Abstract
Key message
Large-scale SNP discovery and dense genetic mapping in a lentil intraspecific cross permitted identification of a single chromosomal region controlling tolerance to boron toxicity, an important breeding objective.
Abstract
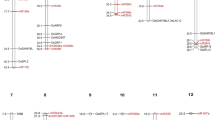
Lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) is a highly nutritious food legume crop that is cultivated world-wide. Until recently, lentil has been considered a genomic ‘orphan’ crop, limiting the feasibility of marker-assisted selection strategies in breeding programs. The present study reports on the identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from transcriptome sequencing data, utilisation of expressed sequence tag (EST)-derived simple sequence repeat (SSR) and SNP markers for construction of a gene-based genetic linkage map, and identification of markers in close linkage to major QTLs for tolerance to boron (B) toxicity. A total of 2,956 high-quality SNP markers were identified from a lentil EST database. Sub-sets of 546 SSRs and 768 SNPs were further used for genetic mapping of an intraspecific mapping population (Cassab × ILL2024) that exhibits segregation for B tolerance. Comparative analysis of the lentil linkage map with the sequenced genomes of Medicago truncatula Gaertn., soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) and Lotus japonicus L. indicated blocks of conserved macrosynteny, as well as a number of rearrangements. A single genomic region was found to be associated with variation for B tolerance in lentil, based on evaluation performed over 2 years. Comparison of flanking markers to genome sequences of model species (M. truncatula, soybean and Arabidopsis thaliana) identified candidate genes that are functionally associated with B tolerance, and could potentially be used for diagnostic marker development in lentil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal G, Jhanwar S, Priya P, Singh VK, Saxena MS et al (2012) Comparative analysis of kabuli chickpea transcriptome with desi and wild chickpea provides a rich resource for development of functional markers. PLoS One 7(12):e52443. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052443
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Bennetzen JL (2000) Comparative sequence analysis of plant nuclear genomes: microcolinearity and its many exceptions. Plant Cell 12:1021–1030
Bogacki P, Peck DM, Nair RM, Howie J, Oldach KH (2013) Genetic analysis of tolerance to boron toxicity in the legume Medicago truncatula. BMC Genom 13:54
Cannon SB, May GD, Jackson SA (2009) Three sequenced legume genomes and many crop species: rich opportunities for translational genomics. Plant Physiol 151:970–977
Cartwright B, Zarcinas BA, Mayfield AH (1984) Toxic concentrations of B in a red–brown earth at Gladstone, South Australia. Aust J Soil Res 22:261–272
Chabane K, Ablett GA, Cordeiro GM, Valkoun J, Henry RJ (2005) EST versus genomic derived microsatellites for genotyping wild and cultivated barley. Genet Res Crop Evol 52:903–909
Choi HK, Kim DJ, Uhm T, Limpens E, Lim H, Mun JH, Kalo P, Penmesta RV, Seres A, Kulikova O et al (2004) A sequence based genetic map of Medicago truncatula and comparison of marker colinearity with M. sativa. Genetics 166:1463–1502
Choi I-Y, Hyten DL, Matukumalli LK, Song Q, Chaky JM, Quigley CV, Chase K, Lark KG, Reiter RS, Yoon M-S, Hwang E-Y, Yi S-I et al (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Genetics 176:685–696
Choudhary S, Gaur R, Gupta S (2012) EST-derived genic molecular markers: development and utilization for generating an advanced transcript map of chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 124:1449–1462
Doyle JJ, Luckow MA (2003) The rest of the iceberg. Legume diversity and evolution in a phylogenetic context. Plant Physiol 131(900):910
Durán Y, Fratini R, García P, Pérez de la Vega M (2004) An intersubspecific genetic map of Lens. Theor Appl Genet 108:1265–1273
Ellis JR, Burke JM (2007) EST-SSRs as a resource for population genetic analyses. Heredity 99:125–132
Ellwood SR, Phan HTT, Jordan M, Hane J, Torres AM, Avila CM, Cruz-Izquierdo S, Oliver RP (2008) Construction of a comparative genetic map in faba bean (Vicia faba L.); conservation of genome structure with Lens culinaris. BMC Genom 9:380
Eujayl I, Baum M, Powell W, Erskine W, Pehu E (1998) A genetic linkage map of lentil (Lens sp.) based on RAPD and AFLP markers using recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 97:83–89
Genstat Committee (2002) Genstat Release 6.1. Reference manual, Parts 1–3. VSN Int., Oxford
Gupta M, Verma B, Kumar N, Chahota RK, Rathour R, Sharma SK, Bhatia S, Sharma TR (2012) Construction of intersubspecific molecular genetic map of lentil based on ISSR, RAPD and SSR markers. J Genet 91:3
Hamwieh A, Udupa SM, Choumane W, Sarkar A, Dreyer F, Jung C, Baum M (2005) A genetic linkage map of Lens sp. based on microsatellite and AFLP markers and the localization of fusarium vascular wilt resistance. Theor Appl Genet 110:669–677
Hand ML, Cogan NOI, Sawbridge TI, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2010) Comparison of homoeolocus organisation in paired BAC clones from white clover (Trifolium repens L.) and microcolinearity with model legume species. BMC Plant Biol 10:94
Havey MH, Muehlbauer FJ (1989) Linkages between restriction fragment length, isozyme and morphological markers in lentil. Theor Appl Genet 77:395–401
Hayes JE, Reid RJ (2004) Boron tolerance in barley is mediated by efflux of boron from the roots. Plant Physiol 136:3376–3382
Hobson KB (2007) Investigation of boron toxicity in lentil. PhD thesis, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne
Hyten DL, Cannon SB, Song Q, Weeks N, Fickus EW, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE, Farmer AD, May GD, Cregan PB (2010) High-throughput SNP discovery through deep resequencing of a reduced representation library to anchor and orient scaffolds in the soybean whole genome sequence. BMC Genom 11:38
Jefferies SP, Barr AR, Karakousis A, Kretschmer JM, Manning S, Chalmers KJ, Nelson JC, Islam AKMR, Langridge P (1999) Mapping of chromosome regions conferring boron toxicity tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:1293–1303
Jefferies SP, Pallotta MA, Paull JG, Karakousis A, Kretschmer JM, Manning S, Islam AKMR, Langridge P, Chalmers KJ (2000) Mapping and validation of chromosome regions conferring boron toxicity tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Theor Appl Genet 101:767–777
Kaur S, Cogan NOI, Pembleton LW, Shinozuka M, Savin KW, Materne M, Forster JW (2011) Transcriptome sequencing of lentil based on second-generation technology permits large-scale unigene assembly and SSR marker discovery. BMC Genom 12:265
Kaur S, Pembleton L, Cogan N, Savin K, Leonforte T, Paull J, Materne M, Forster J (2012) Transcriptome sequencing of field pea and faba bean for discovery and validation of SSR genetic markers. BMC Genom 13:104
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen. 12:172–175
Lavin M, Herendeen PS, Wojciechowski MF (2005) Evolutionary rates analysis of leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the tertiary. Syst Biol 54:575–594
Manly KF, Cudmore RH, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Mattioni C, Cherubini M, Taurchini D, Villani F, Martin MA (2010) Evaluation of genomic SSRs and EST-SSRs markers in genetic diversity studies in european chestnut populations. Acta Hort 866:151–156
Muehlbauer FJ, Cho S, Sarkar A, McPhee KE, Coyne CJ, Rajesh PN, Ford R (2006) Application of biotechnology in breeding lentil for resistance to biotic and abiotic stress. Euphytica 147:149–165
Nelson M, Phan H, Ellwood S, Moolhuijzen P, Hane J, Williams A, O’Lone C, Fosu-Nyarko J, Scobie M, Cakir M, Jones M, Bellgard M, Ksiarkiewicz M, Wolko B, Barker S, Oliver R, Cowling W (2006) The Wrst gene-based map of Lupinus angustifolius L.-location of domestication genes and conserved synteny with Medicago truncatula. Theor Appl Genet 113:225–238
Nuttall JG, Armstrong RD, Connor DJ, Matassa VJ (2003) Interrelationships between edaphic factors potentially limiting cereal growth on alkaline soils in north–western Victoria. Aust J Soil Res 41:277–292
Phan HTT, Ellwood SR, Ford R, Thomas S, Oliver RP (2006) Differences in syntenic complexity between Medicago truncatula with Lens culinaris and Lupinus albus. Funct Plant Biol 33:775–782
Phan HTT, Ellwood SR, Hane JK, Ford R, Materne M, Oliver RP (2007) Extensive macrosynteny between Medicago truncatula and Lens culinaris ssp. culinaris. Theor Appl Genet 114:549–558
Rubeena, Ford R, Taylor PWJ (2003) Construction of an intraspecific linkage map of lentil (Lens culinaris ssp. culinaris). Theor Appl Genet 107:910–916
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J et al (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Schnurbusch T, Hayes J, Hrmova M, Baumann U, Ramesh SA, Tyerman SD, Langridge P, Sutton T (2010) Boron toxicity tolerance in barley through reduced expression of the multifunctional aquaporin HvNIP2;1. Plant Physiol 153:1706–1715
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nature Biotech 18:233–234
Sharpe AG, Ramsay L, Sanderson L-A, Fedoruk MJ, Clarke WE, Li R, Kagale S, Vijayan P, Vandenberg A, Bett KE (2013) Ancient orphan crop joins modern era: gene-based SNP discovery and mapping in lentil. BMC Genom 14:192
Takano J, Noguchi K, Yasumori M, Kobayashi M, Gajdos Z, Miwa K, Hayashi H, Yoneyama T, Fujiwara T (2002) Arabidopsis boron transporter for xylem loading. Nature 420:337–340
Tanyolac B, Ozatay S, Kahraman A, Muehlbauer F (2010) Linkage mapping of lentil (Lens culinaris L.) genome using recombinant inbred lines revealed by AFLP, ISSR, RAPD and some morphological markers. J Agric Biotech Sustainable Dev 2:001–006
Tullu A, Taran B, Warkentin T, Vandenberg A (2008) Construction of an intraspecific linkage map and QTL analysis for earliness and plant height in lentil. Crop Sci 48:2254–2262
Varshney RK, Song C, Saxena RK, Azam S, Yu S, Sharpe AG, Cannon S, Baek J, Rosen BD, Taran B et al (2013) Draft genome sequence of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) provides a resource for trait improvement. Nature Biotech 31:240–248
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Weeden NF, Muehlbauer FJ, Ladizinsky G (1992) Extensive conservation of linkage relationships between pea and lentil genetic maps. J Hered 83:123–129
Yau SK, Erskine W (2000) Diversity of boron-toxicity tolerance in lentil growth and yield. Genet Resour Crop Ev 47:55–62
Yau SK, Ryan J (2008) Boron toxicity tolerance in crops: a viable alternative to soil amelioration. Crop Sci 48:854–865
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the Victorian Department of Environment and Primary Industries and the Grains Research and Development Council, Australia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments conducted in this study comply with current laws of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. J. Bervillé.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2013_2252_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
ESM 1 Details of the 768plex SNP-OPA design: This file contains names and sequence information for all SNP markers used in linkage mapping (XLSX 239 kb)
122_2013_2252_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
ESM 2 Details of all EST-SSR markers used in linkage mapping analysis: This file contains a list of all EST-SSR marker assays along with statistics on amplification efficiency and polymorphism rate (XLSX 36 kb)
122_2013_2252_MOESM3_ESM.xlsx
ESM 3 Linkage map statistics from the Cassab × ILL2024 RIL mapping population: This file contains details of different markers (SSRs and SNPs) and their corresponding positions on different LGs (XLSX 19 kb)
122_2013_2252_MOESM4_ESM.docx
ESM 4 Frequency distribution of B tolerance score: This file contains frequency histograms generated from phenotypic assessment of B tolerance from RILs of the mapping population (DOCX 146 kb)
122_2013_2252_MOESM5_ESM.pptx
ESM 5 Synteny between LGs of the Cassab × ILL2024 linkage map and chromosomes of M. truncatula: This file shows the visual representation of all LGs from Cassab x ILL2024 linkage map and their macrosyntenic relationships with the M. truncatula genome (PPTX 210 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, S., Cogan, N.O.I., Stephens, A. et al. EST-SNP discovery and dense genetic mapping in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) enable candidate gene selection for boron tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 127, 703–713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2252-0