Abstract
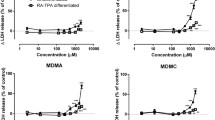
The liver is a vulnerable target for amphetamine toxicity, but the mechanisms involved in the drug’s hepatotoxicity remain poorly understood. The purpose of the current research was to characterize the mode of death elicited by four amphetamines and to evaluate whether their combination triggered similar mechanisms in immortalized human HepG2 cells. The obtained data revealed a time- and temperature-dependent mortality of HepG2 cells exposed to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy; 1.3 mM), methamphetamine (3 mM), 4-methylthioamphetamine (0.5 mM) and d-amphetamine (1.7 mM), alone or combined (1.6 mM mixture). At physiological temperature (37 °C), 24-h exposures caused HepG2 death preferentially by apoptosis, while a rise to 40.5 °C favoured necrosis. ATP levels remained unaltered when the drugs where tested at normothermia, but incubation at 40.5 °C provoked marked ATP depletion for all treatments. Further investigations on the apoptotic mechanisms triggered by the drugs (alone or combined) showed a decline in BCL-2 and BCL- XL mRNA levels, with concurrent upregulation of BAX, BIM, PUMA and BID genes. Elevation of Bax, cleaved Bid, Puma, Bak and Bim protein levels was also seen. To the best of our knowledge, Puma, Bim and Bak have never been linked with the toxicity induced by amphetamines. Time-dependent caspase-3/-7 activation, but not mitochondrial membrane potential (∆ψm) disruption, also mediated amphetamine-induced apoptosis. The cell dismantling was confirmed by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase proteolysis. Overall, for all evaluated parameters, no relevant differences were detected between individual amphetamines and the mixture (all tested at equieffective cytotoxic concentrations), suggesting that the mode of action of the amphetamines in combination does not deviate from the mode of action of the drugs individually, when eliciting HepG2 cell death.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu V, Mas A, Bruguera M, Salmeron JM, Moreno V, Nogue S, Rodes J (1998) Ecstasy: a common cause of severe acute hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol 29(3):394–397
Antolino-Lobo I, Meulenbelt J, van den Berg M, van Duursen MB (2011) A mechanistic insight into 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“ecstasy”)-mediated hepatotoxicity. Vet Q 31(4):193–205. doi:10.1080/01652176.2011.642534
Armenian P, Mamantov TM, Tsutaoka BT, Gerona RR, Silman EF, Wu AH, Olson KR (2012) Multiple MDMA (Ecstasy) overdoses at a rave event: a case series. J Intensive Care Med. doi:10.1177/0885066612445982
Barros LF, Kanaseki T, Sabirov R, Morishima S, Castro J, Bittner CX, Maeno E, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Okada Y (2003) Apoptotic and necrotic blebs in epithelial cells display similar neck diameters but different kinase dependency. Cell Death Differ 10(6):687–697. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401236
Beauvais G, Atwell K, Jayanthi S, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2011) Involvement of dopamine receptors in binge methamphetamine-induced activation of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial stress pathways. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28946. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028946
Beitia G, Cobreros A, Sainz L, Cenarruzabeitia E (1999) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)-induced hepatotoxicity: effect on cytosolic calcium signals in isolated hepatocytes. Liver 19(3):234–241
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brauer RB, Heidecke CD, Nathrath W, Beckurts KT, Vorwald P, Zilker TR, Schweigart U, Holscher AH, Siewert JR (1997) Liver transplantation for the treatment of fulminant hepatic failure induced by the ingestion of ecstasy. Transpl Int 10(3):229–233
Brncic N, Kraus I, Viskovic I, Mijandrusic-Sincic B, Vlahovic-Palcevski V (2006) 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA): an important cause of acute hepatitis. Med Sci Monit 12(11):CS107–CS109
Cadet JL, Ordonez SV, Ordonez JV (1997) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in immortalized neural cells: protection by the proto-oncogene, bcl-2. Synapse 25(2):176–184. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199702)25:2<176::AID-SYN8>3.0.CO;2-9
Capela JP, da Araujo SC, Costa VM, Ruscher K, Fernandes E, Bastos MD, Dirnagl U, Meisel A, Carvalho F (2012) The neurotoxicity of hallucinogenic amphetamines in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. Neurotoxicology. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2012.09.005
Capela JP, Ruscher K, Lautenschlager M, Freyer D, Dirnagl U, Gaio AR, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F (2006) Ecstasy-induced cell death in cortical neuronal cultures is serotonin 2A-receptor-dependent and potentiated under hyperthermia. Neuroscience 139(3):1069–1081. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.007
Carvalho F, Remiao F, Soares ME, Catarino R, Queiroz G, Bastos ML (1997) d-Amphetamine-induced hepatotoxicity: possible contribution of catecholamines and hyperthermia to the effect studied in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 71(7):429–436
Carvalho M, Remiao F, Milhazes N, Borges F, Fernandes E, Carvalho F, Bastos ML (2004a) The toxicity of N-methyl-alpha-methyldopamine to freshly isolated rat hepatocytes is prevented by ascorbic acid and N-acetylcysteine. Toxicology 200(2–3):193–203. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.03.016
Carvalho M, Remiao F, Milhazes N, Borges F, Fernandes E, Monteiro Mdo C, Goncalves MJ, Seabra V, Amado F, Carvalho F, Bastos ML (2004b) Metabolism is required for the expression of ecstasy-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro. Chem Res Toxicol 17(5):623–632. doi:10.1021/tx049960f
Carvalho M, Carmo H, Costa VM, Capela JP, Pontes H, Remiao F, Carvalho F, Bastos ML (2012) Toxicity of amphetamines: an update. Arch Toxicol 86(8):1167–1231. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0815-5
Carvalho M, Carvalho F, Bastos ML (2001) Is hyperthermia the triggering factor for hepatotoxicity induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)? An in vitro study using freshly isolated mouse hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 74(12):789–793
Carvalho M, Pontes H, Remiao F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2010) Mechanisms underlying the hepatotoxic effects of ecstasy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 11(5):476–495
Cerretani D, Bello S, Cantatore S, Fiaschi AI, Montefrancesco G, Neri M, Pomara C, Riezzo I, Fiore C, Bonsignore A, Turillazzi E, Fineschi V (2011) Acute administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) induces oxidative stress, lipoperoxidation and TNFalpha-mediated apoptosis in rat liver. Pharmacol Res 64(5):517–527. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.08.002
Coore JR (1996) A fatal trip with ecstasy: a case of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine/3,4- methylenedioxyamphetamine toxicity. J R Soc Med 89(1):51P–52P
Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM (2003) The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22(53):8590–8607. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207102
Cunha-Oliveira T, Rego AC, Cardoso SM, Borges F, Swerdlow RH, Macedo T, de Oliveira CR (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase activation in rat cortical neurons treated with cocaine or amphetamine. Brain Res 1089(1):44–54. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.061
De Letter EA, Bouche MP, Van Bocxlaer JF, Lambert WE, Piette MH (2004) Interpretation of a 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) blood level: discussion by means of a distribution study in two fatalities. Forensic Sci Int 141(2–3):85–90. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2003.12.015
De Letter EA, Piette MHA, Lambert WE, Cordonnier JACM (2006) Amphetamines as potential inducers of fatalities: a review in the district of Ghent from 1976–2004. Med Sci Law 46(1):37–65
De Miglio MR, Muroni MR, Simile MM, Calvisi DF, Tolu P, Deiana L, Carru A, Bonelli G, Feo F, Pascale RM (2000) Implication of Bcl-2 family genes in basal and D-amphetamine-induced apoptosis in preneoplastic and neoplastic rat liver lesions. Hepatology 31(4):956–965. doi:10.1053/he.2000.5411
Deng X, Cai NS, McCoy MT, Chen W, Trush MA, Cadet JL (2002) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in an immortalized rat striatal cell line by activating the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Neuropharmacology 42(6):837–845
Deng X, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL (2007) Methamphetamine administration causes death of dopaminergic neurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Biol Psychiatry 61(11):1235–1243. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.010
Dias da Silva D, Carmo H, Silva E (2013a) Mixtures of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) and its major human metabolites act additively to induce significant toxicity to liver cells even when combined at low, non-cytotoxic concentrations. J Appl Toxicol. doi:10.1002/jat.2885
Dias da Silva D, Carmo H, Silva E (2013b) The risky cocktail: what combination effects can we expect between ecstasy and other amphetamines? Arch Toxicol 87(1):111–122. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0929-9
Dias da Silva D, Silva E, Carmo H (2013c) Combination effects of amphetamines under hyperthermia—the role played by oxidative stress. J Appl Toxicol. doi:10.1002/jat.2889
Dias da Silva D, Silva E, Carmo H (2013d) Cytotoxic effects of amphetamine mixtures in primary hepatocytes are severely aggravated under hyperthermic conditions. Toxicol In Vitro 27(6):1670–1678. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2013.04.010
Duarte JA, Leao A, Magalhaes J, Ascensao A, Bastos ML, Amado FL, Vilarinho L, Quelhas D, Appell HJ, Carvalho F (2005) Strenuous exercise aggravates MDMA-induced skeletal muscle damage in mice. Toxicology 206(3):349–358. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.07.012
Dykhuizen RS, Brunt PW, Atkinson P, Simpson JG, Smith CC (1995) Ecstasy induced hepatitis mimicking viral hepatitis. Gut 36(6):939–941
Eguchi Y, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y (1997) Intracellular ATP levels determine cell death fate by apoptosis or necrosis. Cancer Res 57(10):1835–1840
Ellis AJ, Wendon JA, Portmann B, Williams R (1996) Acute liver damage and ecstasy ingestion. Gut 38(3):454–458
Fineschi V, Centini F, Mazzeo E, Turillazzi E (1999) Adam (MDMA) and Eve (MDEA) misuse: an immunohistochemical study on three fatal cases. Forensic Sci Int 104(1):65–74
Garbino J, Henry JA, Mentha G, Romand JA (2001) Ecstasy ingestion and fulminant hepatic failure: liver transplantation to be considered as a last therapeutic option. Vet Hum Toxicol 43(2):99–102
Garcia-Repetto R, Moreno E, Soriano T, Jurado C, Gimenez MP, Menendez M (2003) Tissue concentrations of MDMA and its metabolite MDA in three fatal cases of overdose. Forensic Sci Int 135(2):110–114. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(03)00179-8
Garcia-Saez AJ (2012) The secrets of the Bcl-2 family. Cell Death Differ 19(11):1733–1740. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.105
Genc K, Genc S, Kizildag S, Sonmez U, Yilmaz O, Tugyan K, Ergur B, Sonmez A, Buldan Z (2003) Methamphetamine induces oligodendroglial cell death in vitro. Brain Res 982(1):125–130
Golstein P, Kroemer G (2007) Cell death by necrosis: towards a molecular definition. Trends Biochem Sci 32(1):37–43. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.11.001
Green AR, Mechan AO, Elliott JM, O’Shea E, Colado MI (2003) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”). Pharmacol Rev 55(3):463–508
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13(15):1899–1911
Henry JA, Jeffreys KJ, Dawling S (1992) Toxicity and deaths from 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“ecstasy”). Lancet 340(8816):384–387
Ibranyi E, Schonleber J (2003) Acute liver failure caused by Ecstasy. Orv Hetil 144(29):1455–1456
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Bordelon M, McCoy MT, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-death Bcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex. FASEB J 15(10):1745–1752
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Noailles PA, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2004) Methamphetamine induces neuronal apoptosis via cross-talks between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria-dependent death cascades. FASEB J 18(2):238–251. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0295com
Jimenez A, Jorda EG, Verdaguer E, Pubill D, Sureda FX, Canudas AM, Escubedo E, Camarasa J, Camins A, Pallas M (2004) Neurotoxicity of amphetamine derivatives is mediated by caspase pathway activation in rat cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196(2):223–234. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.017
Kalant H (2001) The pharmacology and toxicology of “ecstasy” (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ 165(7):917–928
Kamijo Y, Soma K, Nishida M, Namera A, Ohwada T (2002) Acute liver failure following intravenous methamphetamine. Vet Hum Toxicol 44(4):216–217
Kanthasamy A, Anantharam V, Ali SF, Kanthasamy AG (2006) Methamphetamine induces autophagy and apoptosis in a mesencephalic dopaminergic neuronal culture model: role of cathepsin-D in methamphetamine-induced apoptotic cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1074:234–244. doi:10.1196/annals.1369.022
Kass GE, Eriksson JE, Weis M, Orrenius S, Chow SC (1996) Chromatin condensation during apoptosis requires ATP. Biochem J 318(Pt 3):749–752
Kendrick WC, Hull AR, Knochel JP (1977) Rhabdomyolysis and shock after intravenous amphetamine administration. Ann Intern Med 86(4):381–387
Khakoo SI, Coles CJ, Armstrong JS, Barry RE (1995) Hepatotoxicity and accelerated fibrosis following 3,4-methylenedioxymetamphetamine (“ecstasy”) usage. J Clin Gastroenterol 20(3):244–247
Krasnova IN, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2005) Amphetamine induces apoptosis of medium spiny striatal projection neurons via the mitochondria-dependent pathway. FASEB J 19(7):851–853. doi:10.1096/fj.04-2881fje
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Leist M, Single B, Castoldi AF, Kuhnle S, Nicotera P (1997) Intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) concentration: a switch in the decision between apoptosis and necrosis. J Exp Med 185(8):1481–1486
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94(4):491–501
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91(4):479–489
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X (1998) Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94(4):481–490
Ly JD, Grubb DR, Lawen A (2003) The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 8(2):115–128
Milroy CM (2011) “Ecstasy” associated deaths: what is a fatal concentration ? Analysis of a case series. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 7(3):248–252. doi:10.1007/s12024-010-9220-7
Milroy CM, Clark JC, Forrest AR (1996) Pathology of deaths associated with “ecstasy” and “eve” misuse. J Clin Pathol 49(2):149–153
Montgomery T, Sitte H, McBean G (2010) 4-Methylthioamphetamine (4-MTA) induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells independently of dopamine and noradrenaline transporters. BMC Pharmacol 10(Suppl 1):A22
Montiel-Duarte C, Ansorena E, Lopez-Zabalza MJ, Cenarruzabeitia E, Iraburu MJ (2004) Role of reactive oxygen species, glutathione and NF-kappaB in apoptosis induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“Ecstasy”) on hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Pharmacol 67(6):1025–1033. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2003.10.020
Montiel-Duarte C, Varela-Rey M, Oses-Prieto JA, Lopez-Zabalza MJ, Beitia G, Cenarruzabeitia E, Iraburu MJ (2002) 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“Ecstasy”) induces apoptosis of cultured rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1588(1):26–32
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Lamensdorf I, Yoon SH, Youle RJ (2001) Bax and Bak coalesce into novel mitochondria-associated clusters during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 153(6):1265–1276
Nicotera P, Leist M, Ferrando-May E (1998) Intracellular ATP, a switch in the decision between apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicol Lett 102–103:139–142
Ortyn WE, Hall BE, George TC, Frost K, Basiji DA, Perry DJ, Zimmerman CA, Coder D, Morrissey PJ (2006) Sensitivity measurement and compensation in spectral imaging. Cytometry A 69(8):852–862. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20306
Patel MM, Belson MG, Longwater AB, Olson KR, Miller MA (2005) Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)-related hyperthermia. J Emerg Med 29(4):451–454. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.05.007
Pereira FC, Lourenco ES, Borges F, Morgadinho T, Ribeiro CF, Macedo TR, Ali SF (2006) Single or multiple injections of methamphetamine increased dopamine turnover but did not decrease tyrosine hydroxylase levels or cleave caspase-3 in caudate-putamen. Synapse 60(3):185–193. doi:10.1002/syn.20285
Pontes H, Sousa C, Silva R, Fernandes E, Carmo H, Remiao F, Carvalho F, Bastos ML (2008) Synergistic toxicity of ethanol and MDMA towards primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 254(1–2):42–50. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.09.009
Proskuryakov SY, Konoplyannikov AG, Gabai VL (2003) Necrosis: a specific form of programmed cell death? Exp Cell Res 283(1):1–16
Rajapakse N, Silva E, Scholze M, Kortenkamp A (2004) Deviation from additivity with estrogenic mixtures containing 4-nonylphenol and 4-tert-octylphenol detected in the E-SCREEN assay. Environ Sci Technol 38(23):6343–6352
Richter C, Schweizer M, Cossarizza A, Franceschi C (1996) Control of apoptosis by the cellular ATP level. FEBS Lett 378(2):107–110
Sano R, Hasuike T, Nakano M, Kominato Y, Itoh H (2009) A fatal case of myocardial damage due to misuse of the “designer drug” MDMA. Leg Med (Tokyo) 11(6):294–297. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.09.003
Scaduto RC Jr, Grotyohann LW (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76(1 Pt 1):469–477. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77214-0
Screaton GR, Singer M, Cairns HS, Thrasher A, Sarner M, Cohen SL (1992) Hyperpyrexia and rhabdomyolysis after MDMA (“ecstasy”) abuse. Lancet 339(8794):677–678
Shao X, Hu Z, Hu C, Bu Q, Yan G, Deng P, Lv L, Wu D, Deng Y, Zhao J, Zhu R, Li Y, Li H, Xu Y, Yang H, Zhao Y, Cen X (2012) Taurine protects methamphetamine-induced developmental angiogenesis defect through antioxidant mechanism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 260(3):260–270. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.03.003
Silva E, Kabil A, Kortenkamp A (2010) Cross-talk between non-genomic and genomic signalling pathways–distinct effect profiles of environmental estrogens. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245(2):160–170. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2010.02.015
Simantov R, Tauber M (1997) The abused drug MDMA (Ecstasy) induces programmed death of human serotonergic cells. FASEB J 11(2):141–146
Strobbe L, de Jaer CP, Louwerse ES, Rozendaal FW (2007) Fatal ecstasy intoxication in a 22-year-old man. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 151(30):1690–1694
Stumm G, Schlegel J, Schafer T, Wurz C, Mennel HD, Krieg JC, Vedder H (1999) Amphetamines induce apoptosis and regulation of bcl-x splice variants in neocortical neurons. FASEB J 13(9):1065–1072
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler M, Larochette N, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Siderovski DP, Penninger JM, Kroemer G (1999) Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397(6718):441–446. doi:10.1038/17135
Upreti VV, Moon KH, Yu LR, Lee IJ, Eddington ND, Ye X, Veenstra TD, Song BJ (2011) Increased oxidative-modifications of cytosolic proteins in 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy)-exposed rat liver. Proteomics 11(2):202–211. doi:10.1002/pmic.201000203
Vanden Eede H, Montenij LJ, Touw DJ, Norris EM (2012) Rhabdomyolysis in MDMA intoxication: a rapid and underestimated killer “Clean” ecstasy, a safe party drug? J Emerg Med 42(6):655–658. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.04.057
Verhagen AM, Vaux DL (2002) Cell death regulation by the mammalian IAP antagonist Diablo/Smac. Apoptosis 7(2):163–166
Warren MW, Larner SF, Kobeissy FH, Brezing CA, Jeung JA, Hayes RL, Gold MS, Wang KK (2007) Calpain and caspase proteolytic markers co-localize with rat cortical neurons after exposure to methamphetamine and MDMA. Acta Neuropathol 114(3):277–286. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0259-9
Wirth I, Correns A, Pragst F, Schmeling A (2007) Fatal MDMA-intoxication with postmortem diagnosis of hyperthermia. Arch Kriminol 220(5–6):141–151
Yin XM, Wang K, Gross A, Zhao Y, Zinkel S, Klocke B, Roth KA, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 400(6747):886–891. doi:10.1038/23730
Zamaraeva MV, Sabirov RZ, Maeno E, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Bessonova SV, Okada Y (2005) Cells die with increased cytosolic ATP during apoptosis: a bioluminescence study with intracellular luciferase. Cell Death Differ 12(11):1390–1397. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401661
Zhu JP, Xu W, Angulo JA (2005) Disparity in the temporal appearance of methamphetamine-induced apoptosis and depletion of dopamine terminal markers in the striatum of mice. Brain Res 1049(2):171–181. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.089
Acknowledgments
4-MTA hydrochloride (racemic mixture) was a kind gift from Dr. David Nichols (Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN). The authors would like to thank Prof. John Sumpter and Dr. Chris Parris (Brunel University, London) for assistance with the flow cytometry. Dr. Sibylle Ermler (University of Brunel, London) is gratefully acknowledged for insightful discussions and useful suggestions. Thanks are also due to Diogo Fernandes (University of Brunel, London) and Maria Riverso (UCL School of Pharmacy, University of London) for technical assistance with Western blotting methodology. This work was supported by the Portuguese Research Council Fundação para a Ciência e para a Tecnologia (FCT) [SFRH/BD/45617/2008 to D.D.S. and Pest-C/EQB/LA0006/2011] and cofounded by the European Community financial support Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade do Quadro de Referência Estratégico Nacional (QREN POFC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dias da Silva, D., Carmo, H., Lynch, A. et al. An insight into the hepatocellular death induced by amphetamines, individually and in combination: the involvement of necrosis and apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87, 2165–2185 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1082-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1082-9