Abstract
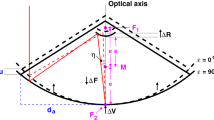
The impact of signal path variations (SPVs) caused by antenna gravitational deformations on geodetic very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) results is evaluated for the first time. Elevation-dependent models of SPV for Medicina and Noto (Italy) telescopes were derived from a combination of terrestrial surveying methods to account for gravitational deformations. After applying these models in geodetic VLBI data analysis, estimates of the antenna reference point positions are shifted upward by 8.9 and 6.7 mm, respectively. The impact on other parameters is negligible. To simulate the impact of antenna gravitational deformations on the entire VLBI network, lacking measurements for other telescopes, we rescaled the SPV models of Medicina and Noto for other antennas according to their size. The effects of the simulations are changes in VLBI heights in the range [−3, 73] mm and a net scale increase of 0.3–0.8 ppb. The height bias is larger than random errors of VLBI position estimates, implying the possibility of significant scale distortions related to antenna gravitational deformations. This demonstrates the need to precisely measure gravitational deformations of other VLBI telescopes, to derive their precise SPV models and to apply them in routine geodetic data analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbondanza C, Sarti P: Effects of illumination functions on the computation of gravity-dependent signal path variation models in primary focus and Cassegrainian VLBI telescopes. J Geodesy 84(8), 515–525 (2010). doi:10.1007/s00190-010-0389-z
Altamimi Z, Collilieux X, Legrand J, Garayt B, Boucher C: ITRF2005: a new release of the international terrestrial reference frame based on time series of station positions and earth orientation parameters. J Geophys Res 112, B09401 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JB004949
Baars JWM (2007) The paraboloidal reflector antenna in radio astronomy and communication, vol 348. Springer, New York, pp 370. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-69734-5, ISSN 0067-0057
Böckmann S, Artz T, Nothnagel A: VLBI terrestrial reference frame contributions to ITRF2008. J Geodesy 84(3), 201–219 (2010). doi:10.1007/s00190-009-0357-7
Carter E, Rogers AEE, Counselman CC, Shapiro II: Comparison of geodetic and radio interferometric measurements of the Haystack-Westford base line vector. J Geophys Res 85, 2685–2687 (1980)
Cha AG: Phase and frequency stability of Cassegrainian antennas. Radio Sci 22(1), 156–166 (1987)
Clark TA, Thomsen P (1988) Deformations in VLBI antennas. Tech. rep., 100696, NASA, Greenbelt, MD. http://www.ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19880009586_1988009586.pdf
Dawson J, Sarti P, Johnston G, Vittuari L: Indirect approach to invariant point determination for SLR and VLBI systems: an assessment. J Geodesy 81(6-8), 433–441 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0125-x
Gambis D, Biancale R, Carlucci T, Lemoine JM, Marty JC, Bourda G, Charlot P, Loyer S, Lalanne T, Soudarin L, Deleflie F (2009) Combination of earth orientation parameters and terrestrial frame at the observation level. In: Drewes H (ed) Geodetic reference frames, international association of geodesy symposia, Munich, October 9-14, 2006, Springer Series, vol 134, Springer, Berlin, pp 3–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00860-3_1
Gross R, Beutler G, Plag HP: Integrated scientific and societal user requirements and functional specifications for the GGOS chap 7, pp. 209–223. Springer, Berlin (2009). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02687-4
Orfei A, Morsiani M, Zacchiroli G, Maccaferri G, Roda J, Fiocchi F: An active surface for large reflector antennas. IEEE Antenn Propag M 46(4), 11–19 (2004). doi:10.1109/MAP.2004.1373995
Petrov L (2008) Introduction to VLBI Time Delay (VTD) package. http://astrogeo.org/vtd/vtd_01.html
Petrov L, Gordon D, Gipson J, MacMillan D, Ma C, Fomalont E, Walker RC, Carabajal C: Precise geodesy with the very long baseline array. J Geodesy 83(9), 859–876 (2009). doi:10.1007/s00190-009-0304-7
Ray J, Altamimi Z: Evaluation of co-locations ties relating the VLBI and GPS reference frames. J Geodesy 79(4–5), 189–195 (2005). doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0456-z
Richter B, Schwegmann W, Dick WR (eds) (2005) Proceedings of the IERS workshop on site co-location, IERS Technical Notes, vol 33, Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main. Matera, 23–24 October 2003, 148 pp. http://www.iers.org/MainDisp.csl?pid=46-25777
Sarti P, Sillard P, Vittuari L: Surveying co-located space geodetic instruments for ITRF computation. J Geodesy 78(3), 210–222 (2004). doi:10.1007/s00190-004-0387-0
Sarti P, Abbondanza C, Vittuari L: Gravity dependent signal path variation in a large VLBI telescope modelled with a combination of surveying methods. J Geodesy 83(11), 1115–1126 (2009). doi:10.1007/s00190-009-0331-4
Sarti P, Vittuari L, Abbondanza C: Laser scanner and terrestrial surveying applied to gravitational deformation monitoring of large VLBI telescopes’ primary reflector. J Surv Eng 135(4), 136–148 (2009). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000008
Schlüter W, Behrend D: The international VLBI service for geodesy and astrometry (IVS): current capabilities and future prospects. J Geodesy 81(6–8), 379–387 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0131-z
Selvadurai APS (2000) Partial differential equations in mechanics, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 698, ISBN: 3 540 67284 2
Sovers OJ, Fanselow JL, Jacobs CS: Astrometry and geodesy with radio interferometry: experiments, models, results. Rev Mod Phys 70(4), 1393–1454 (1998). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.70.1393
Tesmer V, Steigenberger P, Rothacher M, Boehm J, Meisel B (2009) Annual deformation signals from homogeneously reprocessed VLBI and GPS height time series. J Geodesy. doi:10.1007/s00190-009-0316-3.
Thaller D, Krügel M, Rothacher M, Tesmer V, Schmid R, Angermann D: Combined Earth orientation parameters based on homogeneous and continuous VLBI and GPS data. J Geodesy 81(6–8), 529–541 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0115-z
Vennebusch M, Böckmann S, Nothnagel A: The contribution of very long baseline interferometry to ITRF2005. J Geodesy 81(6–8), 553–564 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0117-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarti, P., Abbondanza, C., Petrov, L. et al. Height bias and scale effect induced by antenna gravitational deformations in geodetic VLBI data analysis. J Geod 85, 1–8 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0410-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0410-6