Abstract
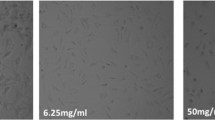
Quinolones cause damage of articular cartilage in different species by forming chelate complexes with divalent cations and inducing magnesium deficiency. Cations are important for regular function of integrins, a group of transmembrane proteins which connect extracellular matrix proteins with the intracellular cytoskeleton. We have shown that cultivation of rat chondrocytes in ciprofloxacin (CFX)-supplemented and Mg2+-free medium led to pronounced changes in the cytoskeleton and decreased adhesion of cells to the culture dish. In order to test whether or not these effects are species-specific, we extended our studies on human chondrocytes. Human chondrocytes cultivated in CFX-supplemented medium (10, 40, 80 and 160 μg/ml) or Mg2+-free medium showed decreased ability to adhere to growth support, cell shape changes, and alterations in actin and vimentin cytoskeleton in a concentration dependent manner. Attachment of human chondrocytes to collagen type II coated cover slips was reduced to 90% in CFX group and 75% in Mg2+-free group on day 1. This effect even increased after 4 days of culture in the respective medium (32% in CFX and 58% in Mg2+-free group). We concluded that Mg2+ deficiency is exerted via integrins, resulting in decreased ability to attach to extracellular matrix proteins and cytoskeletal changes. These effects are not species-specific. The attachment assay proves to be an easy to use experimental set-up to test ciprofloxacin and other quinolones for their chondrotoxic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 August 1999 / Accepted: 21 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egerbacher, M., Seiberl, G., Wolfesberger, B. et al. Ciprofloxacin causes cytoskeletal changes and detachment of human and rat chondrocytes in vitro. Arch Toxicol 73, 557–563 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050008
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050008