Abstract
Background
The goal of this work was to investigate the effects of different methods of using pneumatic tourniquet on reducing blood loss in patients undergoing cemented total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods
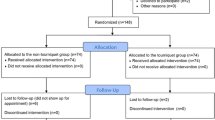
One hundred and fifty patients undergoing unilateral cemented TKA were randomly divided into three groups (50 patients per group). The tourniquet was used during the entire operation (Group A), used from the beginning of operation to the completion of joint replacement (Group B), and from the beginning of osteotomy to the completion of arthroplasty (Group C). The following parameters were recorded: intraoperative blood loss (IBL), postoperative blood loss (PBL), hidden blood loss (HBL), and total blood loss (TBL); operation time and tourniquet time; incidence of postoperative complications; and hospital for special surgery (HSS) score.
Results
IBL, HBL, and TBL in group C was significantly less than that in group B (all P < 0.05). Tourniquet time in group C was significantly less than that in groups A and B (all P < 0.05). The incidence of tourniquet-related complications in group C (6%) was relatively lower than that in group A (10%) during hospitalization (P > 0.05). Post-operative HSS scores at 2 weeks after the operation in group C was significantly higher than that in group A and group B (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that using a tourniquet from the beginning of osteotomy to the completion of arthroplasty could significantly reduce TBL in TKA, and decrease the incidence of complications; thereby facilitating early post-operative functional recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao FQ, Li ZJ, Zhang K, Liu YQ, Tian H, Liu Y, Liu ZJ (2011) Impact factors for hidden blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 49(5):419–423
Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM, Chang CW, Lai KA, Yang CY (2011) Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1121–1130. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1342-7
Yi S, Tan J, Chen C, Chen H, Huang W (2014) The use of pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134(10):1469–1476. doi:10.1007/s00402-014-2056-y
Matsuda K, Nozawa M, Katsube S, Maezawa K, Kurosawa H (2009) Reinfusion of unwashed salvaged blood after total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop 33(6):1615–1618. doi:10.1007/s00264-008-0661-5
Zhang FJ, Xiao Y, Liu YB, Tian X, Gao ZG (2010) Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss. Chin Med J (Engl) 123(21):3030–3033
Anderson LA, Engel GM, Bruckner JD, Stoddard GJ, Peters CL (2009) Reduced blood loss after total knee arthroplasty with local injection of bupivacaine and epinephrine. J Knee Surg 22(2):130–136
Erskine JG, Fraser C, Simpson R, Protheroe K, Walker ID (1981) Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coll Surg Edinb 26(5):295–297
Zhang H, Chen J, Chen F, Que W (2012) The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and use of blood products in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(9):1742–1752. doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1754-z
Tarwala R, Dorr LD, Gilbert PK, Wan Z, Long WT (2014) Tourniquet use during cementation only during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(1):169–174. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3124-2
Zhang W, Liu A, Hu D, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Pan Z (2014) Effects of the timing of tourniquet release in cemented total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res 9:125. doi:10.1186/s13018-014-0125-0
Horlocker TT, Hebl JR, Gali B, Jankowski CJ, Burkle CM, Berry DJ, Zepeda FA, Stevens SR, Schroeder DR (2006) Anesthetic, patient, and surgical risk factors for neurologic complications after prolonged total tourniquet time during total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg 102(3):950–955. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000194875.05587.7e
Kumar SN, Chapman JA, Rawlins I (1998) Vascular injuries in total knee arthroplasty. A review of the problem with special reference to the possible effects of the tourniquet. J Arthroplasty 13(2):211–216
Clarke MT, Longstaff L, Edwards D, Rushton N (2001) Tourniquet-induced wound hypoxia after total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Br 83(1):40–44
Saunders KC, Louis DL, Weingarden SI, Waylonis GW (1979) Effect of tourniquet time on postoperative quadriceps function. Clin Orthop Relat Res 143:194–199
Tetro AM, Rudan JF (2001) The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 44(1):33–38
Fan Y, Jin J, Sun Z, Li W, Lin J, Weng X, Qiu G (2014) The limited use of a tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee 21(6):1263–1268. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2014.08.002
Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH (2000) How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?. Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee 7(3):151–155
Gross JB (1983) Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology 58(3):277–280
Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T (1962) Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery 51(2):224–232
Ward C, Meathe E, Benumof J, Trousdale F (1980) A computer nomogram for blood loss replacement. Anesthesiology 53(3 Suppl):S126
Odinsson A, Finsen V (2006) Tourniquet use and its complications in Norway. J Bone Jt Surg Br 88(8):1090–1092. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.88B8.17668
Huang CH, Wang MJ, Chen TL, Huang HH, Hsu HW, Susetio L, Liu CC (1996) Blood and central venous pressure responses after serial tourniquet deflation during bilateral total knee replacement. J Formos Med Assoc 95(6):496–499
Husted H, Toftgaard Jensen T (2005) Influence of the pneumatic tourniquet on patella tracking in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study in 100 patients. J Arthroplast 20(6):694–697. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2004.11.016
Heinrich HC (1978) Demonstration and quantification of occult fecal blood loss. Critical evaluation of chemical and nuclear medicine technics. Med Klin 73(34):1163–1169
Markov AK (1986) Hemodynamics and metabolic effects of fructose 1-6 diphosphate in ischemia and shock—experimental and clinical observations. Ann Emerg Med 15(12):1470–1477
Sinclair KC, Clarke HD, Noble BN (2009) Blood management in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of techniques. Orthopedics 32(1):19
Rao VK, Dyga R, Bartels C, Waters JH (2012) A cost study of postoperative cell salvage in the setting of elective primary hip and knee arthroplasty. Transfusion 52(8):1750–1760. doi:10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03531.x
Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD (2012) Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 94(13):1153–1159. doi:10.2106/JBJS.K.00873
Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH (2004) Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Jt Surg Br 86(4):561–565
Healy WL, Della Valle CJ, Iorio R, Berend KR, Cushner FD, Dalury DF, Lonner JH (2013) Complications of total knee arthroplasty: standardized list and definitions of the Knee Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(1):215–220. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2489-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest
The authors Yuankai Zhang, Deqiang Li, Peilai Liu, Xing Wang, and Ming Li declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethical committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University and was in accordance with the Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, D., Liu, P. et al. Effects of different methods of using pneumatic tourniquet in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomized control trial. Ir J Med Sci 186, 953–959 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-017-1585-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-017-1585-0