Abstract.
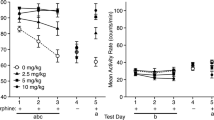
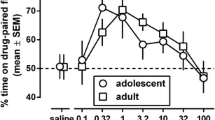
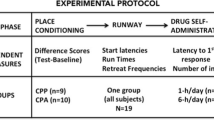
Rationale: The drug-abuse literature suggests that benzodiazepines may be preferentially abused in conjunction with opioids rather than stimulants. Objective: To investigate possible effects of diazepam on the reinforcing effects of morphine and amphetamine. Methods: The effects of diazepam (0.5, 1 or 2 mg/kg) on the formation and expression of conditioned place preferences (CPP) induced by morphine sulphate (0.3, 0.8, 2 and 8 mg/kg) or d-amphetamine (0.4, 0.8, 2 or 2.5 mg/kg) were studied in an unbiased CPP paradigm. The action of diazepam (1 mg/kg) on conditioned and unconditioned locomotion induced by morphine (2 mg/kg) or amphetamine (2 mg/kg) was assessed. Results: Rats that received conditioning injections of morphine in one environment displayed a preference for this environment. Pre-testing injections of diazepam did not alter the magnitude of this CPP. When diazepam was given with morphine during training, rats displayed a CPP for the environment paired with the two drugs. Injections of amphetamine in one environment also induced a preference for this environment. However, pre-testing injections of diazepam blocked the expression of amphetamine-induced CPP, and co-injections of diazepam blocked the formation of amphetamine CPP. Diazepam itself did not produce a CPP nor did it alter spontaneous place preferences. Diazepam equally blocked both morphine and amphetamine unconditioned and conditioned locomotor hyperactivity. This indicates that its effects on morphine and amphetamine CPP were not due to a differential effect on locomotion. Conclusions: Diazepam interferes with the reinforcing properties of amphetamines but not of morphine. The reinforcing effects of morphine and amphetamine are pharmacologically dissociable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leri, F., Franklin, K. Effects of diazepam on conditioned place preference induced by morphine or amphetamine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 150, 351–360 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000448
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000448