Abstract
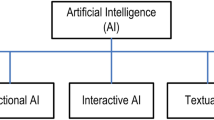
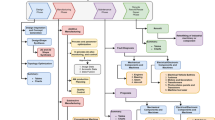
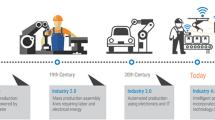
With the breakthroughs in artificial intelligence technology and the rapid development of intelligent manufacturing, industry and artificial intelligence (AI) are gradually being deeply integrated. On the basis of artificial intelligence, we systematically expounded the generation, definition, characteristics, classification, technical system, and current situation of industrial artificial intelligence (I-AI). Combining existing research and industrial projects, we propose a detailed framework and a reference model for I-AI in industry. The framework contains seven dimensions: objects of I-AI, domain of I-AI, application stages of I-AI, application requirements of I-AI, intelligent technology of I-AI, intelligent function of I-AI, and solutions of I-AI. Secondly, based on the application scenarios of artificial intelligence and industrial convergence, we propose a detailed overall planning for I-AI. Finally, five typical industrial fields are selected, and the I-AI solutions based on TFV (technology and function integration in industrial value chain) unit and 6W1H method are used for new application scenarios of the proposed framework. In addition, a detailed case of implementing for I-AI in port equipment industry is given. The research results of this paper have achieved good results in the related industrial field and can provide some reference for other industrial enterprises to plan, design, implement, and apply artificial intelligence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xuejiao T, Xiaofeng H, Yang L (2013) Overview of big data research. Journal of System Simulation. http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-xtfz2013s1035.htm
Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh Y (2006) A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 18(7):1527–1554 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7017915
Farid AM (2017) Measures of reconfigurability and its key characteristics in intelligent manufacturing systems. J Intell Manuf 28(2):353–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0983-7
Yang F, Zhang R, Yao Y, Yuan Y (2016) Locating the propagation source on complex networks with propagation centrality algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 100(C):112–123 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/297597666
Li H, Ota K, Dong M (2018) Learning IoT in edge: deep learning for the internet of things with edge computing. IEEE Netw 32(1):96–101 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322728184
Moor J (2006) The Dartmouth College artificial intelligence conference: the next fifty years. AI Mag 27(4):87–91 http://www.dartmouth.edu/~ai50/homepage.html
Hassler S (2016) Marvin Minsky and the pursuit of machine understanding - making machines-and people-think [spectral lines] IEEE Spectrum 53 (3):7–7. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296693726
Boyd AB, Crutchfield JP (2016) Maxwell Demon Dynamics: Deterministic Chaos, the Szilard Map, and the Intelligence of Thermodynamic Systems. Phys Rev Lett 116(19):190601 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278413864
Kuipers B, Feigenbaum EA, Hart PE, Nilsson NJ (2017) Shakey: from conception to history. AI Mag 38(1):88–103 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315737206
Zhuanng Y-t, Wu F, Chen C, Pan Y-h (2017) Challenges and opportunities: from big data to knowledge in AI2.0. Front Inform Tech El 18 (1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1601883
Li W, Wu WJ, Wang HM, Cheng XQ, Chen HJ, Zhou ZH, Ding R (2017) Crowd intelligence in AI 2.0 era. Frontiers of information technology. Electron Eng 18(1):15–43. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1601859
Peng Y-x, Zhu W-w, Zhao Y, Xu C-s, Huang Q-m, Lu H-q, Zheng Q-h (2017) Cross-media analysis and reasoning: advances and directions. Front Inform Tech El 18(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1601787
Zheng NN, Liu ZY, Ren PJ, Yong-Qiang MA, Chen ST, Si-Yu YU, Xue JR, Chen BD, Wang FY (2017) Hybrid-augmented intelligence: collaboration and cognition. Front Inform Tech El 18(2):153–179. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1700053
Liu W, Cheraghi SH (2006) A hybrid approach to nonconformance tracking and recovery. J Intell Manuf 17(1):149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-005-5518-9
Zhang T, Li Q, Zhang CS, Liang HW, Li P, Wang TM, Li S, Zhu YL, Wu C (2017) Current trends in the development of intelligent unmanned autonomous systems. Front Inform Tech El 18(1):68–85. https://doi.org/10.1631/2FFITEE.1601650
Chen T, Wang Y-C, Lin Z (2017) Predictive distant operation and virtual control of computer numerical control machines. J Intell Manuf 28(5):1061–1077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-1029-x https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10845-014-1029-x
York WW, Ekbia HR (2013) Slippage in cognition, perception, and action: from aesthetics to artificial intelligence. Beyond Artificial Intelligence: Contemplations, Expectations; Applications 4(1):27–47 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/302212164
Wagman BM (2019) Artificial intelligence and human cognition. Q Rev Biol 68(1) https://www.abc-clio.com/Praeger/product.aspx?pc=C2353C
Mazinan AH (2012) On the practice of artificial intelligence based predictive control scheme: a case study. Appl Intell 36(1):178–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-010-0253-0
Cook DJ, Varnell RC (2011) Adaptive parallel iterative deepening search. J Artif Intell Res 9(1):139–166 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51893578
Guo R, Palmerbrown D, Lee SW, Cai FF (2014) Intelligent diagnostic feedback for online multiple-choice questions. Artif Intell Rev 42(3):369–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-013-9419-6
Froese T, Ziemke T (2009) Enactive artificial intelligence: investigating the systemic organization of life and mind. Artif Intell 173(3):466–500 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220546367
Schölkopf B (2015) Artificial intelligence: learning to see and act. Nature 518(7540):486. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272837230–487
Stocker M (2016) Decision-making: be wary of ‘ethical’ artificial intelligence. Nature 540(7634):525–525 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311781254
Bryson J, Winfield A (2017) Standardizing ethical design for artificial intelligence and autonomous systems. Computer 50(5):116–119 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316898639
Goertzel B, Orseau L, Snaider J (2006) Artificial general intelligence. IEEE Trans Comput 10(3):295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/2F978-3-319-09274-4
Russell S (2017) Artificial intelligence: the future is superintelligent. Nature 548(7669):520–521 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319368099
Manju A, Nigam MJ (2014) Applications of quantum inspired computational intelligence: a survey. Artif Intell Rev 42(1):79–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-012-9330-6
Pentland A (1999) Perceptual intelligence. Commun ACM 43(3):74–88 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221568749
Cassimatis NL (2006) A cognitive substrate for achieving human-level intelligence. AI Mag 27(2):45–56 https://aaai.org/ojs/index.php/aimagazine/article/download/1879/1777
Beaulac CD, Larribe F (2017) Narrow artificial intelligence with machine learning for real time estimation of a mobile agent’s location using hidden Markov models. International Journal of Computer Games Technology 2017(2017-02-14). http://cn.arxiv.org/abs/1802.03417):1–10
Kuehnberger KU, Rudolph S, Wang P (2013) Report on the sixth conference on artificial general intelligence. AI Mag 34(4):123–125 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295572346
Davis E (2015) Ethical guidelines for a superintelligence. Artif Intell 220(C):121–124 https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2741446
Yang J, Kim E, Hur M, Cho S, Han M, Seo I (2018) Knowledge extraction and visualization of digital design process. Expert Syst Appl 92:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.002 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417417306036
Li YW, Jiang WF, Yang L, Wu T (2018) On neural networks and learning systems for business computing. Neurocomputing 275:1150–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.054 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231217315734
Anghel CI, Ozunu A (2006) Prediction of gaseous emissions from industrial stacks using an artificial intelligence method. Chem Pap 60(6):410–415. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-006-0075-z
Hokey M (2015) Genetic algorithm for supply chain modelling: basic concepts and applications. Int J Serv Oper Manag (Switzerland) 22(2):143–164 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220691204
Hu ZY, Yang JM, Zhao ZW, Sun H, Che HJ (2016) Multi-objective optimization of rolling schedules on aluminum hot tandem rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(1–4):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7909-1
Cupek R, Ziebinski A, Drewniak M, Fojcik M (2018) Improving KPI based performance analysis in discrete, multi-variant production. Intelligent Information and Database Systems 10th Asian Conference, ACIIDS 2018 Proceedings: LNAI 10752:661–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75420-8_62
Abellan-Nebot JV, Subiron FR (2010) A review of machining monitoring systems based on artificial intelligence process models. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(1–4):237–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2191-8
Mundada V, Narala SKR (2018) Optimization of milling operations using artificial neural networks (ANN) and simulated annealing algorithm (SAA). Materials Today-Proceedings 5(2):4971–4985 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/323990064
Ahmed AN, Noor CWM, Allawi MF, El-Shafie A (2018) RBF-NN-based model for prediction of weld bead geometry in shielded metal arc welding (SMAW). Neural Comput Applic 29(3):889–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2496-0
Gershwin SB (2018) The future of manufacturing systems engineering. Int J Prod Res 56(1–2):224–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1395491 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320903701
Wang HR, Chen HF, Fu GL, Xiao HP (2016) Relationship between grinding process and the parameters of subsurface damage based on the image processing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(9–12):1707–1715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7691-0
Xu K, Xu Y, Zhou P, Wang L (2018) Application of RNAMlet to surface defect identification of steels. Opt Lasers Eng 105:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.01.010 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325500736
Kang S (2018) On effectiveness of transfer learning approach for neural network-based virtual metrology modeling. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 31(1):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsm.2017.2787550 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322093298
Fernandes H, Zhang H, Figueiredo A, Malheiros F, Ignacio LH, Sfarra S, Ibarra-Castanedo C, Guimaraes G, Maldague X (2018) Machine learning and infrared thermography for fiber orientation assessment on randomly-oriented strands parts. Sensors 18(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010288 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322625184
Bai Y, Sun ZZ, Deng J, Li L, Long JY, Li C (2018) Manufacturing quality prediction using intelligent learning approaches: a comparative study. Sustainability 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010085 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322241384
Valluri A, North MJ, Macal CM (2009) Reinforcement learning in supply chains. Int J Neural Syst 19(5):331–344. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065709002063 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/38063993
Kaneko Y, Yada K (2016) A deep learning approach for the prediction of retail store sales. In: Domeniconi C, Gullo F, Bonchi F et al (eds) 2016 Ieee 16th international conference on data mining workshops. International conference on data mining workshops, pp 531–537. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdmw.2016.154 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313454339
Kesheng W, Yi W (2018) How AI affects the future predictive maintenance: a primer of deep learning. Advanced manufacturing and automation VII:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5768-7_1. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323107352
Mesloub H, Benchouia MT, Golea A, Golea N, Benbouzid MEH (2017) A comparative experimental study of direct torque control based on adaptive fuzzy logic controller and particle swarm optimization algorithms of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90(1–4):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9092-4
Chen T (2008) A SOM-FBPN-ensemble approach with error feedback to adjust classification for wafer-lot completion time prediction. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37(7–8):782–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1007-y
Chen TT, Tian XC (2014) An intelligent self-learning method for dimensional error pre-compensation in CNC grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 75(9–12):1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6249-x
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced Manufacturing Environment, Shanghai Research Center, for industrial Informatics (SRCI2).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 71632008), Transformation and Upgrading of Industry in 2017 (China Manufacturing 2025) (grant number ZL35060009002), and Innovation and Development of Industrial Internet in Shanghai of China (grant number 2017-GYHLW-01009). This research was funded by SJTU Innovation Center of Producer Service Development (SICPSD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ming, X., Liu, Z. et al. A reference framework and overall planning of industrial artificial intelligence (I-AI) for new application scenarios. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 101, 2367–2389 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3106-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3106-3