Abstract
Rationale
Many abused solvents share a profile of effects with classical antidepressants. For example, toluene, which is a representative and widely abused solvent, has been reported to increase both serotonin and noradrenaline levels in several brain areas after an acute exposure and to act as a noncompetitive antagonist of the glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor subtype. Therefore, it is possible that toluene could possess antidepressant-like actions.
Objective
To provide an initial screening of toluene’s antidepressant-like actions in the forced swimming test (FST) and the tail suspension test (TST) in mice and to analyze its possible mechanism of action.
Materials and methods
Two series of experiments were performed. In the first one, male animals were exposed to toluene (0, 500, 1,000, 2,000, or 4,000 ppm) in a static exposure chamber for 30 min, and immediately after, evaluated for antidepressant-like effects. The results were compared with those obtained from mice treated with the serotonergic antidepressant clomipramine (CMI), the noradrenergic antidepressant desipramine (DMI), and the glutamatergic antidepressants, ketamine and MK-801. In the second part, we analyzed the effect of a combined administration of a subeffective concentration of toluene with a suboptimal dose of the various antidepressants acting at different neurotransmitter systems.
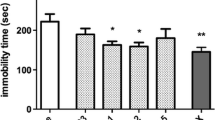
Results
Toluene produced a concentration-dependent antidepressant-like action in the FST and TST and facilitated both MK-801 and ketamine antidepressant-like effects, but not those of DMI or CMI.
Conclusions
Toluene has antidepressant-like effects that are synergized with NMDA receptor antagonists.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arito H, Tsuruta H, Nakagaki K (1984) Acute effects of toluene on circadian rhythms of sleep-wakefulness and brain monoamine metabolism in rats. Toxicology 33:291–301
Bale AS, Tu Y, Carpenter-Hyland EP, Chandler LJ, Woodward JJ (2005) Alterations in glutamatergic and GABAergic ion channel activity in hippocampal neurons following exposure to the abused inhalant toluene. Neuroscience 130:197–206
Beckstead MJ, Weiner JL, Eger EI 2nd, Gong DH, Mihic SJ (2000) Glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor function is enhanced by inhaled drugs of abuse. Mol Pharmacol 57:1199–1205
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354
Borsini F, Mancinelli A, D’Aranno V, Evangelista S, Meli A (1988) On the role of endogenous GABA in the forced swimming test in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 29:275–279
Bowen SE, Balster RL (1998) A direct comparison of inhalant effects on locomotor activity and schedule-controlled behavior in mice. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 6:235–247
Bowen SE, Batis JC, Paez-Martinez N, Cruz SL (2006) The last decade of solvent research in animal models of abuse: mechanistic and behavioral studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:636–647
Charney DS (1998) Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl 14):11–14
Chaturvedi HK, Bapna JS, Chandra D (2001) Effect of fluvoxamine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on shock-induced depression in mice. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 45:199–207
Cruz SL, Mirshahi T, Thomas B, Balster RL, Woodward JJ (1998) Effects of the abused solvent toluene on recombinant N-methyl-d-aspartate and non-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:334–340
Cruz SL, Balster RL, Woodward JJ (2000) Effects of volatile solvents on recombinant N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 131:1303–1308
Cruz SL, Gauthereau MY, Camacho-Munoz C, Lopez-Rubalcava C, Balster RL (2003) Effects of inhaled toluene and 1,1,1-trichloroethane on seizures and death produced by N-methyl-d-aspartic acid in mice. Behav Brain Res 140:195–202
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A (2005a) The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:571–625
Cryan JF, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2005b) Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:547–569
D’Aquila PS, Collu M, Gessa GL, Serra G (2000) The role of dopamine in the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 405:365–373
De Ceaurriz J, Desiles JP, Bonnet P, Marignac B, Muller J, Guenier JP (1983) Concentration-dependent behavioral changes in mice following short-term inhalation exposure to various industrial solvents. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 67:383–389
Del Río J, Frechilla D (2005) Glutamate and depression. In: Schmidt WJ, Reith MEA (eds) Dopamine and glutamate in psychiatric disorders. Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp 215–234
Dhir A, Kulkarni SK (2008) Possible involvement of nitric oxide (NO) signaling pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of MK-801(dizocilpine), a NMDA receptor antagonist in mouse forced swim test. Indian J Exp Biol 46:164–170
Eisenberg DP (2003) Neurotoxicity and mechanisms of toluene abuse. Medical scientific review. J Biol Med 19:150–159
Flugy A, Gagliano M, Cannizzaro C, Novara V, Cannizzaro G (1992) Antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of alprazolam versus the conventional antidepressant desipramine and the anxiolytic diazepam in the forced swim test in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 214:233–238
Fujishiro J, Imanishi T, Onozawa K, Tsushima M (2002) Comparison of the anticholinergic effects of the serotonergic antidepressants, paroxetine, fluvoxamine and clomipramine. Eur J Pharmacol 454:183–188
Galeotti N, Bartolini A, Ghelardini C (2002) Role of Gi proteins in the antidepressant-like effect of amitriptyline and clomipramine. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:554–564
Garcia LS, Comim CM, Valvassori SS, Reus GZ, Barbosa LM, Andreazza AC, Stertz L, Fries GR, Gavioli EC, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J (2008) Acute administration of ketamine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases BDNF levels in the rat hippocampus. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:140–144
Greenberg PE, Leong SA, Birnbaum HG, Robinson RL (2003) The economic burden of depression with painful symptoms. J Clin Psychiatry 64(Suppl 7):17–23
Kelley A (1999) Neural integrative activities of nucleus accumbens subregions in relation to learning and motivation. Psychobiology 27:198–213
Koga Y, Higashi S, Kawahara H, Ohsumi T (2007) Toluene inhalation increases extracellular noradrenaline and dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens in freely-moving rats. Journal of the Kyushu Dental Society 61:39–54
Kos T, Legutko B, Danysz W, Samoriski G, Popik P (2006) Enhancement of antidepressant-like effects but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression by the novel N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist neramexane in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:1128–1136
Kudoh A, Takahira Y, Katagai H, Takazawa T (2002) Small-dose ketamine improves the postoperative state of depressed patients. Anesth Analg 95:114–118
Lader M (2004) Tricyclic antidepressants. In: Preskorn SH, Feighner JP, Stanga CY, Ross R (eds) Antidepressants: past, present and future. Springer, Berlin, pp 185–208
Liebrenz M, Borgeat A, Leisinger R, Stohler R (2007) Intravenous ketamine therapy in a patient with a treatment-resistant major depression. Swiss Med Wkly 137:234–236
Lopez-Rubalcava C, Fernandez-Guasti A (1994) Noradrenaline–serotonin interactions in the anxiolytic effects of 5-HT(1A) agonists. Behav Pharmacol 5:42–51
Lucki I, Dalvi A, Mayorga AJ (2001) Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 155:315–322
Maeng S, Zarate CA Jr (2007) The role of glutamate in mood disorders: results from the ketamine in major depression study and the presumed cellular mechanism underlying its antidepressant effects. Curr Psychiatry Rep 9:467–474
Maj J, Rogoz Z, Skuza G, Sowinska H (1992) Effects of MK-801 and antidepressant drugs in the forced swimming test in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2:37–41
Mathew SJ, Keegan K, Smith L (2005) Glutamate modulators as novel interventions for mood disorders. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 27:243–248
Millan MJ (2004) The role of monoamines in the actions of established and “novel” antidepressant agents: a critical review. Eur J Pharmacol 500:371–384
Moryl E, Danysz W, Quack G (1993) Potential antidepressive properties of amantadine, memantine and bifemelane. Pharmacol Toxicol 72:394–397
Moser VC, Balster RL (1985) Acute motor and lethal effects of inhaled toluene, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, halothane, and ethanol in mice: effects of exposure duration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 77:285–291
Nakagawa Y, Ishima T, Ishibashi Y, Yoshii T, Takashima T (1996) Involvement of GABA(B) receptor systems in action of antidepressants: baclofen but not bicuculline attenuates the effects of antidepressants on the forced swim test in rats. Brain Res 709:215–220
Nelson G (1971) Controlled test atmospheres: principles and techniques. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor
Nemeroff CB (1998) Psychopharmacology of affective disorders in the 21st century. Biol Psychiatry 44:517–525
Papp M, Moryl E (1993) New evidence for the antidepressant activity of MK-801, a non-competitive antagonist of NMDA receptors. Pol J Pharmacol 45:549–553
Papp M, Moryl E (1994) Antidepressant activity of non-competitive and competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a chronic mild stress model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 263:1–7
Petit-Demouliere B, Chenu F, Bourin M (2005) Forced swimming test in mice: a review of antidepressant activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 177:245–255
Poleszak E, Wlaz P, Kedzierska E, Nieoczym D, Wrobel A, Fidecka S, Pilc A, Nowak G (2007a) NMDA/glutamate mechanism of antidepressant-like action of magnesium in forced swim test in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:158–164
Poleszak E, Wlaz P, Wrobel A, Dybala M, Sowa M, Fidecka S, Pilc A, Nowak G (2007b) Activation of the NMDA/glutamate receptor complex antagonizes the NMDA antagonist-induced antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test. Pharmacol Rep 59:595–600
Poncelet M, Martin P, Danti S, Simon P, Soubrie P (1987) Noradrenergic rather than GABAergic processes as the common mediation of the antidepressant profile of GABA agonists and imipramine-like drugs in animals. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 28:321–326
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Rea TM, Nash JF, Zabik JE, Born GS, Kessler WV (1984) Effects of toluene inhalation on brain biogenic amines in the rat. Toxicology 31:143–150
Riegel AC, French ED (1999a) Acute toluene induces biphasic changes in rat spontaneous locomotor activity which are blocked by remoxipride. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62:399–402
Riegel AC, French ED (1999b) An electrophysiological analysis of rat ventral tegmental dopamine neuronal activity during acute toluene exposure. Pharmacol Toxicol 85:37–43
Riegel AC, French ED (2002) Abused inhalants and central reward pathways: electrophysiological and behavioral studies in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci 965:281–291
Riegel AC, Ali SF, French ED (2003) Toluene-induced locomotor activity is blocked by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens and the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1440–1447
Ripoll N, David DJ, Dailly E, Hascoet M, Bourin M (2003) Antidepressant-like effects in various mice strains in the tail suspension test. Behav Brain Res 143:193–200
Rodriguez-Landa JF, Contreras CM, Bernal-Morales B, Gutierrez-Garcia AG, Saavedra M (2007) Allopregnanolone reduces immobility in the forced swimming test and increases the firing rate of lateral septal neurons through actions on the GABAA receptor in the rat. J Psychopharmacol 21:76–84
Sanacora G, Saricicek A (2007) GABAergic contributions to the pathophysiology of depression and the mechanism of antidepressant action. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6:127–140
Skolnick P (2005) Dopamine and depression. In: Schmidt W (ed) Dopamine and glutamate in psychiatric disorders. Humana, Totowa, pp 199–214
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 85:367–370
Thierry B, Steru L, Simon P, Porsolt RD (1986) The tail suspension test: ethical considerations. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 90:284–285
Trullas R, Skolnick P (1990) Functional antagonists at the NMDA receptor complex exhibit antidepressant actions. Eur J Pharmacol 185:1–10
Wise RA (2002) Brain reward circuitry: insights from unsensed incentives. Neuron 36:229–240
Yamada J, Sugimoto Y (2002) Differential effects of the 5-HT2 receptor antagonist on the anti-immobility effects of noradrenaline and serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the forced swimming test. Brain Res 958:161–165
Zarate CA Jr, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, Charney DS, Manji HK (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Acknowledgments
This work was taken in part from Paulina Soberanes’ B.Sc. dissertation. The authors wish to express their gratitude to Ms. María Isabel Beltrán, Mr. Abraham Contreras, and Isai Mendez for the animal care and technical assistance. The experimental procedures comply with the Mexican guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. This work was supported by grant 50636-M (to C.L.R) from Conacyt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cruz, S.L., Soberanes-Chávez, P., Páez-Martinez, N. et al. Toluene has antidepressant-like actions in two animal models used for the screening of antidepressant drugs. Psychopharmacology 204, 279–286 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1462-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1462-2