Abstract
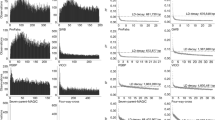
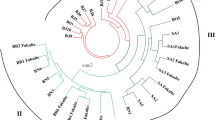
Multilocus digenic linkage disequilibria (LD) and their population structure were investigated in eleven landrace populations of barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare L.) in Sardinia, using 134 dominant simple-sequence amplified polymorphism markers. The analysis of molecular variance for these markers indicated that the populations were partially differentiated (F ST = 0.18), and clustered into three geographic areas. Consistent with this population pattern, STRUCTURE analysis allocated individuals from a bulk of all populations into four genetic groups, and these groups also showed geographic patterns. In agreement with other molecular studies in barley, the general level of LD was low (13 % of locus pairs, with P < 0.01) in the bulk of 337 lines, and decayed steeply with map distance between markers. The partitioning of multilocus associations into various components indicated that genetic drift and founder effects played a major role in determining the overall genetic makeup of the diversity in these landrace populations, but that epistatic homogenising or diversifying selection was also present. Notably, the variance of the disequilibrium component was relatively high, which implies caution in the pooling of barley lines for association studies. Finally, we compared the analyses of multilocus structure in barley landrace populations with parallel analyses in both composite crosses of barley on the one hand and in natural populations of wild barley on the other. Neither of these serves as suitable mimics of landraces in barley, which require their own study. Overall, the results suggest that these populations can be exploited for LD mapping if population structure is controlled.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani AH, Parzies HK, Omary A, Geiger HH (2004) Estimating the outcrossing rate of barley landraces and wild barley populations collected from ecologically different regions of Jordan. Theor Appl Genet 109:588–595
Agapow PM, Burt A (2001) Indices of multilocus linkage disequilibrium. Mol Ecol Notes 1:101–102
Allard RW (1999) History of plant population genetics. Annu Rev Genet 33:1–27
Attene G, Ceccarelli S, Papa R (1996) The barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) of Sardinia, Italy. Genet Resour Crop Evol 43:385–393
Bitocchi E, Nanni L, Rossi M, Bellucci E, Giardini A, Buonamici A, Vendramin GG et al (2009) Introgression from modern hybrid varieties into landrace populations of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.) in central Italy. Mol Ecol 18:603–621
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Briggs DE (1978) Barley. Chapman and Hall, London
Brown AHD (2000) The genetic structure of crop landraces and the challenge to conserve them in situ on farms. In: Brush SB (ed) GENES in the FIELD. On-farm conservation of crop diversity. IPGRI/IDRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 19–48
Brown AHD, Feldman MW (1981) Population structure of multilocus associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5913–5916
Brown AHD, Feldman MW, Nevo E (1980) Multilocus structure in natural populations of Hordeum spontaneum. Genetics 96:523–536
Brush SB (2000) The issues of in situ conservation of crop genetic resources. In: Brush SB (ed) GENES in the FIELD. On-farm conservation of crop diversity. IPGRI/IDRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 3–26
Caldwell KS, Russell J, Langridge P, Powell W (2006) Extreme population dependent linkage disequilibrium detected in an inbreeding plant species, Hordeum vulgare. Genetics 172:557–567
Ceccarelli S, Grando S (2000) Barley landraces from the Fertile Crescent: a lesson for plant breeders. In: Brush SB (ed) GENES in the FIELD. On-farm conservation of crop diversity. IPGRI/IDRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 3–26
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220
Cockram J, White J, Leigh FJ, Lea VJ, Chiapparino E, Laurie DA, Meckay IJ, Powell W, O’Sullivan DM (2008) Association mapping of partitioning loci in barley. BMC Genet 9:16. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-9-16
Comadran J, Thomas WTB, van Eeuwijk FA, Ceccarelli S, Grando S, Stanca AM, Pecchioni N, Akar T, Al-Yassin A, Benbelkacem A, Ouabbou H, Bort J, Romagosa I, Hackett CA, Russell JR (2009) Patterns of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in a highly structured Hordeum vulgare association-mapping population for the Mediterranean basin. Theor Appl Genet 119:175–187
Comadran J, Ramsay L, MacKenzie K, Hayes P, Close TJ, Muehlbauer G, Stein N, Waugh R (2011) Patterns of polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium in cultivated barley. Theor Appl Genet 122:523–531. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1466-7
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2007) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles. Mol Ecol Notes. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Frankel OH, Brown AHD, Burdon JJ (1995) The conservation of plant biodiversity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fu HH, Zheng ZW, Dooner HK (2002) Recombination rates between adjacent genic and retrotransposon regions in maize vary by 2 orders of magnitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1082–1087
Gao H, Williamson S, Bustamante CD (2007) An MCMC approach for joint inference of population structure and inbreeding rates from multi-locus genotype data. Genetics 176:1635–1651
Gaut BS, Long AD (2003) The lowdown on linkage disequilibrium. Plant Cell 15:1502–1506
Gorham J, Papa R, Aloy-Lleonart M (1994) Varietal differences in sodium uptake in barley cultivars exposed to soil salinity or salt spray. J Exp Bot 45:895–901
Guillot G, Leblois R, Coulon AL, Frantz AC (2009) Statistical methods in spatial genetics. Mol Ecol 18:4734–4756
Harlan JR (1975) Our vanishing genetic resources. Science 188:618–621
Hill WG, Robertson A (1968) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet 38:226–231
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour 9:1322–1332
Jaradat AA, Shahid M (2006) Population and multilocus isozyme structures in a barley landrace. Plant Genet Resour Charact Util 4:108–116
Kraakman ATW, Niks RE, Van den Berg PMMM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446
Landry PA, LaPointe FJ (1996) RAPD problems in phylogenetics. Zool Scr 25:283–290
Leigh F, Kalendar R, Lea V, Lee D, Donini P, Schulman AH (2003) Comparison of the utility of barley retrotransposon families for genetic analysis by molecular marker techniques. Mol Genet Genomics 269:464–474
Liu K, Goodman M, Muse S, Smith JS, Buckler E, Doebley J (2003) Genetic structure and diversity among maize inbred lines as inferred from DNA microsatellites. Genetics 165:2117–2128
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Noli E, Tuberosa R (2005) Population structure and long-range linkage disequilibrium in a durum wheat elite collection. Mol Breed 15:271–289
Mackay I, Powell W (2007) Methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping in crops. Trends Plant Sci 12:57–63
Malysheva-Otto LV, Ganal MW, Röder M (2006) Analysis of molecular diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in a worldwide survey of cultivated barley germplasm (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genet 7:6
Mather KA, Caicedo AL, Polato NR, Olsen KM, McCouch S, Purugganan MD (2007) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 177:2223–2232
Mazzucato A, Papa R, Bitocchi E, Mosconi P, Nanni L, Negri V, Picarella ME et al (2008) Genetic diversity, structure and marker-trait associations in a collection of Italian tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Theor Appl Genet 116:657–669
Miller MP (1997) Tools for population genetic analysis (TFPGA) 1.3: a Windows program for the analysis of allozyme and molecular population genetic data (distributed by the author)
Morrell PL, Toleno DM, Lundy KE, Clegg MT (2005) Low levels of linkage disequilibrium in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite high rates of self-fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2442–2447
Mueller JC (2004) Linkage disequilibrium for different scales and applications. Brief Bioinforma 5:355–364
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Nevo E, Zohary D, Brown AHD, Haber M (1979) Genetic diversity and environmental associations of wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, in Israel. Evolution 33:815–833
Papa R, Attene G, Barcaccia G, Ohgata A, Konishi T (1998) Genetic diversity in landrace populations of Hordeum vulgare L. from Sardinia, Italy, as revealed by RAPDs, isozymes and morphophenological traits. Plant Breed 117:523–530
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Pusadee T, Jamjod S, Chiang Y, Rerkasem B, Schaal BA (2009) Genetic structure and isolation by distance in a landrace of Thai rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13880–13885
Queen RA, Gribbon BM, James C, Jack P, Flavell AJ (2004) Retrotransposon-based molecular markers for linkage and genetic diversity analysis in wheat. Mol Genet Genomics 271(1):91–97. doi:10.1007/s00438-003-0960-x
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR et al (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Rodriguez M, O’Sullivan D, Donini P, Papa R, Chiapparino E, Leigh F, Attene G (2006) Integration of retrotransposon-based markers in a linkage map of barley. Mol Breed 17:173–184
Rodriguez M, Rau D, Papa R, Attene G (2008) Genotype by environment interactions in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): different responses of landraces, recombinant inbred lines and varieties to Mediterranean environment. Euphytica 163:231–247
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1. Exeter Software, Setauket
Rossi M, Bitocchi E, Bellucci E, Nanni L, Rau D, Attene G, Papa R (2009) Linkage disequilibrium and population structure in wild and domesticated populations of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Evol Appl 2:504–522
Rostoks N, Ramsay L, MacKenzie K, Cardle L, Bhat PR et al (2006) Recent history of artificial outcrossing facilitates whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18656–18661
Slatkin M (2008) Linkage disequilibrium: understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat Rev Genet 9:477–485
Soleimani VD, Baum BR, Johnson DA (2007) Analysis of genetic diversity in barley cultivars reveals incongruence between S-SAP, SNP and pedigree data. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:83–97
Song B-H, Windsor AJ, Schmid KJ, Ramos-Onsins S, Schranz ME et al (2009) Multilocus patterns of nucleotide diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in Boechera stricta, a wild relative of Arabidopsis. Genetics 181:1021–1033
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, van der Linde A (2002) Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J R Stat Soc B 64:583–640
Tam SM, Mhiri C, Vogelaar A, Kerkveld M, Pearce SR, Grandbastien MA (2005) Comparative analyses of genetic diversities within tomato and pepper collections detected by retrotransposon-based S-SAP, AFLP and SSR. Theor Appl Genet 110:819–831
Tam SM, Causse M, Garcher C, Burck H, Mhiri C, Grandbastien M-A (2007) The distribution of copia-type retrotransposons and the evolutionary history of tomato and related wild species. J Evol Biol 20:1056–1072
Tanto Hadado T, Rau D, Bitocchi E, Papa R (2010) Adaptation and diversity along an altitudinal gradient in Ethiopian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) landraces revealed by molecular analysis. BMC Plant Biol 10:121
Teshome A, Brown AHD, Hodgkin T (2001) Diversity in landraces of cereal and legume crops. Plant Breed Rev 21:221–261
Thomson MJ, Septiningsih EM, Suwardjo F, Santoso TJ, Silitonga TS, McCouch SR (2007) Genetic diversity analysis of traditional and improved Indonesian rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 114(3):559–568
Vigouroux Y, McMullen M, Hittinger CT, Houchins K, Schulz L, Kresovich S, Matsuoka Y et al (2002) Identifying genes of agronomic importance in maize by screening microsatellites for evidence of selection during domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9650–9655
Waugh R, Bonar N, Baird E, Thomas B, Graner A et al (1997a) Homology of AFLP products in three mapping populations of barley. Mol Gen Genet 255:311–321
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas BBT, Powell W (1997b) Genetic distribution of BARE-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol Gen Genet 253:687–694
Yeh FC, Yang R, Boyle T (1999) Popgene, version 1.32. Microsoft window-based freeware for population genetic analysis. University of Alberta, Edmonton. http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/index.htm
Zhang LY, Marchand S, Tinker NA, Belzile F (2009) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium in barley assessed by DArT markers. Theor Appl Genet 119:43–52
Acknowledgments
MR performed the experiments under the supervision of DOS and analysed the data; MR and DR interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript; AHDB contributed ideas and co-wrote the manuscript; DOS, RP and GA contributed ideas and commented on the manuscript. RP and GA conceived and designed the study. Molecular analyses were carried out by the first author during the 2003 at NIAB (Cambridge, UK) while supported from the EC by a Marie-Curie Training Site Fellowship. This work was also supported by the Sardinian Region (Master and Back Program). The reviewers of the manuscript are thanked for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Graner.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, M., Rau, D., O’Sullivan, D. et al. Genetic structure and linkage disequilibrium in landrace populations of barley in Sardinia. Theor Appl Genet 125, 171–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1824-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1824-8