Abstract
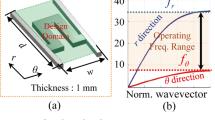
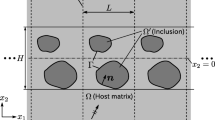
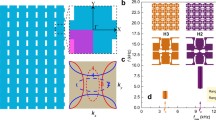
This paper presents a level set-based topology optimization method for the microstructural design of an optical hyperlens. The resolution of conventional optics is generally diffraction limited, but the diffraction limit can be overcome by a hyperlens that converts evanescent waves to propagation waves, utilizing a cylindrical geometry to magnify the subwavelength features of imaged objects, which allows such features to be resolved beyond the diffraction limit at the hyperlens output. To support electromagnetic waves that contain information of subwavelength features, the hyperlens must have material properties that include a positive permittivity in the angular direction and a negative permittivity in the radial direction. Here, an energy-based homogenization method is used to obtain the effective permittivity of a metamaterial hyperlens unit cell. A level set-based topology optimization is applied so that the boundaries of the structure are clearly expressed. Moreover, a finite element mesh regeneration scheme is used to precisely capture the boundaries of the metal and dielectric materials of the unit cell that will ultimately form the hyperlens. The optimization algorithm uses the finite element method (FEM) to solve the equilibrium and adjoint equations. Optimum design examples for the design of a hyperlens microstructure are provided to confirm the utility and validity of the presented method.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andkjær J, Nishiwaki S, Nomura T, Sigmund O (2010) Topology optimization of grating couplers for the efficient excitation of surface plasmons. J Opt Soc Am B 27(9):1828–1832
Andreasen CS, Andreassen E, Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2014) On the realization of the bulk modulus bounds for two-phase viscoelastic composites. J Mech Phys Solids 63:228–241
Andreassen E, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2014) Design of manufacturable 3D extremal elastic microstructure. Mech Mater 69(1):1–10
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Choi JS, Yoo J (2010) Design and application of layered composites with the prescribed magnetic permeability. Int J Numer Meth Engng 82(1):1–25
Diaz AR, Sigmund O (2010) A topology optimization method for design of negative permeability metamaterials. Struct Multidisc Optim 41(2):163–177
El-Kahlout Y, Kiziltas G (2011) Inverse synthesis of electromagnetic materials using homogenization based topology optimization. Prog Elec Res 115:343–380
Fang N, Lee H, Sun C, Zhang X (2005) Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308(5721):534–537
Guest JK, Prévost JH (2007) Design of maximum permeability material structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(4–6):1006–1017
Hashin Z (1983) Analysis of composite materials — a survey. J Appl Mech 50(3):481–505
Jacob Z, Alekseyev LV, Narimanov E (2006) Optical hyperlens: far-field imaging beyond the diffraction limit. Opt Express 14(18):8247–8256
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Nishiwaki S, Nomura T, Kinoshita S, Izui K, Yoshimura M, Sato K, Hirayama K (2009) Topology optimization for cross-section designs of electromagnetic waveguides targeting guiding characteristics. Finite Elem Anal Des 45(12):944–957
Larsen UD, Sigmund O, Bouwstra S (1997) Design and fabrication of compliant micromechanisms and structures with negative Poisson’s ratio. J Microelectromech Syst 6(2):99–106
Liu Z, Lee H, Xiong Y, Sun C, Zhang X (2007) Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science 315(5819):1686
Lu D, Liu Z (2012) Hyperlenses and metalenses for far-field super-resolution imaging. Nat Commun 3:1205
Lu L, Yamamoto T, Otomori M, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2013) Topology optimization of an acoustic metamaterial with negative bulk modulus using local resonance. Finite Elem Anal Des 72:1–12
Ma ZD, Kikuchi N, Cheng HC (1995) Topological design for vibrating structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 121(1–4):259–280
Oh JH, Ahn YK, Kim YY (2015) Maximization of operating frequency ranges of hyperbolic elastic metamaterials by topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 52(1):1–18
Otomori M, Andkjær J, Sigmund O, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2012a) Inverse design of dielectric materials by topology optimization. Prog Elec Res 127:93–120
Otomori M, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S, Andkjær J (2012b) A topology optimization method based on the level set method for the design of negative permeability dielectric metamaterials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 237–240:192–211
Otomori M, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2015) Matlab code for a level set-based topology optimization method using a reaction diffusion equation. Struct Multidisc Optim 51(5):1159–1172
Rho J, Ye Z, Xiong Y, Yin X, Liu Z, Choi H, Bartal G, Zhang X (2010) Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies. Nat Commun 1:143
Sigmund O (1994) Materials with prescribed constitutive parameters: an inverse homogenization problem. Int J Solids Structures 31(17):2313–2329
Sigmund O (2009) Systematic design of metamaterials by topology optimization. In: Pyrz R, Rauhe JC (eds) IUTAM Symposium on modelling nanomaterials and nanosystems, vol 13. Springer, Netherlands, pp 151–159
Sigmund O, Torquato S (1997) Design of materials with extreme thermal expansion using a three-phase topology optimization method. J Mech Phys Solids 45(6):1037–1067
Smith DR, Schurig D (2003) Electromagnetic wave propagation in media with indefinite permittivity and permeability tensors. Phys Rev Lett 90:077405
Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S, Takezawa A (2010) A topology optimization method based on the level set method incorporating a fictitious interface energy. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(45–48):2876–2891
Yamasaki S, Nishiwaki S, Yamada T, Izui K, Yoshimura M (2010) A structural optimization method based on the level set method using a new geometry-based re-initialization scheme. Int J Numer Meth Engng 83(12):1580–1624
Zhou S, Li W, Chen Y, Sun G, Li Q (2011) Topology optimization for negative permeability metamaterials using level-set algorithm. Acta Mater 59(7):2624–2636
Zhou S, Li W, Li Q (2010) Design of 3-D periodic metamaterials for electromagnetic properties. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Techn 58(4):910–916
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otomori, M., Yamada, T., Izui, K. et al. Topology optimization of hyperbolic metamaterials for an optical hyperlens. Struct Multidisc Optim 55, 913–923 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1543-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1543-x