Abstract
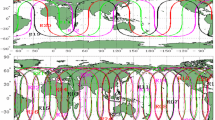
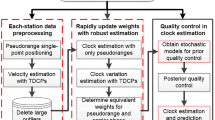
Real-time satellite orbit and clock product is a key prerequisite for real-time precise positioning service based on precise point positioning (PPP). With the rapid development of the multiple global navigation satellite systems (Multi-GNSS), about 120 satellites will be processed for Multi-GNSS real-time clock estimation. Unfortunately, the computation is very time-consuming, especially for quality control since problematic observations are inevitable. Taking advantage of computer technology, sequential least square adjustment with an adapted online quality control procedure is developed to rapidly estimate Multi-GNSS real-time clocks, although various filtering estimators are commonly used now. A globally distributed network including 70 stations tracking mostly satellites of GPS, GLONASS, BDS, and Galileo is employed for experimental validation. The results show that the computation time per epoch is less than 3 s in average and can meet the 5 s update rate of the IGS real-time clock product. Compared to the GeoForschungsZentrum MGEX (GBM) final clock product, the averaged STD values of the estimated clocks of the four GNSS systems are 0.089 ns and 0.153 ns, respectively, for the clock solutions with and without the online quality control, which also confirms the importance of the quality control procedure. The Multi-GNSS kinematic PPP experiment using the estimated clocks with quality control shows that the positioning RMS is about 4 cm and generally 2 cm in vertical and horizontal components, respectively, and the corresponding convergence time is about 15 min.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock H, Dach R, Jäggi A et al (2009) High-rate GPS clock corrections from CODE: support of 1 Hz applications. J Geod 83(11):1083–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0326-1
Boehm J, Niell A, Tregoning P et al (2006) Global Mapping Function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett 33(7):L07304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gl025546
Chen L, Zhao Q, Hu Z et al (2018) GNSS global real-time augmentation positioning: real-time precise satellite clock estimation, prototype system construction and performance analysis. Adv Space Res 61(1):367–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.08.037
Dach R, Schaer S, Hugentobler U (2006) Combined multi-system GNSS analysis for time and frequency transfer. In: Proceedings of the 20th European frequency and time forum EFTF06, Braunsehweig, Germany
Deng Z, Ge M, Uhlemann M et al (2014) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou satellites at GFZ. In: Proceedings of IGS workshop 2014, 23–27 June 2014, Pasadena, USA
Dilssner F, Springer T, Schonemann E et al (2014) Estimation of satellite antenna phase center corrections for BeiDou. In: Proceedings of IGS workshop 2014, 23–27 June 2014, Pasadena, USA
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0300-3
Elsobeiey M, Al-Harbi S (2016) Performance of real-time precise point positioning using IGS real-time service. GPS Solut 20(3):565–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0467-z
Ge M, Gendt G, Dick G et al (2006) A new data processing strategy for huge GNSS global networks. J Geod 80:119–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-006-0044-x
Ge M, Chen J, Douša J et al (2012) A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut 16(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0206-z
Gong X, Gu S, Lou Y et al (2017) An efficient solution of real-time data processing for Multi-GNSS network. J Geod 92(7):797–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1095-x
Hadas T, Bosy J (2015) IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut 19(1):93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0369-5
Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2009) Kalman-filter-based GPS clock estimation for near realtime positioning. GPS Solut 13(3):173–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-008-0110-3
Henderson HV, Searle SR (1981) On deriving the inverse of a sum of matrices. SIAM Rev 23:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1137/1023004
Hutsell ST (1996) Relating the Hadamard variance to MCS Kalman filter clock estimation. In: Proceedings of the 27th annual precise time and time interval (PTTI) meeting, pp 291–302
Johnston G, Riddell A, Hausler G (2017) The international GNSS service. In: Teunissen P, Montenbruck O (eds) Handbook of global navigation satellite systems. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42928-1
Kazmierski K, Sosnica K, Hadas T (2018) Quality assessment of multi-GNSS orbits and clocks for real-time precise point positioning. GPS Solut 22:11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0678-6
Laurichesse D, Cerri L, Berthias JP et al (2013) Real time precise GPS constellation and clocks estimation by means of a Kalman filter. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2013, September 16–20, 2013, Nashville, TN
Low T, van de Geijn R (2004) An API for manipulating matrices stored by blocks. FLAME Working Note #12 TR-2004-15, The University of Texas at Austin, Department of Computer Sciences
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Prange L et al (2017) The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59(7):1671–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.01.011
Petit G, Luzum B (2010) IERS conventions (2010), IERS Technical Note 36 (eds), Verlagdes Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, http://tai.bipm.org/iers/conv2010/
Quintana-Ortí G, Sun X, Bischof CH (1998) A BLAS-3 version of the QR factorization with column pivoting. SIAM J Sci Comput 19(5):1486–1494. https://doi.org/10.1137/s1064827595296732
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Loyer S et al (2015) Galileo orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS experiment. Adv Space Res 55(1):269–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.06.030
Tapley BD, Schutz BE, Born G (2004) Statistical orbit determination. Elsevier, San Diego
Teunissen PJG (1990) Quality control in integrated navigation systems. IEEE Aerosp Electron Syst Mag 5(7):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/62.134219
Teunissen PJG (1998) Quality control and GPS. In: Teunissen PJG, Kleusberg A (eds) GPS for geodesy, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 271–318
Teunissen PJG (2018) Distributional theory for the DIA method. J Geod 92:59–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1045-7
Wang N, Yuan Y, Li Z et al (2016) Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0867-4
Wu JT, Wu SC, Hajj GA et al (1993) Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr Geod 18(2):91–98
Yang Y, He H, Xu G (2001) Adaptively robust filtering for kinematic geodetic positioning. J Geod 75(2/3):109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900000157
Yang Y, Li J, Xu J et al (2011) Contribution of the Compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin Sci Bull 56(26):2813–2819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4627-4
Zhang X, Li X, Guo F (2011) Satellite clock estimation at 1 HZ for realtime kinematic PPP applications. GPS Solut 15(4):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-010-191-7
Zhang W, Lou Y, Gu S (2016) Joint estimation of GPS/BDS real-time clocks and initial results. GPS Solut 20(4):665–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0476-y
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC et al (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96jb03860
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by the scholarship program of China Scholarship Council (CSC), the Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41731066, 41774025), the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (Grant Nos. 310826165014, 310826171004, Chang’an University), and the Grand Projects of the Beidou-2 System (GFZX0301040308). We also thank the MGEX and GFZ for providing the data and products for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, W., Huang, G., Zhang, Q. et al. Multi-GNSS real-time clock estimation using sequential least square adjustment with online quality control. J Geod 93, 963–976 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1218-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1218-z