Abstract
Purpose
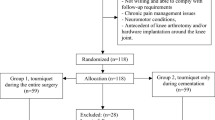
Tourniquets are still widely used in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), although they may be associated with several adverse effects. An observer-blinded, randomized, controlled trial was performed to evaluate the effects of tourniquet use in TKA.
Methods
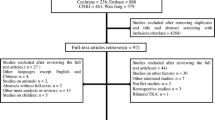
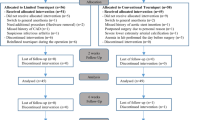
Fifty participants who underwent staged bilateral TKA were recruited for this study. The first-side TKA was randomly allocated to either long-duration tourniquet use or short-duration tourniquet use followed by a 3-month washout period and crossover to the other tourniquet strategy for the opposite-side TKA. Blood loss was monitored perioperatively. The operating time, allogeneic blood transfusion rate, thigh pain, knee pain, limb swelling, clinical outcome as measured by the Likert-type Western Ontario and McMaster University (WOMAC) score, straight leg raising and knee active range of motion (ROM) were also recorded.
Results
The long-duration tourniquet group exhibited reduced total blood loss [−99.1 ml, 95 % confidence interval (CI) −168.1 to −30.1, P = 0.0411] and intraoperative blood loss (−225.2 ml, 95 % CI −369.5 to −80.9, P = 0.0071) compared with the short-duration tourniquet group. However, there were greater postoperative blood loss (69.6 ml, 95 % CI 21.1 to 118.2, P = 0.0282) and hidden blood loss (52.8 ml, 95 % CI 10.5 to 95.1, P = 0.0332) in the long-duration tourniquet group. The short-duration tourniquet group showed better outcomes for thigh and knee pain, limb swelling, WOMAC score at 6-week follow-up, straight leg raising and knee ROM. Similar allogeneic blood transfusion rates were observed for both groups.
Conclusion
Total and intraoperative blood losses were reduced with the long-duration tourniquet use, whereas the short-duration tourniquet use would reduce postoperative and hidden blood losses without increasing the allogeneic blood transfusion rate. In addition, short-duration tourniquet use would result in faster recovery and less pain during the early rehabilitation period following TKA.
Level of evidence
I.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, Abbate R, Fedi S, Falciani M (2000) Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 371:169–177
Alcelik I, Pollock RD, Sukeik M, Bettany-Saltikov J, Armstrong PM, Fismer P (2012) A comparison of outcomes with and without a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplasty 27(3):331–340
Burg A, Dudkiewicz I, Heller S, Salai M, Velkes S (2009) The effects of using a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a study of 77 patients. J Musculoskelet Res 12(03):137–142
Butt U, Ahmad R, Aspros D, Bannister GC (2011) Factors affecting wound ooze in total knee replacement. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 93(1):54–56
Dennis DA, Kittelson AJ, Yang CC, Miner TM, Kim RH, Stevens-Lapsley JE (2015) Does tourniquet use in TKA affect recovery of lower extremity strength and function? A randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. doi:10.1007/s11999-015-4393-8
Ejaz A, Laursen AC, Kappel A, Laursen MB, Jakobsen T, Rasmussen S, Nielsen PT (2014) Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 85(4):422–426
Fukuda A, Hasegawa M, Kato K, Shi D, Sudo A, Uchida A (2007) Effect of tourniquet application on deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(8):671–675
Gross JB (1983) Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology 58(3):277–280
Hernandez AJ, Almeida AM, Favaro E, Sguizzato GT (2012) The influence of tourniquet use and operative time on the incidence of deep vein thrombosis in total knee arthroplasty. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67(9):1053–1057
Horlocker TT, Hebl JR, Gali B, Jankowski CJ, Burkle CM, Berry DJ, Zepeda FA, Stevens SR, Schroeder DR (2006) Anesthetic, patient, and surgical risk factors for neurologic complications after prolonged total tourniquet time during total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg 102(3):950–955
Husted H, Toftgaard Jensen T (2005) Influence of the pneumatic tourniquet on patella tracking in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study in 100 patients. J Arthroplasty 20(6):694–697
Katsumata S, Nagashima M, Kato K, Tachihara A, Wauke K, Saito S, Jin E, Kawanami O, Ogawa R, Yoshino S (2005) Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis marker and neutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty and the influence of neutrophil elastase on thromboembolism. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 49(4):510–516
Komatsu T, Ishibashi Y, Otsuka H, Nagao A, Toh S (2003) The effect of surgical approaches and tourniquet application on patellofemoral tracking in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18(3):308–312
Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, Svensen CH, Ivaskevicius J, Mazunaitis J, Marmaite U, Andrijauskas P (2013) A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(12):2790–2799
Ledin H, Aspenberg P, Good L (2012) Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop 83(5):499–503
Li B, Wen Y, Liu D, Tian L (2012) The effect of knee position on blood loss and range of motion following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(3):594–599
Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, Qian Q, Lin X, Zhao H (2009) The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 33(5):1263–1268
Liu D, Gillies RM, Gillies K, Graham D (2012) Effect of tourniquet use on quadriceps in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 94(Suppl 23):94
Lohmann-Jensen R, Holsgaard-Larsen A, Emmeluth C, Overgaard S, Jensen C (2014) The efficacy of tourniquet assisted total knee arthroplasty on patient-reported and performance-based physical function: a randomized controlled trial protocol. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:110
Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR, Mallory TH, Dodds KL, Adams JB (2003) The relationship of lateral release and tourniquet deflation in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 16(4):209–214
Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T (1962) Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery 51(2):224–232
Olivecrona C, Blomfeldt R, Ponzer S, Stanford BR, Nilsson BY (2013) Tourniquet cuff pressure and nerve injury in knee arthroplasty in a bloodless field: a neurophysiological study. Acta Orthop 84(2):159–164
Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH (2000) How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee 7(3):151–155
Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH (2004) Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(4):561–565
Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, Lin CJ, Yang CY (2012) Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(24):2209–2215
Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM, Chang CW, Lai KA, Yang CY (2011) Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1121–1130
Tamvakopoulos GS, Toms AP, Glasgow M (2005) Subcutaneous thigh fat necrosis as a result of tourniquet control during total knee arthroplasty. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 87(5):W11–W13
Tetro AM, Rudan JF (2001) The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 44(1):33–38
Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, Pidhorz L, Augereau B (2002) The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 26(5):306–309
Xie F, Li SC, Goeree R, Tarride JE, O’Reilly D, Lo NN, Yeo SJ, Yang KY, Thumboo J (2008) Validation of Chinese Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) in patients scheduled for total knee replacement. Qual Life Res 17(4):595–601
Zhang W, Li N, Chen S, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Chen L (2014) The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 9(1):13
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Guangshan Sui MS, Ke Yuan MS, and Jiebing Li MS for their assistance with inpatient testing; Bin Wang Ph.D., for assistance with study coordination, including the randomization of participants and the statistical analysis; and Yuankun Xu Ph.D., for assistance with labVIEW programming. This study was supported by Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Funds (Project No. RDC2013-06). Zhichang Li MD was in charge of this Hospital Fund programme and made a contribution similar to the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Ni, S., Li, Z. et al. The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 2849–2857 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3964-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3964-2