but not psychosis-like behaviours, in the parkinsonian marmoset. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391(12):1339–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1549-6
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Bedard D, Gaudette F, Beaudry F, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018b) The highly selective 5-HT2A antagonist EMD-281,014 reduces dyskinesia and psychosis in the l-DOPA-treated parkinsonian marmoset. Neuropharmacology 139:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.038
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018c) The effect of mianserin on the severity of psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 81:367–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.09.001
Hamadjida A, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Huot P (2018d) Trazodone alleviates both dyskinesia and psychosis in the parkinsonian marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 125(9):1355–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1830-8
Hely MA, Morris JG, Reid WG, Trafficante R (2005) Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: non-L-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov Disord 20(2):190–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20324
Holford NH, Guentert TW, Dingemanse J, Banken L (1994) Monoamine oxidase-A: pharmacodynamics in humans of moclobemide, a reversible and selective inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol 37(5):433–439. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.1994.tb05710.x
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD, Koprich JB, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Piggott MJ, Brotchie JM (2011) Characterization of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) enantiomers in vitro and in the MPTP-lesioned primate: R-MDMA reduces severity of dyskinesia, whereas S-MDMA extends duration of ON-time. J Neurosci 31(19):7190–7198. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1171-11.2011
Huot P, Johnston TH, Gandy MN, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Piggott MJ, Brotchie JM (2012) The monoamine re-uptake inhibitor UWA-101 improves motor fluctuations in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. PLoS One 7(9):e45587. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045587
Huot P, Johnston TH, Lewis KD, Koprich JB, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Piggott MJ, Brotchie JM (2014) UWA-121, a mixed dopamine and serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, enhances L-DOPA anti-parkinsonian action without worsening dyskinesia or psychosis-like behaviours in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. Neuropharmacology 82:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.012
Jansen Steur EN, Ballering LA (1999) Combined and selective monoamine oxidase inhibition in the treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 80:505–508
Korpelainen JT, Hiltunen P, Myllyla VV (1998) Moclobemide-induced hypersexuality in patients with stroke and Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 21(4):251–254
Kwan C, Frouni I, Bedard D, Nuara SG, Gourdon JC, Hamadjida A, Huot P (2019) 5-HT2A blockade for dyskinesia and psychosis in Parkinson’s disease: is there a limit to the efficacy of this approach? A study in the MPTP-lesioned marmoset and a literature mini-review. Exp Brain Res 237(2):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5434-9
Lakshmana MK, Rao BS, Dhingra NK, Ravikumar R, Govindaiah SS, Meti BL, Raju TR (1998) Role of monoamine oxidase type A and B on the dopamine metabolism in discrete regions of the primate brain. Neurochem Res 23(8):1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020799700885
May T, Pawlik M, Rommelspacher H (1991) [3H]harman binding experiments. II: regional and subcellular distribution of specific [3H]harman binding and monoamine oxidase subtypes A and B activity in marmoset and rat. J Neurochem 56(2):500–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08178.x
Mayersohn M, Guentert TW (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics of the monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor moclobemide. Clin Pharmacokinet 29(5):292–332. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199529050-00002
Nair NP, Ahmed SK, Kin NM (1993) Biochemistry and pharmacology of reversible inhibitors of MAO-A agents: focus on moclobemide. J Psychiatry Neurosci 18(5):214–225
O'Carroll AM, Fowler CJ, Phillips JP, Tobbia I, Tipton KF (1983) The deamination of dopamine by human brain monoamine oxidase. Specificity for the two enzyme forms in seven brain regions. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 322(3):198–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00500765
Oie S, Guentert TW, Tolentino L, Hermodsson G (1992) Pharmacokinetics of moclobemide in male, virgin female, pregnant and nursing rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 44(5):413–418. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb03635.x
Riederer P, Laux G (2011) MAO-inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 20(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2011.20.1.1
Seppi K, Ray Chaudhuri K, Coelho M, Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Perez Lloret S, Weintraub D, Sampaio C, the collaborators of the Parkinson’s Disease Update on Non-Motor Symptoms Study Group on behalf of the Movement Disorders Society Evidence-Based Medicine C (2019) Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease-an evidence-based medicine review. Mov Disord 34(2):180–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27602
Sieradzan K, Channon S, Ramponi C, Stern GM, Lees AJ, Youdim MBH (1995) The therapeutic potential of moclobemide, a reversible selective monoamine oxidase A inhibitor in Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol 15:51S–59S
Smith LA, Gordin A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1997) Entacapone enhances levodopa-induced reversal of motor disability in MPTP-treated common marmosets. Mov Disord 12(6):935–945. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870120616
Sternic N, Kacar A, Filipovic S, Svetel M, Kostic VS (1998) The therapeutic effect of moclobemide, a reversible selective monoamine oxidase A inhibitor, in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 21(2):93–96
Steur EN, Ballering LA (1997) Moclobemide and selegeline in the treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63(4):547. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.63.4.547
Takats A, Tarczy M, Simo M, Szombathelyi E, Bodrogi A, Karpati R (1994) Moclobemide/aurorix/treatment in Parkinson’s disease with depression [abstract]. 11th international symposium on Parkinson’s disease:260
Tong J, Meyer JH, Furukawa Y, Boileau I, Chang LJ, Wilson AA, Houle S, Kish SJ (2013) Distribution of monoamine oxidase proteins in human brain: implications for brain imaging studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(6):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.19
Veyres N, Hamadjida A, Huot P (2018) Predictive value of parkinsonian primates in pharmacologic studies: a comparison between the macaque, marmoset, and squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 365(2):379–397. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.117.247171
Wiesel FA, Raaflaub J, Kettler R (1985) Pharmacokinetics of oral moclobemide in healthy human subjects and effects on MAO-activity in platelets and excretion of urine monoamine metabolites. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28(1):89–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00635714
World Group on Major Depressive Disorders (2010) Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder, 3rd edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, D. C
Funding
PH has research support from Parkinson Canada, Fonds de Recherche Québec–Santé, the Weston Brain Institute, the Michael J Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and Healthy Brains for Healthy Lives.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AH, SN, JC and PH conceived and designed research. AH, SN, CK, IF, DB and JC conducted experiments. PH analysed data. PH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Experiments were approved by McGill University and the Montreal Neurological Institute Animal Care Committees, which are in accordance with the regulations defined by the Canadian Council on Animal Care.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PZFX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamadjida, A., Nuara, S.G., Kwan, C. et al. Monoamine oxidase A inhibition with moclobemide enhances the anti-parkinsonian effect of L-DOPA in the MPTP-lesioned marmoset. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 2157–2164 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01933-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01933-y