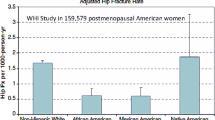
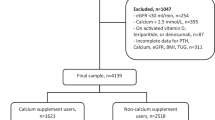
Abstract
Bone disease is a major complication of chronic liver disease. Osteomalacia is quite uncommon despite low vitamin D levels in the majority of patients with cirrhosis. In contrast, osteoporosis is quite common, occurring in up to 50% of patients. Osteoporosis can result in spontaneous or low-impact fractures in patients with chronic liver diseases, adversely affecting morbidity, quality of life, and survival. The general biology of osteoporosis, including its pathogenesis, diagnostic tools, and rationale for treatment, have been determined largely empirically from studies of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Treatment regimens with modification of risk factors, use of vitamin D, and supplementation with calcium and bisphosphonates have been shown to be effective in select groups of patients with chronic liver diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Courbebaisse M, Souberbielle JC, Thervet E: Potential nonclassical effects of vitamin D in transplant recipients. Transplantation 2010, 89(2):131–137.
Crawford BA, Labio ED, Strasser SI, et al.: Vitamin D replacement for cirrhosis-related bone disease. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006, 3(12):689–699.
WHO: Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 1994, 843:1–129.
Collier JD, Ninkovic M, Compston JE: Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease. Gut 2002, 50 Suppl 1(1):i1–9.
Leslie WD, Bernstein CN, Leboff MS: AGA technical review on osteoporosis in hepatic disorders. Gastroenterology 2003, 125(3):941–966.
Marshall D, Johnell O, Wedel H: Meta-analysis of how well measures of bone mineral density predict occurrence of osteoporotic fractures. BMJ 1996, 312(7041):1254–1259.
Stellon AJ, Webb A, Compston J, et al.: Low bone turnover state in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1987, 7(1):137–142.
Guanabens N, Pares A: Liver and bone. Arch Biochem Biophys 2010, ePub ahead of print.
Janes CH, Dickson ER, Okazaki R, et al.: Role of hyperbilirubinemia in the impairment of osteoblast proliferation associated with cholestatic jaundice. J Clin Invest 1995, 95(6):2581–2586.
Diamond TH, Stiel D, Lunzer M, et al.: Hepatic osteodystrophy. Static and dynamic bone histomorphometry and serum bone Gla-protein in 80 patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 1989, 96(1):213–221.
Cemborain A, Castilla-Cortazar I, Garcia M, et al.: Effects of IGF-I treatment on osteopenia in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis. J Physiol Biochem 2000, 56(2):91–99.
Nakchbandi IA, van der Merwe SW: Current understanding of osteoporosis associated with liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009, 6(11):660–670.
Ninkovic M, Love SA, Tom B, et al.: High prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with chronic liver disease prior to liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int 2001, 69(6):321–326.
Collier J: Bone disorders in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2007, 46(4):1271–1278.
Angulo P, Therneau TM, Jorgensen A, et al.: Bone disease in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: prevalence, severity and prediction of progression. J Hepatol 1998, 29(5):729–735.
Guichelaar MM, Schmoll J, Malinchoc M, et al.: Fractures and avascular necrosis before and after orthotopic liver transplantation: long-term follow-up and predictive factors. Hepatology 2007, 46(4):1198–1207.
Guanabens N, Pares A, Ros I, et al.: Severity of cholestasis and advanced histological stage but not menopausal status are the major risk factors for osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2005, 42(4):573–577.
Solaymani-Dodaran M, Card TR, Aithal GP, et al.: Fracture risk in people with primary biliary cirrhosis: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2006, 131(6):1752–1757.
Masaki K, Shiomi S, Kuroki T, et al.: Longitudinal changes of bone mineral content with age in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Gastroenterol 1998, 33(2):236–240.
Schiefke I, Fach A, Wiedmann M, et al.: Reduced bone mineral density and altered bone turnover markers in patients with non-cirrhotic chronic hepatitis B or C infection. World J Gastroenterol 2005, 11(12):1843–1847.
Guggenbuhl P, Deugnier Y, Boisdet JF, et al.: Bone mineral density in men with genetic hemochromatosis and HFE gene mutation. Osteoporos Int 2005, 16(12):1809–1814.
Peris P, Guanabens N, Pares A, et al.: Vertebral fractures and osteopenia in chronic alcoholic patients. Calcif Tissue Int 1995, 57(2):111–114.
Navasa M, Monegal A, Guanabens N, et al.: Bone fractures in liver transplant patients. Br J Rheumatol 1994, 33(1):52–55.
Sokhi RP, Anantharaju A, Kondaveeti R, et al.: Bone mineral density among cirrhotic patients awaiting liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2004, 10(5):648–653.
Eastell R, Dickson ER, Hodgson SF, et al.: Rates of vertebral bone loss before and after liver transplantation in women with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1991, 14(2):296–300.
Atamaz F, Hepguler S, Karasu Z, et al.: The prevention of bone fractures after liver transplantation: experience with alendronate treatment. Transplant Proc 2006, 38(5):1448–1452.
Pares A, Guanabens N, Pares A, et al.: Treatment of bone disorders in liver disease. Osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: pathogenesis and treatment. J Hepatol 2006, 45(3):445–453.
• Pares A, Guanabens N: Osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Clin Liver Dis 2008, 12(2):407–424. A good review of osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis with discussions about the prevalence, pathogenesis, and recommendations for treatment.
Crippin JS, Jorgensen RA, Dickson ER, et al.: Hepatic osteodystrophy in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of medical treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 1994, 89(1):47–50.
Shiomi S, Masaki K, Habu D, et al.: Calcitriol for bone loss in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 1999, 34(2):241–245.
Guanabens N, Pares A, Ros I, et al.: Alendronate is more effective than etidronate for increasing bone mass in osteopenic patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2003, 98(10):2268–2274.
•• Zein CO, Jorgensen RA, Clarke B, et al.: Alendronate improves bone mineral density in primary biliary cirrhosis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology 2005, 42(4):762–771. This is the only randomized, placebo-controlled trial of a bisphosphonate in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis.
Guanabens N, Enjuanes A, Alvarez L, et al.: High osteoprotegerin serum levels in primary biliary cirrhosis are associated with disease severity but not with the mRNA gene expression in liver tissue. J Bone Miner Metab 2009, 27(3):347–354.
Monegal A, Guanabens N, Suarez MJ, et al.: Pamidronate in the prevention of bone loss after liver transplantation: a randomized controlled trial. Transpl Int 2009, 22(2):198–206.
Crawford BA, Kam C, Pavlovic J, et al.: Zoledronic acid prevents bone loss after liver transplantation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 2006, 144(4):239–248.
Olsson R, Mattsson LA, Obrant K, et al.: Estrogen-progestogen therapy for low bone mineral density in primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver 1999, 19(3):188–192.
Hulley S, Furberg C, Barrett-Connor E, et al.: Noncardiovascular disease outcomes during 6.8 years of hormone therapy: Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study follow-up (HERS II). Jama 2002, 288(1):58–66.
Levy C, Harnois DM, Angulo P, et al.: Raloxifene improves bone mass in osteopenic women with primary biliary cirrhosis: results of a pilot study. Liver Int 2005, 25(1):117–121.
Floreani A, Zappala F, Fries W, et al.: A 3-year pilot study with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, calcium, and calcitonin for severe osteodystrophy in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1997, 24(4):239–244.
Camisasca M, Crosignani A, Battezzati PM, et al.: Parenteral calcitonin for metabolic bone disease associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1994, 20(3):633–637.
Feitelberg S, Epstein S, Ismail F, et al.: Deranged bone mineral metabolism in chronic alcoholism. Metabolism 1987, 36(4):322–326.
Laitinen K, Karkkainen M, Lalla M, et al.: Is alcohol an osteoporosis-inducing agent for young and middle-aged women? Metabolism 1993, 42(7):875–881.
Mitchison HC, Malcolm AJ, Bassendine MF, et al.: Metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis at presentation. Gastroenterology 1988, 94(2):463–470.
Van Berkum FN, Beukers R, Birkenhager JC, et al.: Bone mass in women with primary biliary cirrhosis: the relation with histological stage and use of glucocorticoids. Gastroenterology 1990, 99(4):1134–1139.
Guanabens N, Pares A, Marinoso L, et al.: Factors influencing the development of metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 1990, 85(10):1356–1362.
Lindor KD, Janes CH, Crippin JS, et al.: Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: does ursodeoxycholic acid make a difference? Hepatology 1995, 21(2):389–392.
• Guichelaar MM, Kendall R, Malinchoc M, et al.: Bone mineral density before and after OLT: long-term follow-up and predictive factors. Liver Transpl 2006, 12(9):1390–1402. A thorough review of hepatic osteodystrophy in patients with end stage liver disease before and after liver transplantation. Recommendations are given for screening patients for osteoporosis and for treatment.
Chen CC, Wang SS, Jeng FS, et al.: Metabolic bone disease of liver cirrhosis: is it parallel to the clinical severity of cirrhosis? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996, 11(5):417–421.
Gallego-Rojo FJ, Gonzalez-Calvin JL, Munoz-Torres M, et al.: Bone mineral density, serum insulin-like growth factor I, and bone turnover markers in viral cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998, 28(3):695–699.
Bonkovsky HL, Hawkins M, Steinberg K, et al.: Prevalence and prediction of osteopenia in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 1990, 12(2):273–280.
Monegal A, Navasa M, Guanabens N, et al.: Osteoporosis and bone mineral metabolism disorders in cirrhotic patients referred for orthotopic liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int 1997, 60(2):148–154.
Sinigaglia L, Fargion S, Fracanzani AL, et al.: Bone and joint involvement in genetic hemochromatosis: role of cirrhosis and iron overload. J Rheumatol 1997, 24(9):1809–1813.
Pares A, Guanabens N, and Ros I: Alendronate is more effective than etidronate for increasing bone mass in osteopenic patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1999, 30:472A.
Epstein O, Kato Y, Dick R, et al.: Vitamin D, hydroxyapatite, and calcium gluconate in treatment of cortical bone thinning in postmenopausal women with primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Clin Nutr 1982, 36(3):426–430.
Guanabens N, Pares A, Monegal A, et al.: Etidronate versus fluoride for treatment of osteopenia in primary biliary cirrhosis: preliminary results after 2 years. Gastroenterology 1997, 113(1):219–224.
Wolfhagen FH, van Buuren HR, den Ouden JW, et al.: Cyclical etidronate in the prevention of bone loss in corticosteroid-treated primary biliary cirrhosis. A prospective, controlled pilot study. J Hepatol 1997, 26(2):325–330.
Disclosure
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luxon, B.A. Bone Disorders in Chronic Liver Diseases. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13, 40–48 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0166-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0166-4