Abstract
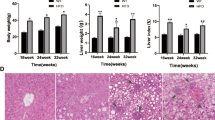
Patients with chronic liver diseases frequently exhibit decreased bone mineral densities (BMD), which is defined as hepatic osteodystrophy (HOD). HOD is a multifactorial disease whose regulatory mechanisms are barely understood. Thus, an early diagnosis and therapy is hardly possible. Therefore, the aim of our study consisted in characterizing a mouse model reflecting the human pathomechanism. Serum samples were collected from patients with chronic liver diseases and 12-week old C57Bl6/N mice after 6-week treatment with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Repetitive injections of CCl4 induced liver damage in mice, resembling liver fibrosis in patients, as assessed by serum analysis and histological staining. Although CCl4 did not affect primary osteoblast cultures, μCT analysis revealed significantly decreased BMD, bone volume, trabecular number and thickness in CCl4-treated mice. In both HOD patients and CCl4-treated mice, an altered vitamin D metabolism with decreased CYP27A1, CYP2R1, vitamin D-binding protein GC and increased 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase hepatic gene expression, results in decreased 25-OH vitamin D serum levels. Moreover, both groups exhibit excessively high active transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) serum levels, inhibiting osteoblast function in vitro. Summarizing, our mouse model presents possible mediators of HOD, e.g. altered vitamin D metabolism and increased active TGF-β. Liver damage and significant changes in bone structure and mineralization are already visible by μCT analysis after 6 weeks of CCl4 treatment. This fast response and easy transferability makes it an ideal model to investigate specific gene functions in HOD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
- CYP2R1:
-
Cytochrome P450 2R1
- CYP27A1:
-
Cytochrome P450 27A1
- DHCR7:
-
7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase
- GC:
-
Vitamin D-binding protein
- HOD:
-
Hepatic osteodystrophy
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- OPG:
-
Osteoprotegerin
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand
References
Angulo P, Grandison GA, Fong DG, Keach JC, Lindor KD, Bjornsson E, Koch A (2011) Bone disease in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 140(1):180–188. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.10.014
Arteh J, Narra S, Nair S (2010) Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 55(9):2624–2628. doi:10.1007/s10620-009-1069-9
Bu FX, Armas L, Lappe J, Zhou Y, Gao G, Wang HW, Recker R, Zhao LJ (2010) Comprehensive association analysis of nine candidate genes with serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels among healthy Caucasian subjects. Hum Genet 128(5):549–556. doi:10.1007/s00439-010-0881-9
Choudhary NS, Tomar M, Chawla YK, Bhadada SK, Khandelwal N, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Bhansali A (2011) Hepatic osteodystrophy is common in patients with noncholestatic liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 56(11):3323–3327. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1722-y
Christensen MH, Apalset EM, Nordbo Y, Varhaug JE, Mellgren G, Lien EA (2013) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and the vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism Apa1 influence bone mineral density in primary hyperparathyroidism. PLoS ONE 8(2):e56019. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056019PONE-D-12-36460
Collier J (2007) Bone disorders in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 46(4):1271–1278. doi:10.1002/hep.21852
Compston JE (1986) Hepatic osteodystrophy: vitamin D metabolism in patients with liver disease. Gut 27(9):1073–1090
Cunningham J (2005) Posttransplantation bone disease. Transplantation 79(6):629–634
Diamond T, Stiel D, Lunzer M, Wilkinson M, Roche J, Posen S (1990) Osteoporosis and skeletal fractures in chronic liver disease. Gut 31(1):82–87
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Ciuclan L, Godoy P, Ilkavets I, Ehnert S, Ueberham E, Gebhardt R, Kanzler S, Geier A, Breitkopf K, Weng H, Mertens PR (2008) Hepatocyte-specific Smad7 expression attenuates TGF-beta-mediated fibrogenesis and protects against liver damage. Gastroenterology 135(2):642–659. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.04.038
Ehnert S, Baur J, Schmitt A, Neumaier M, Lucke M, Dooley S, Vester H, Wildemann B, Stockle U, Nussler AK (2010) TGF-beta1 as possible link between loss of bone mineral density and chronic inflammation. PLoS One 5(11):e14073. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014073
Ehnert S, Seeliger C, Vester H, Schmitt A, Saidy-Rad S, Lin J, Neumaier M, Gillen S, Kleeff J, Friess H, Burkhart J, Stockle U, Nussler AK (2011) Autologous serum improves yield and metabolic capacity of monocyte-derived hepatocyte-like cells: possible implication for cell transplantation. Cell Transplant 20(9):1465–1477. doi:10.3727/096368910X550224
Gaudio A, Lasco A, Morabito N, Atteritano M, Vergara C, Catalano A, Fries W, Trifiletti A, Frisina N (2005) Hepatic osteodystrophy: does the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand system play a role? J Endocrinol Invest 28(8):677–682
George J, Ganesh HK, Acharya S, Bandgar TR, Shivane V, Karvat A, Bhatia SJ, Shah S, Menon PS, Shah N (2009) Bone mineral density and disorders of mineral metabolism in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 15(28):3516–3522
Goel V, Kar P (2010) Hepatic osteodystrophy. Trop Gastroenterol 31(2):82–86
Guanabens N, Pares A (2011) Management of osteoporosis in liver disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 35(6–7):438–445. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2011.03.007
Guanabens N, Enjuanes A, Alvarez L, Peris P, Caballeria L, Martinez J, de Osaba M, Cerda D, Monegal A, Pons F, Pares A (2009) High osteoprotegerin serum levels in primary biliary cirrhosis are associated with disease severity but not with the mRNA gene expression in liver tissue. J Bone Miner Metab 27(3):347–354. doi:10.1007/s00774-009-0042-1
Guanabens N, Cerda D, Monegal A, Pons F, Caballeria L, Peris P, Pares A (2010) Low bone mass and severity of cholestasis affect fracture risk in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 138(7):2348–2356. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.02.016
Hamburg SM, Piers DA, van den Berg AP, Slooff MJ, Haagsma EB (2000) Bone mineral density in the long term after liver transplantation. Osteoporos Int 11(7):600–606
Hamzavi J, Ehnert S, Godoy P, Ciuclan L, Weng H, Mertens PR, Heuchel R, Dooley S (2008) Disruption of the Smad7 gene enhances CCI4-dependent liver damage and fibrogenesis in mice. J Cell Mol Med 12(5B):2130–2144. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00262.x
Hildebrand T, Ruegsegger P (1997) Quantification of Bone Microarchitecture with the Structure Model Index. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 1(1):15–23. doi:10.1080/01495739708936692
Hochrath K, Ehnert S, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Lau Y, Schmid A, Krawczyk M, Hengstler JG, Dunn J, Hiththetiya K, Rathkolb B, Micklich K, Hans W, Fuchs H, Gailus-Durner V, Wolf E, de Angelis MH, Dooley S, Paigen B, Wildemann B, Lammert F, Nussler AK (2013) Modeling hepatic osteodystrophy in Abcb4 deficient mice. Bone 55(2):501–511. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.03.012
Hogler W, Baumann U, Kelly D (2011) Endocrine and bone metabolic complications in chronic liver disease and after liver transplantation in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54(3):313–321. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e31823e9412
Knobeloch D, Ehnert S, Schyschka L, Buchler P, Schoenberg M, Kleeff J, Thasler WE, Nussler NC, Godoy P, Hengstler J, Nussler AK (2012) Human hepatocytes: isolation, culture, and quality procedures. Methods Mol Biol 806:99–120. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-367-7_8
Konstantynowicz J, Lebensztejn DM, Skiba E, Sobaniec-Lotowska ME, Abramowicz P, Piotrowska-Jastrzebska J, Kaczmarski M (2011) Chronic non-cholestatic liver disease is not associated with an increased fracture rate in children. J Bone Miner Metab 29(3):315–320. doi:10.1007/s00774-010-0219-7
Lavi-Moshayoff V, Wasserman G, Meir T, Silver J, Naveh-Many T (2010) PTH increases FGF23 gene expression and mediates the high-FGF23 levels of experimental kidney failure: a bone parathyroid feedback loop. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299(4):F882–F889. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00360.2010
Lind M (1998) Growth factor stimulation of bone healing. Effects on osteoblasts, osteomies, and implants fixation. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 283:2–37
Liu T, Wang X, Karsdal MA, Leeming DJ, Genovese F (2012) Molecular serum markers of liver fibrosis. Biomark Insights 7:105–117. doi:10.4137/BMI.S10009bmi-7-2012-105
Loria I, Albanese C, Giusto M, Galtieri PA, Giannelli V, Lucidi C, Di Menna S, Pirazzi C, Corradini SG, Mennini G, Rossi M, Berloco P, Merli M (2010) Bone disorders in patients with chronic liver disease awaiting liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 42(4):1191–1193. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.03.096
Luxon BA (2012) Bone disorders in chronic liver diseases. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13(1):40–48. doi:10.1007/s11894-010-0166-4
Maalouf NM, Sakhaee K (2006) Treatment of osteoporosis in patients with chronic liver disease and in liver transplant recipients. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 9(6):456–463
Mansueto P, Carroccio A, Seidita A, Di Fede G, Craxi A (2012) Osteodystrophy in chronic liver diseases. Intern Emerg Med. doi:10.1007/s11739-012-0753-5
Mitchell R, McDermid J, Ma MM, Chik CL (2011) MELD score, insulin-like growth factor 1 and cytokines on bone density in end-stage liver disease. World J Hepatol 3(6):157–163. doi:10.4254/wjh.v3.i6.157
Monegal A, Navasa M, Peris P, Alvarez L, Pons F, Rodes J, Guanabens N (2007) Serum osteoprotegerin and its ligand in cirrhotic patients referred for orthotopic liver transplantation: relationship with metabolic bone disease. Liver Int 27(4):492–497. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01448.x
Mounach A, Ouzzif Z, Wariaghli G, Achemlal L, Benbaghdadi I, Aouragh A, Bezza A, El Maghraoui A (2008) Primary biliary cirrhosis and osteoporosis: a case-control study. J Bone Miner Metab 26(4):379–384. doi:10.1007/s00774-007-0833-1
Nakano A, Kanda T, Abe H (1996) Bone changes and mineral metabolism disorders in rats with experimental liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(12):1143–1154
Pfeilschifter J, Bonewald L, Mundy GR (1990) Characterization of the latent transforming growth factor beta complex in bone. J Bone Miner Res 5(1):49–58. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650050109
Putz-Bankuti C, Pilz S, Stojakovic T, Scharnagl H, Pieber TR, Trauner M, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Stauber RE (2012) Association of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with liver dysfunction and mortality in chronic liver disease. Liver Int. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02735.x
Ritter CS, Brown AJ (2011) Direct suppression of Pth gene expression by the vitamin D prohormones doxercalciferol and calcidiol requires the vitamin D receptor. J Mol Endocrinol 46(2):63–66. doi:10.1677/JME-10-0128
Robey PG, Young MF, Flanders KC, Roche NS, Kondaiah P, Reddi AH, Termine JD, Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1987) Osteoblasts synthesize and respond to transforming growth factor-type beta (TGF-beta) in vitro. J Cell Biol 105(1):457–463
Rode A, Fourlanos S, Nicoll A (2010) Oral vitamin D replacement is effective in chronic liver disease. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 34(11):618–620. doi:10.1016/j.gcb.2010.07.009
Rudic JS, Giljaca V, Krstic MN, Bjelakovic G, Gluud C (2011) Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD009144. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009144.pub2
Sarahrudi K, Thomas A, Mousavi M, Kaiser G, Kottstorfer J, Kecht M, Hajdu S, Aharinejad S (2011) Elevated transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) levels in human fracture healing. Injury 42(8):833–837. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.03.055
Tejwani V, Qian Q (2013) Calcium regulation and bone mineral metabolism in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 5(6):1913–1936. doi:10.3390/nu5061913
van der Merwe SW, van den Bogaerde JB, Goosen C, Maree FF, Milner RJ, Schnitzler CM, Biscardi A, Mesquita JM, Engelbrecht G, Kahn D, Fevery J (2003) Hepatic osteodystrophy in rats results mainly from portasystemic shunting. Gut 52(4):580–585
Wariaghli G, Allali F, El Maghraoui A, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2010) Osteoporosis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(12):1397–1401. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283405939
Weng HL, Liu Y, Chen JL, Huang T, Xu LJ, Godoy P, Hu JH, Zhou C, Stickel F, Marx A, Bohle RM, Zimmer V, Lammert F, Mueller S, Gigou M, Samuel D, Mertens PR, Singer MV, Seitz HK, Dooley S (2009) The etiology of liver damage imparts cytokines transforming growth factor beta1 or interleukin-13 as driving forces in fibrogenesis. Hepatology 50(1):230–243. doi:10.1002/hep.22934
Wibaux C, Legroux-Gerot I, Dharancy S, Boleslawski E, Declerck N, Canva V, Mathurin P, Pruvot FR, Cortet B (2010) Assessing bone status in patients awaiting liver transplantation. Joint Bone Spine 78(4):387–391. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.03.001
Yurci A, Kalkan AO, Ozbakir O, Karaman A, Torun E, Kula M, Baskol M, Gursoy S, Yucesoy M, Bayram F (2011) Efficacy of different therapeutic regimens on hepatic osteodystrophy in chronic viral liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(12):1206–1212. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e32834cd6f6
Acknowledgments
The work was partially supported by funding of the BG trauma clinic and by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF—0315741—Virtual Liver).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
204_2013_1191_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure: CCl4 treatment damages hepatocytes but not osteoblasts. (a) Primary human hepatocytes (N = 5, n ≥ 4) and primary human osteoblasts (N = 6, n = 4) were stimulated repeatedly (4 times) with 0, 1, 2 and 10 mM CCl4. After 96 h cell viability was determined by resazurin conversion. Reduced cell viability was observed only in hepatocytes but not in osteoblasts. (b) The CCl4 treated osteoblasts were further analysed for AP activity and matrix mineralization as functional characteristics. CCl4 treatment did not alter AP activity and matrix mineralization in osteoblasts. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 as compared to untreated controls. (TIFF 1052 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nussler, A.K., Wildemann, B., Freude, T. et al. Chronic CCl4 intoxication causes liver and bone damage similar to the human pathology of hepatic osteodystrophy: a mouse model to analyse the liver–bone axis. Arch Toxicol 88, 997–1006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1191-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1191-5