Abstract
Rationale
With the development of various imaging techniques, the deformation-based morphometry (DBM) method provides an objective automatic examination of the whole brain.
Objectives
This study aims to assess the abnormalities in the brains of first-episode schizophrenia (FES) patients treated with quetiapine using another advanced nonrigid registration method, hierarchical attribute matching mechanism for elastic registration, through the application of DBM in the entire brain.
Methods
Thirty FES patients and 30 normal controls were grouped by age and handedness and subjected to magnetic resonance imaging examination. The patients had relatively short durations of untreated psychosis (DUP; 6.4 ± 5.2 months), and only a single antipsychotic drug, quetiapine (dosage, 200 ± 75 mg), was used for treatment. Statistically significant changes in regional volume were analyzed via DBM. In addition, a voxel-wise analysis of correlations between the duration of treatment or dosage and volume was also performed.
Results
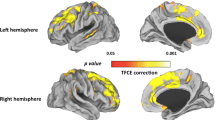
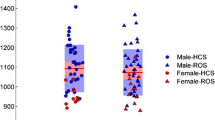
Compared with control subjects, FES patients showed contracted regions located in Brodmann area (BA) 42 and BA 19. By contrast, expanded regions were observed in BA 38, BA 21, BA 6 and 8, and left cerebellum. A negative correlation was observed between dosage and volume in the hippocampus, while a positive correlation was found in the caudate. Meanwhile, a negative correlation was observed between duration of treatment and volume in BA 38.
Conclusion
Both regional volume reductions and increases were detected in the brains of FES patients treated with quetiapine compared with healthy control subjects. Such differences may be partially relevant to dosage and treatment duration in clinic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasen NC, Pierson R (2008) The role of the cerebellum in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiat 64:81–88
Angelucci F, Aloe L, Iannitelli A et al (2005) Effect of chronic olanzapine treatment on nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:311–317
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2004) High-dimensional image warping. In: Frackowiak R, editor. Human brain function. 2nd edn. Academic Press, pp 673–694
Chew SH, Ho JL (1994) Hope: an empirical study of attitude toward the timing of uncertainty resolution. J Risk Uncertain 8:267–288
Cosi C, Waget A, Rollet K et al (2005) Clozapine, ziprasidone and aripiprazole but not haloperidol protect against kainic acid-induced lesion of the striatum in mice, in vivo: role of 5-HT1A receptor activation. Brain Res 1043:32–41
Crespo-Facorro B, Roiz-Santianez R, Perez-Iglesias R et al (2008) Effect of antipsychotic drugs on brain morphometry: a randomized controlled one-year follow-up study of haloperidol, risperidone and olanzapine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1936–1943
Davatzikos C, Vaillant M, Resnick SM et al (1996) A computerized approach for morphological analysis of the corpus callosum. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:88–97
Ding SL, Van HGW, Cassell MD et al (2009) Parcellation of human temporal polar cortex: a combined analysis of multiple cytoarchitectonic, chemoarchitectonic, and pathological markers. J Comp Neurol 514:595–623
Ebdrup BH, Glenthøj B, Rasmussen H et al (2010) Hippocampal and caudate volume reductions in antipsychotic-naive first-episode schizophrenia. J Psychiatry Neurosci 35:95–104
Ebdrup BH, Skimminge A, Rasmussen H et al (2011) Progressive striatal and hippocampal volume loss in initially antipsychotic-naïve, first-episode schizophrenia patients treated with quetiapine: relationship to dose and symptoms. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14:69–82
Ellison-Wright L, Glahn DC, Laird AR et al (2008) The anatomy of first-episode and chronic schizophrenia: an anatomical likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 165:1015–1023
Fabre LF Jr, Arvanitis L, Pultz J et al (1995) ICI 204, 636, a novel, atypical antipsychotic: early indication of safety and efficacy in patients with chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. Clin Ther 17:366–378
Farmer CM, O’Donnell BF, Niznikiewicz MA et al (2000) Visual perception and working memory in schizotypal personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry 157:781–788
First M, Spitzer R, Gibbon M, et al. (1995) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorder-Patient Edition (SCID-I/P, Version 2.0), Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute. New York
Fornito A, Yücel M, Patti J et al (2009) Mapping grey matter reductions in schizophrenia: an anatomical likelihood estimation analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Schizophr Res 108:104–113
Fumagalli F, Molteni R, Bedogni F et al (2004) Quetiapine regulates FGF-2 and BDNF expression in the hippocampus of animals treated with MK-801. Neuroreport 15:2109–2112
Gaser C, Volz HP, Kiebel S et al (1999) Detecting structural changes in whole brain based on nonlinear deformations: application to schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 10:107–113
Glahn DC, Laird AR, Ellison-Wright L et al (2008) Meta-analysis of gray matter anomalies in schizophrenia: application of anatomic likelihood estimation and network analysis. Biol Psychiat 64:774–781
Halim ND, Weickert CS, McClintock BW et al (2004) Effects of chronic haloperidol and clozapine treatment on neurogenesis in the adult rat hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1063–1069
Jacobsen LK, Giedd JN, Vaituzis AC et al (1996) Temporal lobe morphology in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Am J Psychiat 153:355–361
Kasai K, Shenton ME, Salisbury DF et al (2003) Progressive decrease of left superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiat 160:156–164
Kašpárek T, Mareček R, Schwarz D et al (2010) Source-based morphometry of gray matter volume in men with first-episode schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp 31:300–310
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bull 13:261–276
Keshavan MS, Haas GL, Kahn CE et al (1998) Superior temporal gyrus and the course of early schizophrenia: progressive, static, or reversible? J Psychiatr Res 32:161–167
Kumra S, Giedd JN, Vaituzis AC et al (2000) Childhood-onset psychotic disorders magnetic resonance imaging of volumetric differences in brain structure. Am J Psychiat 157:1467–1474
Laakso MP, Tiihonen J, Syvalahti E et al (2001) A morphometric MRI study of the hippocampus in first-episode, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 50:3–7
Levitt JJ, McCarley RW, Nestor PG et al (1999) Quantitative volumetric MRI study of the cerebellum and vermis in schizophrenia: clinical and cognitive correlates. Am J Psychiat 156:1105–1107
Levitt JG, Blanton RE, Caplan R et al (2001) Medial temporal lobe in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Psychiat Res 108:17–27
Lewis DA, Lieberman JA (2000) Catching up on schizophrenia: natural history and neurobiology. Neuron 28:325–334
McEvoy JP, Lieberman JA, Perkins DO et al (2007) Efficacy and tolerability of olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in the treatment of early psychosis: a randomized, double-blind 52-week comparison. Am J Psychiatry 164:1050–1060
Millan MJ (2005) N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors as a target for improved antipsychotic agents: novel insights and clinical perspectives. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:30–53
Mitelman SA, Shihabuddin L, Brickman AM et al (2003) MRI assessment of gray and white matter distribution in Brodmann’s areas of the cortex in patients with schizophrenia with good and poor outcomes. Am J Psychiat 160:2154–2168
Newton SS, Duman RS (2007) Neurogenic actions of atypical antipsychotic drugs and therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs 21:715–725
Ohnishi T, Hashimoto R, Mori T et al (2006) The association between the Val158Met polymorphism of the catechol-O-methyl transferase gene and morphological abnormalities of the brain in chronic schizophrenia. Brain 129:399–410
Purdon SE, Malla A, Labelle A et al (2001) Neuropsychological change in patients with schizophrenia after treatment with quetiapine or haloperidol. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:137–149
Riedel M, Müller N, Strassnig M et al (2007) Quetiapine in the treatment of schizophrenia and related disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 3:219–235
Rimol LM, Hartberg CB, Nesvag R et al (2010) Cortical thickness and subcortical volumes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Biol psychiat 68:41–50
Shattuck DW, Leahy RM (2001) Graph based analysis and correction of cortical volume topology. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:1167–1177
Shen DG, Davatzikos C (2002) HAMMER: hierarchical attribute matching mechanism for elastic registration. IEEE T Med Imaging 21:1421–1439
Shen D, Liu D, Liu H et al (2004) Automated morphometric study of brain variation in XXY males. Neuroimage 23:648–653
Small JG, Hirsch SR, Arvanitis LA et al (1997) Quetiapine in patients with schizophrenia. A high- and low-dose double-blind comparison with placebo. Seroquel study group. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:549–557
Steen RG, Mull C, McClure R et al (2006) Brain volume in first-episode schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Br J Psychiatry 188:510–518
Takahashi T, Suzuki M, Tanino R et al (2007) Volume reduction of the left planum temporal gray matter associated with long duration of untreated psychosis in schizophrenia: a preliminary report. Psychiat Res 154:209–219
Tarazi FI, Zhang K, Baldessarini RJ (2001) Long-term effects of olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine on dopamine receptor types in regions of rat brain: implications for antipsychotic drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:711–717
Taylor JL, Blanton RE, Levitt JG et al (2005) Superior temporal gyrus differences in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 73:235–241
Tek C, Gold J, Blaxton T et al (2002) Visual perceptual and working memory impairments in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:146–153
Vita A, De Peri L (2007) Hippocampal and amygdala volume reductions in first-episode schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 190:271
Vita A, De Peri L, Silenzi C et al (2006) Brain morphology in first-episode schizophrenia: a meta analysis of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging studies. Schizophr Res 82:75–88
Volz KG, Schubotz RL, Cramon DY (2005) Variants of uncertainty in decision-making and their neural correlates. Brain Res Bull 67:403–412
Wang HD, Dunnavant FD, Jarman T et al (2004) Effects of antipsychotic drugs on neurogenesis in the forebrain of the adult rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1230–1238
Whitford TJ, Grieve SM, Farrow TFD et al (2006) Progressive grey matter atrophy over the first 2–3 years of illness in first-episode schizophrenia: a tensor-based morphometry study. Neuroimage 32:511–519
Whitford TJ, Grieve SM, Farrow TFD et al (2007) Volumetric white matter abnormalities in first-episode schizophrenia: a longitudinal, tensor-based morphometry study. Am J Psychiatry 164:1082–1089
Whitwell JL (2009) Voxel-based morphometry: an automated technique for assessing structural changes in the brain. J Neurosci 29:9661–9664
Yamada M, Hirao K, Namiki C et al (2007) Social cognition and frontal lobe pathology in schizophrenia: a voxel-based morphometric study. Neuroimage 35:292–298
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (Grant No. 3112005) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81101107).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial interests in the current data and report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Wu, S., Lu, W. et al. Brain differences in first-episode schizophrenia treated with quetiapine: a deformation-based morphometric study. Psychopharmacology 232, 369–377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3670-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3670-7