Abstract
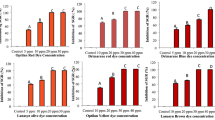
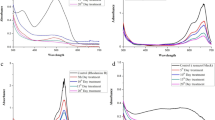
Toxicity of three textile dyes—Optilan yellow, Drimarene blue and Lanasyn brown, was evaluated in a green alga Chlorella vulgaris. The unialgal populations of the alga showed a concentration-dependent decrease in specific growth rate and pigments after exposure to graded concentrations of above dyes. The elemental profile (C, H, N, S) of the treated and untreated cells showed a change which was evident from a significant decrease in the quantity of elements after exposure to the dyes. The observations provide convincing evidence that the textile dyes inhibited the growth, pigment and elemental composition of the algal cells. The findings of the present investigation will contribute to gaining a better understanding of the impacts of textile dyes on ecologically important aquatic organisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM (1968) Simple conditions for growth of unicellular blue-green algae on plates. J Phycol 4:1–4
Chamovitz D, Sandmann G, Hirschberg J (1993) Molecular and biochemical characterization of herbicide-resistant mutants of cyanobacteria reveals that phytoene desaturation is a rate-limiting step in carotenoid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 268:17348–17353
Chequer FMD, de Oliveira GAR, Ferraz ERA, Cardoso JC, Zanoni MVB, de Oliveira DP (2013) Textile dyes: dyeing process and environmental impact. In Eco-friendly textile dyeing and finishing. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/53659
Chowdhury S, Saha P (2010) Sea shell powder as a new adsorbent to remove Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 164:168–177
Dwivedi S (2013) Effect of textile dyes on Spirulina platensis. J Chem Pharm Res 5:66–80
Fernández-Naveira A, Rioboo C, Cid A, Herrero C (2016) Atrazine induced changes in elemental and biochemical composition and nitrate reductase activity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Phycol 51:338–345
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hu TL, Wu SC (2001) Assessment of the effect of azo dye RP2B on the growth of a nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium–Anabaena sp. Bioresour Technol 77:93–95
Jin X, Liu G, Xu Z, Yao W (2007) Decolorization of a dye industry effluent by Aspergillus fumigatus XC6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:239–243
Kratz WA, Myers J (1955) Nutrition and growth of several blue-green algae. Am J Bot 42:282
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal RJ (1951) Proteins estimation by folin phenol method. J Biol Chem 193:265–265
Mahalakshmi S, Lakshmi D, Menaga U (2015) Biodegradation of different concentration of dye (Congo red dye) by using green and blue green algae. Int J Environ Res 9:735–744
Mansour HB, Houas I, Montassar F, Ghedira K, Barillier D, Mosrati R, Chekir-Ghedira L (2012) Alteration of in vitro and acute in vivo toxicity of textile dyeing wastewater after chemical and biological remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2634–2643
Mathias AC, Rilwan IM (2013) Effect of indigo dye effluent on the growth, biomass production and phenotypic plasticity of Scenedesmus quadricauda (Chlorococcales). An Acad Bras Cienc 86:19–428
Moosvi S, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2005) Decolorization of textile dye Reactive violet 5 by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM11.1.World. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–672
Moran R (1982) Formulae for determination of chlorophyllous pigments extracted with N, N-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol 69:1376–1381
Naik DJ, Desai HH, Desai TN (2013) Characterization and treatment of untreated wastewater generated from dyes and dye intermediates manufacturing industries of Sachin industrial area, Gujarat, India. J Environ Res Develop 7(4A):1602
OECD 201 (1984) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. ‘alga, growth inhibition test
Pinheiro HM, Touraud E, Thomas O (2004) Aromatic amines from azo dye reduction: status review with emphasis on direct UV spectrophotometric detection in textile industry wastewaters. Dyes Pigment 61:121–139
Przystaś W, Zabłocka-Godlewska E, Grabińska-Sota E (2012) Biological removal of Azo and Triphenylmethane dyes and toxicity of process by-products. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1581–1592
Samchetshabam G, Hussan A, Choudhury TG (2017) Impact of textile dyes waste on aquatic environments and its treatment. Environ Ecology 35:2349–2353
Shukla SP, Kumar A, Tiwari DN, Mishra BP, Gupta GS (1992) Assessment of the effect of the toxicity of a textile dye on Nostoc muscorum ISU, a diazotrophic cyanobacterium. Environ Pollut 84:23–25
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2018a) Comparision of experimental ponds for the treatment of dye wastewater under controlled and semi-natural conditions. Env Sci Pollut Res 24:16031–16040
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2018b) Treatment of synthetic textile wastewater containing dye mixtures with microcosms. Env Sci Pollut Res 25:1980–1997
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Education for providing the necessary facilities. S. Gita acknowledges the valuable inputs from the advisory committee members. Archroma, Mumbai is acknowledged for gifting the dyes. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gita, S., Shukla, S.P., Saharan, N. et al. Toxic Effects of Selected Textile Dyes on Elemental Composition, Photosynthetic Pigments, Protein Content and Growth of a Freshwater Chlorophycean Alga Chlorella vulgaris. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102, 795–801 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02599-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02599-w