Abstract
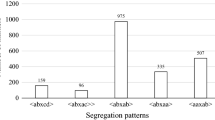
Downy mildew, caused by the oomycete Plasmopara viticola, is one of the major threats to grapevine. All traditional cultivars of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) are susceptible to downy mildew, the control of which requires regular application of fungicides. In contrast, many sources of resistance to P. viticola have been described in the Vitis wild species, among which is V. amurensis Rupr. (Vitaceae), a species originating from East Asia. A genetic linkage map of V. amurensis, based on 122 simple sequence repeat and 6 resistance gene analogue markers, was established using S1 progeny. This map covers 975 cM on 19 linkage groups, which represent 82% of the physical coverage of the V. vinifera reference genetic map. To measure the general level of resistance, the sporulation of P. viticola and the necrosis produced in response to infection, five quantitative and semi-quantitative parameters were scored 6 days post-inoculation on the S1 progeny. A quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis allowed us to identify on linkage group 14 a major QTL controlling the resistance to downy mildew found in V. amurensis, which explained up to 86.3% of the total phenotypic variance. This QTL was named ‘Resistance to Plasmopara viticola 8’ (Rpv8).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam-Blondon AF, Roux C, Claux D, Butterlin G, Merdinoglu D, This P (2004) Mapping 245 SSR markers on the Vitis vinifera genome: a tool for grape genetics. Theor Appl Genet 109:1017–1027
Alleweldt G, Possingham JV (1988) Progress in grapevine breeding. Theor Appl Genet 75:669–673
Anonymous (2009) Descriptor list for grapevine varieties and Vitis species, 2nd edn. Office International de la Vigne et du Vin (OIV), Paris
Becker H (1981) Erste Ergebnisse der Züchtung interspezifisher Ertragssorten mit de Erbmasse der Vitis amurensis Ruprecht in Geisenheim. Deutsches Weinbau Jahrbuch, pp 25–35
Bellin D, Peressotti E, Merdinoglu D, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Adam-Blondon AF, Cipriani G et al (2009) Resistance to Plasmopara viticola in grapevine ‘Bianca’ is controlled by a major dominant gene causing localised necrosis at the infection site. Theor Appl Genet 120:163–176
Boubals D (1959) Amélioration de la résistance de la vigne au mildiou (Plasmopara viticola (Berk et Curt.) Berlese et de Toni). Recherche de géniteurs de résistance. Annales de l’amélioration des plantes 6:481–525
Bowers JE, Dangl GS, Vignani R, Meredith CP (1996) Isolation and characterization of new polymorphic simple sequence repeat loci in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Genome 39:628–633
Bowers JE, Dangl GS, Meredith CP (1999) Development and characterization of additional microsatellite DNA markers for grape. Am J Enol Vitic 50
Brown M, Moore JN, Fenn P, McNew RW (1999) Comparison of leaf disk, greenhouse, and field screening procedures for evaluation of grape seedlings for downy mildew resistance. HortScience 34:331–333
Brun LA, Le Corff J, Maillet J (2003) Effects of elevated soil copper on phenology, growth and reproduction of five ruderal plant species. Environ Pollut 122:361–368
Cadle-Davidson L (2008) Variation within and between Vitis spp. for foliar resistance to the downy mildew pathogen Plasmopara viticola. Plant Dis 92:1577–1584
Csizmazia J, Bereznai L (1968) A szõlõ Plasmopara viticola és a Viteus vitifolii elleni rezisztencia nemesités eredményei. Orsz Szõl Bor Kut Int Évkönyve, Budapest, pp 191–200
Cus F, Basa Cesnik H, Velikonja Bolta S, Gregorcic A (2010) Pesticide residues and microbiological quality of bottled wines. Food Control 21:150–154
Dai GH, Andary C, Mondolot-Cosson L, Boubals D (1995). Histochemical studies on the interaction between three species of grapevine, Vitis vinifera, V. rupestris, V. rotundifolia and the downy mildew fungus, Plasmopara viticola. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 177–188
Dalbó MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Steinkellner H, Sefc KM, Reisch BI (2000) A gene controlling sex in grapevines placed on a molecular marker-based genetic map. Genome 43:333–340
Dick MW (2002) Binomials in the Peronosporales, Sclerosporales and Pythiales. In: Spencer PTN, Gisi U, Lebeda A (eds) Advances in Downy Mildew research. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 225–266
Diez-Navajas A, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Greif C, Merdinoglu D (2008) Nonhost versus host resistance to the grapevine downy mildew, Plasmopara viticola, studied at the tissue level. Phytopathology 98:776–780
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G (2003) Nucleotide binding site/leucine-rich repeats, Pto-like and receptor like kinases related to disease resistance in grapevine. Mol Genet Genomics 269:612–623
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G, Marrazzo MT, Andreetta D, Castro MJ, Peterlunger E et al (2005) Isolation of (AC)n-microsatellites in Vitis vinifera L. and analysis of genetic background in grapevines under marker assisted selection. Mol Breed 15:11–20
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G, Adam-Blondon AF, Testolin R (2007) Linkage maps of grapevine displaying the chromosomal locations of 420 microsatellite markers and 82 markers for R-gene candidates. Theor Appl Genet 114:1249–1263
Doligez A, Bouquet A, Danglot Y, Lahogue L, Riaz S, Meredith P et al (2002) Genetic mapping of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) applied to the detection of QTLs for seedlessness and berry weight. Theor Appl Genet 105:780–795
Doligez A, Adam-Blondon AF, Cipriani G, Di Gaspero G, Laucou V, Merdinoglu D et al (2006) An integrated SSR map of grapevine based on five mapping populations. Theor Appl Genet 113:369–382
Doucleff M, Jin Y, Gao F, Riaz S, Krivanek AF, Walker MA (2004) A genetic linkage map of grape, utilizing Vitis rupestris and Vitis arizonica. Theor Appl Genet 109:1178–1187
Dubos B (2002) Maladies cryptogamiques de la vigne. Féret edn, Bordeaux
Eibach R, Töpfer R (2003) Success in resistance breeding: ‘Regent’ and its steps into the market. Acta Hortic 687–691
Fischer BM, Salakhutdinov I, Akkurt M, Eibach R, Edwards KJ, Töpfer R et al (2004) Quantitative trait locus analysis of fungal disease resistance factors on a molecular map of grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 108:501–515
Frye CA, Tang D, Innes RW (2001) Negative regulation of defense responses in plants by a conserved MAPKK kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:373–378
Galet P (1977) Les maladies et les parasites de la vigne, vol I. Imp. Paysan du Midi, Montpellier
Gallais A (1990) Quantitative genetics of doubled haploid populations and application to the theory of line development. Genetics 124:199–206
Gisi U (2002) Chemical control of downy mildews. In: Spencer-Phillips PTN, Gisi U, Lebeda A (eds) Advances in Downy Mildew research. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 119–159
Gisi U, Waldner M, Kraus N, Dubuis PH, Sierotzki H (2007) Inheritance of resistance to carboxylic acid amide (CAA) fungicides in Plasmopara viticola. Plant Pathol 56:199–208
Grando MS, Bellin D, Edwards KJ, Pozzi C, Stefanini M, Velasco R (2003) Molecular linkage maps of Vitis vinifera L. and Vitis riparia Mchx. Theor Appl Genet 106:1213–1224
Ha do T, Kim H, Thuong PT, Ngoc TM, Lee I, Hung ND et al (2009) Antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of oligostilbenes from the leaf and stem of Vitis amurensis. J Ethnopharmacol 125:304–309
Huang K, Lin M, Cheng G (2001) Anti-inflammatory tetramers of resveratrol from the roots of Vitis amurensis and the conformations of the seven-membered ring in some oligostilbenes. Phytochemistry 58:357–362
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C et al (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–467
Kortekamp A, Zyprian E (2003) Characterization of Plasmopara-resistance in grapevine using in vitro plants. J Plant Physiol 160:1393–1400
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lafon R, Clerjeau M (1988) Downy mildew. In: Pearson RC, Goheen AC (eds) Compendium of grape diseases. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, pp 11–13
Li D, Wan Y, Wang Y, He P (2008) Relatedness of resistance to anthracnose and to white rot in Chinese wild grapes. Vitis 47:213–215
Lodhi MA, Daly MJ, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1995) A molecular marker based linkage map of Vitis. Genome 38:786–794
Lowe KM, Walker MA (2006) Genetic linkage map of the interspecific grape rootstock cross Ramsey (Vitis champinii) × Riparia Gloire (Vitis riparia). Theor Appl Genet 112:1582–1592
Ma YY, Zhang YL, Shao H, Lu J (2010) Differential physio-biochemical responses to cold stress of cold-tolerant and non-tolerant grapes (Vitis L.) from China. J Agron Crop Sci 196:212–219
Marguerit E, Boury C, Manicki A, Donnart M, Butterlin G, Némorin A et al (2009) Genetic dissection of sex determinism, inflorescence morphology and downy mildew resistance in grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 118:1261–1278
Merdinoglu D, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Coste P, Dumas V, Haetty S, Butterlin G et al (2003) Genetic analysis of downy mildew resistance derived from Muscadinia rotundifolia. Acta Hortic 603:451–456
Merdinoglu D, Butterlin G, Bevilacqua L, Chiquet V, Adam-Blondon AF, Decroocq S (2005) Development and characterization of a large set of microsatellite markers in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) suitable for multiplex PCR. Mol Breed 15:349–366
Merdinoglu D, Merdinoglu-Wiedemann S, Mestre P, Prado E, Schneider C (2009) Apport de l’innovation variétale dans la réduction des intrants phytosanitaires au vignoble: exemple de la résistance au mildiou et à l’oïdium. Progrès Agric Vitic 12:290–293
Moreira FM, Madini A, Marino R, Zulini L, Stefanini M, Velasco R, Kozma P, Grando MS (2010) Genetic linkage maps of two interspecific grape crosses (Vitis spp.) used to localize quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance. Tree Genet Genomes. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0322-x
Moroldo M, Paillard S, Marconi R, Fabrice L, Canaguier A, Cruaud C et al (2008) A physical map of the heterozygous grapevine ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ allows mapping candidate genes for disease resistance. BMC Plant Biol 8:66
Moriondo M, Orlandini S, Giuntoli A, Bindi M (2005) The effect of downy and powdery mildew on grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) leaf gas exchange. Vitis 357:350–357
Olmo H (1971) Vinifera-rotundifolia hybrids as wine grapes. Am J Enol Vitic 22:87–91
Riaz S, Dangl GS, Edward KJ, Meredith CP (2004) A microsatellite marker based framework linkage map of Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 108:864–872
Salmaso M, Malacarne G, Troggio M, Faes G, Stefanini M, Grando MS et al (2008) A grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) genetic map integrating the position of 139 expressed genes. Theor Appl Genet 116:1129–1143
Sefc KM, Regner F, Turetschek E, Glössl J, Steinkellner H (1999) Identification of microsatellite sequences in Vitis riparia and their applicability for genotyping of different Vitis species. Genome 42:367–373
Staudt G, Kassemeyer HH (1995) Evaluation of downy mildew resistance in various accessions of wild Vitis species. Vitis 34:225–228
Thomas MR, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphism when analysed as sequence-tagged sites (STSs). Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Troggio M, Malacarne G, Coppola G, Segala C, Cartwright DA, Pindo M et al (2007) A dense single-nucleotide polymorphism-based genetic linkage map of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) anchoring Pinot Noir bacterial artificial chromosome contigs. Genetics 176:2637–2650
Unger S, Büche C, Boso S, Kassemeyer HH (2007) The course of colonization of two different Vitis genotypes by Plasmopara viticola indicates compatible and incompatible host-pathogen interactions. Phytopathology 97:780–786
Van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MapQTL4.0, Software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research Int, The Netherlands
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) Joinmap3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research Int, Wageningen
Wan Y, Schwaninger H, He P, Wang Y (2007) Comparison of resistance to powdery mildew and downy mildew in Chinese wild grapes. Vitis 46:132–136
Wang J, Chen Y, Hano Y, Nomura T, Tan R (2000) Antioxidant activity of polyphenols from seeds of Vitis amurensis in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21:633–636
Welter LJ, Göktürk-Baydar N, Akkurt M, Maul E, Eibach R, Töpfer R et al (2007) Genetic mapping and localization of quantitative trait loci affecting fungal disease resistance and leaf morphology in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Mol Breed 20:359–374
Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Prado E, Coste P, Dumas V, Butterlin G, Merdinoglu D (2006) Genetic analysis of resistance to downy mildew derived from Muscadinia rotundifolia. Ninth international conference on grape genetics and breeding, Udine, Italy, July 2–6
Wielgoss A, Kortekamp A (2006) Comparison of PR1 expression in grapevine cultivar cultures after inoculation with a host and a non-host pathogen. Vitis 45:9–13
Yim N, Ha do T, Trung TN, Kim JP, Lee S, Na M et al (2010) The antimicrobial activity of compounds from the leaf and stem of Vitis amurensis against two oral pathogens. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:1165–1168
Acknowledgments
This work was partially financed by the Agence Nationale de Recherche (ERA-NET Plant Genomics Program-GRASP GRAPE WINE 074B). We are grateful to E. Duchêne for useful discussions on statistical methods. We thank P. Coste, M.-A. Dorne and C. Onimus for excellent technical assistance in plant growing and inoculum maintenance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Gebhardt.
P. Blasi and S. Blanc contributed equally to the present work and should therefore be considered first co-authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blasi, P., Blanc, S., Wiedemann-Merdinoglu, S. et al. Construction of a reference linkage map of Vitis amurensis and genetic mapping of Rpv8, a locus conferring resistance to grapevine downy mildew. Theor Appl Genet 123, 43–53 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1565-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1565-0