Abstract
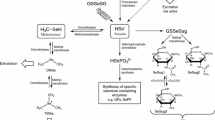
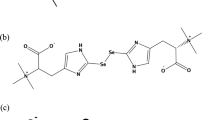
Mechanisms and metabolic significance in rats of methylation to the reduced form of selenium (Se), i.e., selenide (Se2−), were studied by dose- and time-related experiments with injection of selenite. Urinary Se-metabolites were determined by HPLC using an inductively coupled argon plasma-mass spectrometer as an in-line detector (HPLC/ICP-MS method). Although only monomethylselenol (MMSe) has been detected in urine of normal rats even in those fed a Se-excess diet, the␣three types of Se-metabolites – MMSe, trimethylselenonium ion (TMSe), and inorganic Se, were detected in urine of Wistar rats injected with selenite (0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 and 1.0 mg Se/kg body weight) into the tail vein. The amount of the three Se-metabolites was plotted against the total urinary Se concentration and shown to change dose- and time-dependently. The monomethylated metabolite, i.e., MMSe, increased in urine rapidly at first and was slowly followed by linear dose-dependent excretion of the trimethylated metabolite, TMSe. The new methylation pathway of MMSe leading to TMSe was assumed to be induced or activated when the dose of Se exceeds the limit of the normal capacity for monomethylation. Progressive methylation reactions were suggested to be regulated enzymatically.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 November 1996 / Accepted: 5 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itoh, M., Suzuki, K. Effects of dose on the methylation of selenium to monomethylselenol and trimethylselenonium ion in rats. Arch Toxicol 71, 461–466 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050412
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050412