Abstract
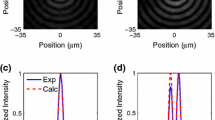
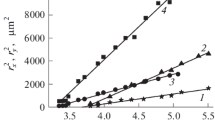
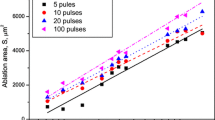
This study investigated ablation from a copper metal surface using a scanning femtosecond laser beam with a Gaussian beam profile. A method was developed herein to calculate the ablation profile with experimentally identified parameters (e.g., effective focused Gaussian incident beam radius, ablation threshold fluence, effective energy penetration depth). The results show the relationship between the maximum ablation depth and maximum ablation width. The calculated ablation profile agrees well with the experimental measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimov SI, Kapeliovich BL, Perel’man TL (1974) Electron emission from metal surfaces exposed to ultrashort laser pulses. J Exp Theor Phys 39:375–377
Nolte S, Momma C, Jacobs H, Tunnermann A, Chichkov BN, Wellegehausen B et al (1997) Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. Journal of the Optical Society of America B-Optical Physics 14:2716–2722
Yang J, Zhao Y, Zhu X (2007) Theoretical studies of ultrafast ablation of metal targets dominated by phase explosion. Applied Physics a-Materials Science & Processing 89:571–578
Wu B, Shin YC (2007) A simple model for high fluence ultra-short pulsed laser metal ablation. Appl Surf Sci 253:4079–4084
Byskov-Nielsen J, Savolainen J-M, Christensen MS, Balling P (May 2011) Ultra-short pulse laser ablation of copper, silver and tungsten: experimental data and two-temperature model simulations. Applied Physics a-Materials Science & Processing 103:447–453
Zhao X, Shin YC (2013) Femtosecond laser ablation of aluminum in vacuum and air at high laser intensity. Appl Surf Sci 283:94–99
Cheng CW, Wang SY, Chang KP, Chen JK (2016) Femtosecond laser ablation of copper at high laser fluence: modeling and experimental comparison. Appl Surf Sci 361:41–48
Wang SY, Ren Y, Cheng CW, Chen JK, Tzou DY (2013) Micromachining of copper by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl Surf Sci 265:302–308
J. P. Colombier, P. Combis, F. Bonneau, R. Le Harzic, and E. Audouard (2005) Hydrodynamic simulations of metal ablation by femtosecond laser irradiation. Phys Rev B, vol. 71
Hashida M, Semerok AF, Gobert O, Petite G, Izawa Y, Wagner JF (2002) Ablation threshold dependence on pulse duration for copper. Appl Surf Sci 197:862–867
Byskov-Nielsen J, Savolainen JM, Christensen MS, Balling P (2010) Ultra-short pulse laser ablation of metals: threshold fluence, incubation coefficient and ablation rates. Applied Physics a-Materials Science & Processing 101:97–101
Kirkwood SE, van Popta AC, Tsui YY, Fedosejevs R (2005) Single and multiple shot near-infrared femtosecond laser pulse ablation thresholds of copper. Applied Physics a-Materials Science & Processing 81:729–735
Mannion PT, Magee J, Coyne E, O'Connor GM, Glynn TJ (2004) The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl Surf Sci 233:275–287
Le Harzic R, Breitling D, Weikert M, Sommer S, Fohl C, Valette S et al (2005) Pulse width and energy influence on laser micromachining of metals in a range of 100 fs to 5 ps. Appl Surf Sci 249:322–331
Miyasaka Y, Hashida M, Nishii T, Inoue S, Sakabe S (2015) Derivation of effective penetration depth of femtosecond laser pulses in metal from ablation rate dependence on laser fluence, incidence angle, and polarization. Appl Phys Lett 106:013101
P. Gonzales, R. Bernath, J. Duncan, T. Olmstead, and M. Richardson (2004) Femtosecond ablation scaling for different materials, In Proceedings of SPIE. pp. 265–272
Cheng J, Perrie W, Sharp M, Edwardson SP, Semaltianos NG, Dearden G et al (2009) Single-pulse drilling study on Au, Al and Ti alloy by using a picosecond laser. Applied Physics a-Materials Science & Processing 95:739–746
Wang SY, Ren Y, Chang KP, Cheng CW, Chen JK, Tzou DY (2014) Ablation of copper by a single ultrashort laser pulse. Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 9:88–92
Liu JM (1982) Simple technique for measurements of pulsed Gaussian-beam spot sizes. Opt Lett 7:196–198
Cheng CW, Tsai XZ, Chen JS (2016) Micromachining of stainless steel with controllable ablation depth using femtosecond laser pulses. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85:1947–1954
Byskov-Nielsen J, Savolainen J-M, Christensen M, Balling P (2010) Ultra-short pulse laser ablation of metals: threshold fluence, incubation coefficient and ablation rates. Applied Physics A 101:97–101
Sun Z, Lenzner M, Rudolph W (2015) Generic incubation law for laser damage and ablation thresholds. J Appl Phys 117:073102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C.W. Ablation of copper by a scanning Gaussian beam of a femtosecond laser pulse. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 151–156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0101-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0101-z