Abstract.
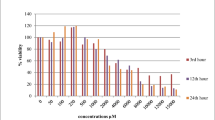
Even though fluoride toxicity is increasingly being considered to be important, very little information is available on the mechanism of action of fluoride. In the present study, the toxicity of fluoride on human leukemia (HL-60) cells was investigated and the involvement of caspase-3 was also studied. Fluoride induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Annexin staining and DNA ladder formation on agarose gel electrophoresis further revealed that HL-60 cells underwent apoptosis on exposure to 2–5 mM fluoride. Western blotting using polyclonal anti-caspase-3 antibody and mouse anti-human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) monoclonal antibody was performed to investigate caspase-3 and PARP activity. Fluoride led to the activation of caspase-3 which was evident by the loss of the 32 kDa precursor and appearance of the 17 kDa subunit. Furthermore, intact 116 kDa PARP was cleaved by fluoride treatment as shown by the appearance of a cleaved 89 kDa fragment. The results clearly suggest that fluoride causes cell death in HL-60 cells by causing the activation of caspase-3 which in turn cleaves PARP leading to DNA damage and ultimately cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anuradha, C., Kanno, S. & Hirano, S. Fluoride induces apoptosis by caspase-3 activation in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Arch Toxicol 74, 226–230 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000132
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000132