Abstract
Purpose
The design of the trochlear compartment is crucial in patellofemoral arthroplasty (PFA), because 78 % of patients with isolated patellofemoral arthritis present concomitant trochlear dysplasia with patellar maltracking and therefore remain predisposed to post-operative patellar subluxation and dislocation. The study investigated whether current PFA implants are designed with anatomic trochlear parameters such as the sulcus angle, lateral facet height and groove orientation.
Methods
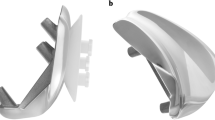
Five trochlear components of commercially available PFA implants were scanned, and the generated three-dimensional surfaces were measured using engineering design software. The mediolateral trochlear profiles were plotted at various flexion angles (0°, 15°, 30° and 45°) to deduce the following variables: sulcus angle, height of lateral facet and trochlear groove orientation.
Results
Four specimens had sulcus angle >144° in the 45° of flexion, and all five specimens had sulcus angle >143° in 30° of flexion. Three specimens had a facet <5 mm high through the entire range of early flexion (0°–30°), and two specimens had a facet <5 mm high beyond early flexion (30°–45°). The trochlear groove was oriented laterally in all specimens (range 1.6°–13.5°).
Conclusion
Current PFA trochlear components are not always designed with anatomic parameters, and some models exhibit characteristics of trochlear dysplasia. Surgeons are therefore advised to implant components with a deep sulcus, particularly in patients with history of patellofemoral disorders, and to adapt the surgical technique and extensor mechanism if the component implanted has a shallow sulcus, to ensure normal patellar tracking.
Level of evidence
III.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanslik L (1971) Patellofemoral sliding bearing in total knee prosthesis. Preliminary report on the implantation of a modified McKeever endoprosthesis combined with Young’s alloarthroplasty. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 109(3):435–440
Hanslik L (1973) Technic of implantation for the McKeever patella endoprosthesis using a new forceps instrumentarium. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 111(1):103–105
Hanslik L, Scholz J (1978) Retropatellar facet replacement using the McKeever patellar prosthesis (author’s transl). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 116(1):7–19
McKeever DC (1955) Patellar prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 37-A(5):1074–1084
Blazina ME, Fox JM, Del Pizzo W, Broukhim B, Ivey FM (1979) Patellofemoral replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 144:98–102
Lubinus HH (1979) Patella glide bearing total replacement. Orthopedics 2:119–127
Amis AA, Senavongse W, Darcy P (2005) Biomechanics of patellofemoral joint prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:20–29
Dy CJ, Franco N, Ma Y, Mazumdar M, McCarthy MM, Gonzalez Della Valle A (2012) Complications after patello-femoral versus total knee replacement in the treatment of isolated patello-femoral osteoarthritis. A meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(11):2174–2190
Lonner JH (2008) Patellofemoral arthroplasty: the impact of design on outcomes. Orthop Clin N Am 39(3):347–354
Lonner JH (2010) Patellofemoral arthroplasty. Orthopedics 33(9):653
Mont MA, Johnson AJ, Naziri Q, Kolisek FR, Leadbetter WB (2012) Patellofemoral arthroplasty: 7-year mean follow-up. J Arthroplasty 27(3):358–361
Lustig S, Magnussen RA, Dahm DL, Parker D (2012) Patellofemoral arthroplasty, where are we today? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(7):1216–1226
Monk AP, van Duren BH, Pandit H, Shakespeare D, Murray DW, Gill HS (2011) In vivo sagittal plane kinematics of the FPV patellofemoral replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(6):1104–1109
Leadbetter WB, Kolisek FR, Levitt RL, Brooker AF, Zietz P, Marker DR, Bonutti PM, Mont MA (2009) Patellofemoral arthroplasty: a multi-centre study with minimum 2-year follow-up. Int Orthop 33(6):1597–1601
Lonner JH (2007) Patellofemoral arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15(8):495–506
Lonner JH (2004) Patellofemoral arthroplasty: pros, cons, and design considerations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:158–165
Sisto DJ, Sarin VK (2008) Patellofemoral arthroplasty with a customized trochlear prosthesis. Orthop Clin N Am 39(3):355–362
Merchant AC (1997) Femoral sulcus angle measurements. Am J Orthop 26(12):820–822
Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, Cool CR (1974) Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg Am 56(7):1391–1396
Brattström H (1964) Shape of the intercondylar groove normally and in recurrent dislocation of patella. A clinical and X-ray-anatomical investigation. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 68:1–148
Mulligan ME, Jones ED Jr (1997) Femoral sulcus angle measurements. Am J Orthop 26(8):541–543
Tecklenburg K, Dejour D, Hoser C, Fink C (2006) Bony and cartilaginous anatomy of the patellofemoral joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14(3):235–240
Davies AP, Costa ML, Shepstone L, Glasgow MM, Donell S (2000) The sulcus angle and malalignment of the extensor mechanism of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82(8):1162–1166
Shih YF, Bull AM, Amis AA (2004) The cartilaginous and osseous geometry of the femoral trochlear groove. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12(4):300–306
Dejour D, Ntagiopoulos PG, Saffarini M (2012) Evidence of trochlear dysplasia in femoral component designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-2268-z
Merchant AC (2005) A modular prosthesis for patellofemoral arthroplasty: design and initial results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:40–46
Dejour D, Allain J (2003) L’arthrose fémoropatéllaire isolée: Histoire naturelle (Isolated patellofemoral osteoarthritis: natural history and clinical presentation), vol 1S. In: Symposim—SoFCOT 2003, pp 89–93
Varadarajan KM, Freiberg AA, Gill TJ, Rubash HE, Li G (2010) Relationship between three-dimensional geometry of the trochlear groove and in vivo patellar tracking during weight-bearing knee flexion. J Biomech Eng 132(6):061008
Varadarajan KM, Rubash HE, Li G (2011) Are current total knee arthroplasty implants designed to restore normal trochlear groove anatomy? J Arthroplasty 26(2):274–281
Mulford JS, Wakeley CJ, Eldridge JD (2007) Assessment and management of chronic patellofemoral instability. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(6):709–716
Senavongse W, Amis AA (2005) The effects of articular, retinacular, or muscular deficiencies on patellofemoral joint stability: a biomechanical study in vitro. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(4):577–582
Arendt E (2005) Anatomy and malalignment of the patellofemoral joint: its relation to patellofemoral arthrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:71–75
Dejour H, Walch G, Nove-Josserand L, Guier C (1994) Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2(1):19–26
Amis AA (2007) Current concepts on anatomy and biomechanics of patellar stability. Sports Med Arthrosc 15(2):48–56
Bicos J, Fulkerson JP, Amis A (2007) Current concepts review: the medial patellofemoral ligament. Am J Sports Med 35(3):484–492
Kulkarni SK, Freeman MA, Poal-Manresa JC, Asencio JI, Rodriguez JJ (2001) The patello-femoral joint in total knee arthroplasty: is the design of the trochlea the critical factor? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9(Suppl 1):S8–S12
Barink M, Van de Groes S, Verdonschot N, De Waal Malefijt M (2006) The difference in trochlear orientation between the natural knee and current prosthetic knee designs; towards a truly physiological prosthetic groove orientation. J Biomech 39(9):1708–1715
Indelli PF, Marcucci M, Cariello D, Poli P, Innocenti M (2012) Contemporary femoral designs in total knee arthroplasty: effects on the patello-femoral congruence. Int Orthop 36(6):1167–1173
Iranpour F, Merican AM, Dandachli W, Amis AA, Cobb JP (2010) The geometry of the trochlear groove. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(3):782–788
Varadarajan KM, Gill TJ, Freiberg AA, Rubash HE, Li G (2009) Gender differences in trochlear groove orientation and rotational kinematics of human knees. J Orthop Res 27(7):871–878
Yoshioka Y, Siu D, Cooke TD (1987) The anatomy and functional axes of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(6):873–880
Eckhoff DG, Burke BJ, Dwyer TF, Pring ME, Spitzer VM, VanGerwen DP (1996) The Ranawat Award. Sulcus morphology of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:23–28
Eckhoff DG, Montgomery WK, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RF (1996) Location of the femoral sulcus in the osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 11(2):163–165
Barink M, van de Groes S, Verdonschot N, De Waal Malefijt M (2003) The trochlea is bilinear and oriented medially. Clin Orthop Relat Res 411:288–295
Feinstein WK, Noble PC, Kamaric E, Tullos HS (1996) Anatomic alignment of the patellar groove. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:64–73
Leadbetter WB (2008) Patellofemoral arthroplasty in the treatment of patellofemoral arthritis: rationale and outcomes in younger patients. Orthop Clin North Am 39(3):363–380
Conflict of interest
D.D. receives royalties from Tornier SA. M.S., P.G.N., G.D. and B.L.N. have not included a conflict of interest disclosure statement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saffarini, M., Ntagiopoulos, P.G., Demey, G. et al. Evidence of trochlear dysplasia in patellofemoral arthroplasty designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22, 2574–2581 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2967-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2967-8