Abstract
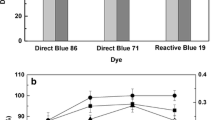
The strain Aspergillus fumigatus XC6 isolated from mildewing rice straw was evaluated for its ability to decolorize a dye industry effluent. The strain was capable of decolorizing dyes effluent over a pH range 3.0–8.0 with the dyes as sole carbon and nitrogen sources. The optimum pH was 3.0; however, supplemented with either appropriate nitrogen sources (0.2% NH4Cl or (NH4)2SO4 ) or carbon sources (1.0% sucrose or potato starch), the strain decolorized the effluent completely at the original pH of the dyes effluent. Therefore, A. fumigatus XC6 is an efficient strain for the decolorization of reactive textile dyes effluents, and it might be a practical alternative in dyeing wastewater treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald F, Paice MG, Jurasek L (1990) Decolorization of Kraft bleachery effluent on chromophores by Coriolus (Trametes) versicolor. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:846–853
Baldrian P, Gabriel J (2003) Lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus in the presence of cadmium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220:235–240
Barclay CD, Moore DM, Lander SR, Legge RL (1990) Heat denaturation kinetics of lignin peroxidases from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:778–782
Boer CG, Obici L, Souza CG, Peralta RM (2004) Decolourization of synthetic dyes by solid state cultures of Lentinula (Lentinus) edodes producing manganese peroxidase as the main lignolytic enzyme. Bioresour Technol 94:107–112
Brodkorb TS, Legge RL (1992) Enhanced biodegradation of phenanthrene in oil tar-contaminated soils supplemented with Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3117–3121
Cai Q, Baruch M (2001) A simple, reliable, and fast protocol for Thraustochytrid DNA extraction. Mar Biotechnol 3:100–102
Chung KT, Stevens S Jr (1993) Decolourization of azo dyes by environmental microorganisms and helminthes. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:2121–2132
Eaton D, Chang H, Kirk T (1980) Fungal decolorization of Kraft bleach effluents. Tappi 63:103–106
Heinfling A, Bergbauer M, Szewzyk U (1997) Biodegradation of azo and phthalocyanin dyes by Trametes versicolor and Bjerkandera adusta. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:261–266
Kamitsuji HY, Watanabe T, Kuwahara M (2005) Mn2+ is dispensable for the production of active MnP2 by Pleurotus ostreatus. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 327:871–876
Knapp JS, Zhang F, Tapley NK (1997) Decolourization of Orange II by a wood-rotting fungus. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 69:289–296
Maas R, Chaudhari S (2005) Adsorption and biological decolorization of azo dye reactive red 2 in semicontinuous anaerobic reactors. Process Biochem 40:699–705
Mazmanci MA, Unyayar A (2005) Decolourization of reactive black 5 by Funalia trogii immobilized on Luffa cylindrica sponge. Process Biochem 40:337–342
Mehna A, Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1995) Studies on decolorization of effluent from a small pulp mill utilizing agriresidues with Trametes versicolor. Enzyme Microb Technol 17:18–22
Mittar D, Khanna PK, Marwaha SS, Kennedy JF (1992) Biobleaching of pulp and paper mill effluents by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 53:81–92
Nagai M, Sato T, Watanabe H, Saito K, Kawata M, Enei H (2002) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase from the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes, and decolorization of chemically different dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:327–335
O’Neill C, Hawkes FR, Hawkes DL, Lourenco ND, Pinheiro HM, Delee W (1999) Colour in textile effluents: sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:1009–1018
Pala A, Toket E (2002) Color removal from cotton textile industry wastewater by an activated sludge system with various additives. Water Res 36:2920–2925
Prasad DY, Joyce TW (1991) Color removal from Kraft bleach plant effluent by Trichoderma sp. Tappi 74:165–169
Ramaswamy V (1987) Biotechnology application in waste utilization and pollution abatement. In: Saharanpur (ed) IPPTA convention issue. Indian Pulp and Paper Association, India, pp 361–364
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255
Shaul GM, Holdsworth TJ, Dempsey CR, Dostal KA (1991) Fate of water soluble azo dyes in the activated sludge process. Chemosphere 22:107–119
Swamy J, Ramsay JA (1999) The evaluation of white-rot fungi in the decolouration of textile dyes. Enzyme Microb Technol 24:130–137
Vaidya AA, Date KV (1982) Environmental pollution during chemical processing of synthetic fibers. Colourage 14:3–10
Wei JC (1979) Handbook for identification of fungi. Shanghai Scientific Press, Shanghai, pp 495–499
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S (1990) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Willmott N, Guthrie J, Nelson G (1998) The biotechnology approach to colour removal from textile effluent. J Soc Dyers Colour 114:38–41
Zhang SJ, Yang M, Yang QX, Zhang Y, Xin BP, Pan F (2003) Biosorption of reactive dyes by mycelium pellets of a new isolate of Penicillium oxalicum. Biotechnol Lett 25:1479–1488
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the financial support of The 10th Five Years Key Programs for Science and Technology Development of China (2002BA404A23C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, XC., Liu, GQ., Xu, ZH. et al. Decolorization of a dye industry effluent by Aspergillus fumigatus XC6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 239–243 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0658-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0658-1