Abstract
Purpose
Although a tourniquet can effectively control intraoperative blood loss and offer clear surgical field in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), its optimal usage has been controversial. The aim of this research was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare and explore the best application of a tourniquet in TKA.
Methods
MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, Wanfang database, and Web of Science were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the four different strategies of tourniquet application in TKA. In Group I, a tourniquet was not used and was called the non-tourniquet (NT) group. In Group II, a tourniquet was only used during the cementation of implants and was called the specific duration tourniquet (SDT) group. In Group III, the tourniquet was only released before wound closure to control the bleeding sources and was called the majority duration tourniquet (MDT) group. In Group IV, a tourniquet was used throughout the procedure, from skin incision to wound closure and was called the whole duration tourniquet (WDT) group.
Results
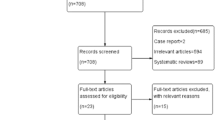
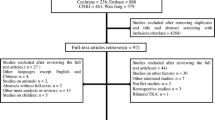
Forty-six RCTs were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. In a comparison between the NT and WDT groups (25 RCTs), intraoperative blood loss (IBL) (P = 0.0001) and range of motion (ROM) (P = 0.0001) were significantly increased in the NT group, while the visual analog score (VAS) (P = 0.0001), rate of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) (P = 0.01), and all complications (AC) (P = 0.0001) were significantly decreased in the NT group. In a comparison between the SDT and WDT groups (10 RCTs), IBL (P = 0.0001), TBL (P = 0.009), and ROM (P = 0.0001) were significantly increased in the SDT group, while thigh pain (P = 0.04) and the rate of DVT (P = 0.03) were significantly decreased in the SDT group. There were no significant differences between the MDT and WDT groups (12 RCTs) except for the rate of all complications (P = 0.01).
Conclusion
Despite the decrease in IBL with a tourniquet, no difference was found in TBL. In conclusion, not using a tourniquet or only using it during the cementation of implants was preferable based on the faster functional recovery, lower rate of DVTs and complications compared with using a tourniquet throughout the TKA procedure.
Level of evidence
I.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, Abbate R, Fedi S, Falciani M (2000) Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 371:169–177
Alcelik I, Pollock RD, Sukeik M, Bettany-Saltikov J, Armstrong PM, Fismer P (2012) A comparison of outcomes with and without a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplast 27:331–340
Alexandersson M, Wang EY, Eriksson S (2018) A small difference in recovery between total knee arthroplasty with and without tourniquet use the first 3 months after surgery: a randomized controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5196-8
Abdel-Salam A, Eyres KS (1995) Effects of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Jt Surg 77:250–253
Bao HX, Wang JF, Cai YH, Chu XB, Lv C, Tong PJ (2011) Tourniquet ischemia reperfusion injury after total knee arthroplasty in clinical research. Chin J Orthop Trauma 13:242–246
Li B, Qian Q-R, Hai-Shan W, Zhao H, Ling X-B, Zhu J, Wen J-F (2008) The use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. Zhonghua wai ke za zhi 46:1054–1057
Steffin B, Green-Riviere E, Giori NJ (2009) Timing of tourniquet release in total knee arthroplasty when using a postoperative blood salvage drain. J Arthroplast 24:539–542
Burkart BC, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Kirk PG, Nott L (1994) The efficacy of tourniquet release in blood conservation after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:147–152
Chen S, Li J, Peng H, Zhou J, Fang H, Zheng H (2014) The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 38:355–359
Christodoulou AG, Ploumis AL, Terzidis IP, Chantzidis P, Metsovitis SR, Nikiforos DG (2004) The role of timing of tourniquet release and cementing on perioperative blood loss in total knee replacement. Knee 11:313–317
Ejaz A, Laursen AC, Kappel A, Laursen MB, Jakobsen T, Rasmussen S et al (2014) Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 85:422–426
Vandenbussche E, Duranthon L-D, Couturier M, Pidhorz L, Augereau B (2002) The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 26:306–309
Thorey F, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Windhagen H, Joachim C (2008) The effect of tourniquet release timing on perioperative blood loss in simultaneous bilateral cemented total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Technol Health Care 16:85–92
Fan Y, Jin J, Sun Z, Li W, Lin J, Weng X et al (2014) The limited use of a tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee 21:1263–1268
Fu-Jiang Zhang Yu, Xiao Y-BL, Tian X, Gao Z-G (2010) Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss. Chin Med J 123:3030–3033
Matziolis G, Drahn T, Schroder JH, Krocker D, Tuischer J, Perka C (2005) Endothelin-1 is secreted after total knee arthroplasty regardless of the use of a tourniquet. J Orthop Res 23:392–396
Hakkalamani S, Clark V, Pradhan N (2015) Short versus standard duration tourniquet use during total knee replacement: a pilot study. Acta Orthop Belg 81:52–56
Harsten A, Bandholm T, Kehlet H, Toksvig-Larsen S (2015) Tourniquet versus no tourniquet on knee-extension strength early after fast-track total knee arthroplasty; a randomized controlled trial. Knee 22:126–130
Hartling L, Ospina M, Liang Y, Dryden DM, Hooton N, Krebs Seida J, Klassen TP (2009) Risk of bias versus quality assessment of randomised controlled trials: cross sectional study. BMJ 339:b4012
Hernández-Castaños DM, Ponce VV, Gil F (2008) Release of ischaemia prior to wound closure in total knee arthroplasty: a better method? Int Orthop 32:635–638
Hersekli MA, Akpinar S, Ozkoc G, Ozalay M, Uysal M, Cesur N, Tandogan RN (2004) The timing of tourniquet release and its influence on blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 28:138–141
Huang Z, Xie X, Li L, Huang Q, Ma J, Shen B et al (2017) Intravenous and topical tranexamic acid alone are superior to tourniquet use for primary total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Jt Surg Am 99:2053–2061
Ishii Y, Matsuda Y (2005) Effect of the timing of tourniquet release on perioperative blood loss associated with cementless total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplast 20:977–983
Barwell J, Erson G, Hassan A, Rawlings I (1997) The effects of early tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study. J Bone Jt Surg Br 79:265–268
Jawhar A, Stetzelberger V, Kollowa K, Obertacke U (2018) Tourniquet application does not affect the periprosthetic bone cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5330-7
Jiang FZ, Zhong HM, Hong YC, Zhao GF (2015) Use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Sci 20:110–123
Jorn LP, Lindstrand A, Toksvig-Larsen S (1999) Tourniquet release for hemostasis increases bleeding. A randomized study of 77 knee replacements. Acta Orthop Scand 70:265–267
Kageyama K, Nakajima Y, Shibasaki M, Hashimoto S, Mizobe T (2007) Increased platelet, leukocyte, and endothelial cell activity are associated with increased coagulability in patients after total knee arthroplasty. J Thromb Haemost 5:738–745
Kato N, Nakanishi K, Yoshino S, Ogawa R (2002) Abnormal echogenic findings detected by transesophageal echocardiography and cardiorespiratory impairment during total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Anesthesiology 97:1123–1128
Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, Svensen CH, Ivaskevicius J, Mazunaitis J et al (2013) A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2790–2799
Larsson J, Lewis DH, Liljedahl SO, Löfström JB (1977) Early biochemical and hemodynamic changes after operation in a bloodless field. Eur Surg Res 9:311–320
Ledin H, Aspenberg P, Good L (2012) Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop 83:499–503
Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, Qian Q, Lin X, Zhao H (2009) The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 33:1263–1268
Li X, Yin L, Chen ZY, Zhu L, Wang HL, Chen W et al (2014) The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: grading the evidence through an updated meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24:973–986
Liu D, Graham D, Gillies K, Gillies RM (2014) Effects of tourniquet use on quadriceps function and pain in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res 26:207–213
Leão MGDS, Souza HAPD, Ferreira YMC (2013) Evaluation of blood loss after early or late release of ischemia in patients undergoing total knee replacement. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia (English Edition) 48:152–158
Mittal R, Ko V, Adie S, Naylor J, Dave J, Dave C et al (2012) Tourniquet application only during cement fixation in total knee arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. ANZ J Surg 82:428–433
Mori N, Kimura S, Onodera T, Iwasaki N, Nakagawa I, Masuda T (2016) Use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty increases the risk of distal deep vein thrombosis: a prospective, randomized study. Knee 23:887–889
Ozkunt O, Sariyilmaz K, Gemalmaz HC, Dikici F (2018) The effect of tourniquet usage on cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study of 3 methods. Medicine (Baltimore) 97:e9668
Pfitzner T, von Roth P, Voerkelius N, Mayr H, Perka C, Hube R (2016) Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:96–101
Schnettler T, Papillon N, Rees H (2017) Use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty causes a paradoxical increase in total blood loss. J Bone Jt Surg Am 99:1331–1336
Schuh A, Hausel M, Salminen S (2003) Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Zentralbl Chir 128:866–870
Sherman OH, Fox JM, Snyder SJ, Del Pizzo W, Friedman MJ, Ferkel RD, Lawley MJ (1986) Arthroscopy–”no-problem surgery”. An analysis of complications in two thousand six hundred and forty cases. J Bone Jt Surg Am 68:256–265
Shimoyama Y, Sawai T, Tatsumi S, Nakahira J, Oka M, Nakajima M, Jotoku T, Minami T (2012) Perioperative risk factors for deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Anesth 24:531–536
Smith TO, Hing CB (2010) Is a tourniquet beneficial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee 17:141–147
Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, Lin CJ, Yang CY (2012) Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Jt Surg Am 94:2209–2215
Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM, Chang CW, Lai KA, Yang CY (2011) Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:1121–1130
Tarwala R, Dorr LD, Gilbert PK, Wan Z, Long WT (2014) Tourniquet use during cementation only during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:169–174
Tetro AM, Rudan JF (2001) The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 44:33–38
Tie K, Hu D, Qi Y, Wang H, Chen L (2016) Effects of tourniquet release on total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics 39:e642–e650
Vaishya R, Agarwal AK, Vijay V, Tiwari MK (2018) Short term outcomes of long duration versus short duration tourniquet in primary total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma 9:46–50
Wang C, Zhou C, Qu H, Yan S, Pan Z (2018) Comparison of tourniquet application only during cementation and long-duration tourniquet application in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 13:216
Wang K, Ni S, Li Z, Zhong Q, Li R, Li H et al (2017) The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:2849–2857
Wauke K, Nagashima M, Kato N, Ogawa R, Yoshino S (2002) Comparative study between thromboembolism and total knee arthroplasty with or without tourniquet in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122:442–446
Widman J, Isacson J (1999) Surgical hemostasis after tourniquet release does not reduce blood loss in knee replacement. A prospective randomized study of 81 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 70:268–270
Worland RL, Arredondo J, Angles F, Lopez-Jimenez F, Jessup DE (1997) Thigh pain following tourniquet application in simultaneous bilateral total knee replacement arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 12:848–852
Yavarikia A, Amjad GG, Davoudpour K (2010) The influence of tourniquet use and timing of its release on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Pak J Biol Sci 13:249–252
Yi S, Tan J, Chen C, Chen H, Huang W (2014) The use of pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:1469–1476
Zan PF, Yang Y, Fu D, Yu X, Li GD (2015) Releasing of tourniquet before wound closure or not in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplast 30:31–37
Zhang W, Li N, Chen S, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Chen L (2014) The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 9:13
Zhang W, Liu A, Hu D, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Pan Z (2014) Effects of the timing of tourniquet release in cemented total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res 9:125
Zhang Y, Li D, Liu P, Wang X, Li M (2017) Effects of different methods of using pneumatic tourniquet in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomized control trial. Ir J Med Sci 186:953–959
Zhang Y, Qian QR, Wu HS, Liu HB, Li XH, Wu YL et al (2009) Effect of tourniquet on deep venous thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Chin J Orthop 29:910–914
Zhou K, Ling T, Wang H, Zhou Z, Shen B, Yang J et al (2017) Influence of tourniquet use in primary total knee arthroplasty with drainage: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res 12:172
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Zhen-ru Wu in Laboratory of Pathology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University for help with Picture making and English polishing.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Yuan Liu, Author Haibo Si, Author Yi Zeng, Author Mingyang Li, and Author Huiqi Xie declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not necessary for this review article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Si, H., Zeng, Y. et al. More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28, 1842–1860 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05617-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05617-w