Abstract
Key message
The rye-derived dwarfing gene Ddw1 on chromosome 5R acts in triticale in considerably reducing plant height, increasing FHB severity and delaying heading stage.
Abstract
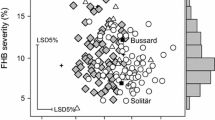
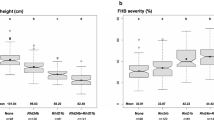
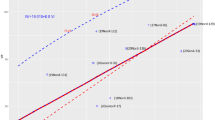
Triticale, an amphiploid hybrid between durum wheat and rye, is an European cereal mainly grown in Germany, France, Poland, and Belarus for feeding purposes. Dwarfing genes might further improve the genetic potential of triticale concerning lodging resistance and yield. However, they might have pleiotropic effects on other, agronomically important traits including Fusarium head blight. Therefore, we analyzed a population of 199 doubled haploid (DH) lines of the cross HeTi117-06 × Pigmej for plant height, heading stage, and FHB severity across 2 locations and 2 years. The most prominent QTL was detected on chromosome 5R explaining 48, 77, and 71 % of genotypic variation for FHB severity, plant height, and heading stage, respectively. The frequency of recovery in cross validation was ≥90 % for all three traits. Because the markers that detect dwarfing gene Ddw1 in rye are also in our population the most closely linked markers, we assume that this major QTL resembles Ddw1. For FHB severity two, for plant height three, and for heading stage five additional QTL were detected. Caused by the considerable genetic variation for heading stage and FHB severity within the progeny with the dwarfing allele, short-strawed, early heading and FHB-resistant lines can be developed when population size is large enough.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alheit KV, Reif JC, Maurer HP, Hahn V, Weissmann EA, Miedaner T, Würschum T (2011) Detection of segregation distortion loci in triticale (×Triticosecale Wittmack) based on a high-density DArT marker consensus genetic linkage map. BMC Genomics 12:380. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-380
Alheit KV, Busemeyer L, Liu W, Maurer HP, Gowda M, Hahn V, Weissmann S, Ruckelshausen A, Reif JC, Würschum T (2014) Multiple-line cross QTL mapping for biomass yield and plant height in triticale (×Triticosecale Wittmack). Theor Appl Genet 127:251–260. doi:10.1007/s00122-013-2214-6
Anonymus (2001) Growth stages of mono-and dicotyledonous plants BBCH Monograph. Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry. http://www.bba.de/veroeff/bbch/bbcheng.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
Arseniuk E (1996) Triticale diseases: A review. In: Guedes-Pinto H, Darvey N, Carnide VP (eds) Triticale today and tomorrow. Kluwer Acad: Publ Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 499–525
Arseniuk E, Góral T, Czembor HJ (1993) Reaction of triticale, wheat and rye accessions to gramineous Fusarium spp. infection at the seedling and adult plant growth stages. Euphytica 70:175–183
Bai G, Shaner G (1994) Scab of wheat: prospects for control. Plant Dis 78:760–766
Baierl A, Bogdan M, Frommlet F, Futschik A (2006) On locating multiple interacting quantitative trait loci in intercross designs. Genetics 173:1693–1703
Banaszak Z (2010) Breeding of triticale in DANKO. In: 61. Tagung der Vereinigung der Pflanzenzüchter und Saatgutkaufleute Österreichs 61:65–68
Becher R, Miedaner T, Wirsel SGR (2013) Biology, diversity, and management of FHB-causing Fusarium species in small-grain cereals. In: Kempken F (ed) The mycota XI—agricultural applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 199–241
Börner A, Korzun V, Worland AJ (1998) Comparative genetic mapping of mutant loci affecting plant height and development in cereals. Euphytica 100:245–248
Börner A, Korzun V, Voylokov AV, Worland AJ, Weber WE (2000) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in rye (Secale cereale L.). Euphytica 116:203–209
BSL (2013) Beschreibende Sortenliste Getreide, Mais, Öl- und Faserpflanzen, Leguminosen, Rüben, Zwischenfrüchte. http://www.bundessortenamt.de/internet30/index.php?id=23&L=0. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
Buerstmayr H, Ban T, Anderson JA (2009) QTL mapping and marker-assisted selection for Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat a review. Plant Breed 128:1–26
Churchill G, Doerge R (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
DLG (2013) Fungizidempfehlungen für Getreide Ergänzung zu DLG-Mitteilungen 2/2013.http://www.dlg-mitteilungen.de/fileadmin/img/content/start/mehrdazu/1302_volle_spektrum_text.doc. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
EFSA (2004) Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to deoxynivalenol (DON) as undesirable substance in animal feed. EFSA J 73:1–41
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, London
FAOSTAT (2013) Production Crops. http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=567#ancor. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
Fehr WR (1987) Principles of cultivar development. Theory and technique, vol 1. Macmillan, New York
Fisher RA (1921) On the “probable error” of a coefficient of correlation deduced from a small sample. Metron 1:1–32
Foulkes MJ, Slafer GA, Davies WJ, Berry PM, Sylvester-Bradley R, Martre P, Calderini DF, Griffiths S, Reynolds MP (2011) Raising yield potential of wheat. III. Optimizing partitioning to grain while maintaining lodging resistance. J Exp Bot 62:469–486
Gale MD, Youssefian S (1985) Dwarfing genes in wheat. In: Russell GE (ed) Progress in plant breeding, 1st edn. Butterworth, London, pp 1–35
Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ, Cullis BR, Thompson R (2009) ASReml user guide release 3.0. VSN International Hemel Ltd, Hempstead. http://www.vsni.co.uk. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
Griffiths S, Simmonds J, Leverington M, Wang Y, Fish L, Sayers L, Alibert L, Orford S, Wingen L, Herry L, Faure S, Laurie D, Bilham L, Snape J (2009) Meta-QTL analysis of the genetic control of ear emergence in elite European winter wheat germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 119:383–395
Hackauf B, Korzun V, Wortmann H, Wilde P, Wehling P (2012) Development of conserved ortholog set markers linked to the restorer gene Rfp1 in rye. Mol Breed 30:1507–1518
Haldane JBS (1919) The combination of linkage values, and the calculation of distances between the loci of linked factors. J Genet 8:299–309
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324
Holzapfel J, Voss HH, Miedaner T, Korzun V, Haberle J, Schweizer G, Mohler V, Zimmermann G, Hartl L (2008) Inheritance of resistance to Fusarium head blight in three European winter wheat populations. Theor Appl Genet 117:1119–1128
Kobyljanski VD (1972) On the genetics of the dominant factor of short-strawed rye. Genetika 8:12–17
Korzun V, Melz G, Börner A (1996) RFLP mapping of the dwarfing (Ddw1) and hairy peduncle (Hp) genes on chromosome 5 of rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 92:1073–1077
Law CN, Snape JW, Worland AJ (1978) The genetical relationship between height and yield in wheat. Heredity 40:133–151
Liu S, Hall MD, Griffey CA, McKendry AL (2009) Meta-analysis of QTL associated with Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Crop Sci 49:1955–1968
Löffler M, Schön CC, Miedaner T (2009) Revealing the genetic architecture of FHB resistance in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by QTL meta-analysis. Mol Breed 23:473–488
Lu Q, Szabo-Hever A, Bjornstad A, Lillemo M, Semagn K, Mesterhazy A, Ji F, Shi J, Skinnes H (2011) Two major resistance quantitative trait loci are required to counteract the increased susceptibility to Fusarium head blight of the Rht-D1B dwarfing gene in wheat. Crop Sci 51:2430–2438
Ma HX, Bai GH, Zhang X, Lu WZ (2006) Main effects, epistasis, and environmental interactions of quantitative trait loci for Fusarium head blight resistance in a recombinant inbred population. Phytopathology 96:534–541
Mao SL, Wei YM, Cao W, Lan XJ, Yu M, Chen ZM, Chen GY, Zheng YL (2010) Confirmation of the relationship between plant height and Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by QTL meta-analysis. Euphytica 174:343–356
Mesterhazy A (1995) Types and components of resistance to Fusarium head blight of wheat. Plant Breed 114:377–386
Miedaner T (1997) Breeding wheat and rye for resistance to Fusarium disease. Plant Breed 116:201–220
Miedaner T, Geiger HH (1996) Estimates of combining ability for resistance of winter rye to Fusarium culmorum head blight. Euphytica 89:339–344
Miedaner T, Voss HH (2008) Effect of dwarfing Rht genes on Fusarium head blight resistance in two sets of near-isogenic lines of wheat and check cultivars. Crop Sci 48:2115–2122
Miedaner T, Gang G, Geiger HH (1996) Quantitative-genetic basis of aggressiveness of 42 isolates of Fusarium culmorum for winter rye head blight. Plant Dis 80:500–504
Miedaner T, Heinrich N, Schneider B, Oettler G, Rohde S, Rabenstein F (2004) Estimation of deoxynivalenol (DON) content by symptom severity and exoantigen content for resistance selection in wheat and triticale. Euphytica 139:123–132
Miedaner T, Schneider B, Oettler G (2006) Means and variances for Fusarium head blight resistance of F2–derived lines from winter triticale and winter wheat crosses. Euphytica 152:405–411
Miedaner T, Würschum T, Maurer HP, Korzun V, Ebmeyer E, Reif JC (2011) Association mapping for Fusarium head blight resistance in soft European winter wheat. Mol Breed 28:647–655
Miedaner T, Hübner M, Korzun V, Schmiedchen B, Bauer E, Haseneyer G, Wilde P, Reif JC (2012) Genetic architecture of complex agronomic traits examined in two testcross populations of rye (Secale cereale L.). BMC Genomics 13:706
Oettler G, Wahle G (2001) Genotypic and environmental variation of resistance to head blight in triticale inoculated with Fusarium culmorum. Plant Breed 120:297–300
Oettler G, Heinrich N, Miedaner T (2004) Estimates of additive and dominance effects for Fusarium head blight resistance of winter triticale. Plant Breed 123:525–530
Piepho H-P, Williams ER, Fleck M (2006) A note on the analysis of designed experiments with complex treatment structure. Hort Science 41:446–452
R Development Core Team (2012) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.r-project.org. Accessed 6 Dec 2013
Rieseberg LH, Widmer A, Arntz AM, Burke JM (2003) The genetic architecture necessary for transgressive segregation is common in both natural and domesticated populations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 358:1141–1147
Snijders CHA (1990) Genetic variation for resistance to Fusarium head blight in bread wheat. Euphytica 50:171–179
Snijders CHA, Perkowski J (1990) Effects of head blight caused by Fusarium culmorum on toxin content and weight of wheat kernels. Phytopathology 80:566–570
Srinivasachary Gosman N, Steed A, Simmonds J, Leverington-Waite M, Wang Y, Snape J, Nicholson P (2008) Susceptibility to Fusarium head blight is associated with the Rht-D1b semi-dwarfing allele in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 116:1145–1153
Stram DO, Lee JW (1994) Variance component testing in the longitudinal mixed effects model. Biometrics 50:1171–1177
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Utz HF (2012) PlabMQTL—software for meta-QTL analysis with composite interval mapping. Version 0.5s. PlabMQTL manual. Institute of Plant Breeding, Seed Science, and Population Genetics, Stuttgart
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap® 4. Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Wageningen, Netherlands
Voss HH, Holzapfel J, Hartl L, Korzun V, Rabenstein F, Ebmeyer E, Coester H, Kempf H, Miedaner T (2008) Effect of the Rht-D1 dwarfing locus on Fusarium head blight severity in three segregating populations of winter wheat. Plant Breed 127:333–339
Würschum T, Tucker MR, Reif JC, Maurer HP (2012) Improved efficiency of doubled haploid generation in hexaploid triticale by in vitro chromosome doubling. BMC Plant Biol 12:109
Zeng ZB (1993) Theoretical basis for separation of multiple linked gene effects in mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10972–10976
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Elmar A. Weissmann, Saatzucht Dr. Hege GbR, Waldenburg, for sharing the population with us and Jens Möhring for suggestions on the statistical analysis. We highly appreciate the excellent technical support of the teams at Hohenheim and Oberer Lindenhof. This research was partially funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the promotional reference 0315414. Rasha Kalih had a grant from the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), Bonn. The responsibility of the content of this publication rests with the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments comply with the current laws of Germany in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by X. Qi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalih, R., Maurer, H.P., Hackauf, B. et al. Effect of a rye dwarfing gene on plant height, heading stage, and Fusarium head blight in triticale (×Triticosecale Wittmack). Theor Appl Genet 127, 1527–1536 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2316-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2316-9