Abstract
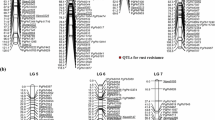
A mapping population was created to detect quantitative trait loci (QTL) for resistance to stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis subsp. graminicola in Lolium perenne. A susceptible and a resistant plant were crossed to produce a pseudo-testcross population of 193 F1 individuals. Markers were produced by the restriction-site associated DNA (RAD) process, which uses massively parallel and multiplexed sequencing of reduced-representation libraries. Additional simple sequence repeat (SSR) and sequence-tagged site (STS) markers were combined with the RAD markers to produce maps for the female (738 cM) and male (721 cM) parents. Stem rust phenotypes (number of pustules per plant) were determined in replicated greenhouse trials by inoculation with a field-collected, genetically heterogeneous population of urediniospores. The F1 progeny displayed continuous distribution of phenotypes and transgressive segregation. We detected three resistance QTL. The most prominent QTL (qLpPg1) is located near 41 cM on linkage group (LG) 7 with a 2-LOD interval of 8 cM, and accounts for 30–38% of the stem rust phenotypic variance. QTL were detected also on LG1 (qLpPg2) and LG6 (qLpPg3), each accounting for approximately 10% of phenotypic variance. Alleles of loci closely linked to these QTL originated from the resistant parent for qLpPg1 and from both parents for qLpPg2 and qLpPg3. Observed quantitative nature of the resistance may be due to partial-resistance effects against all pathogen genotypes, or qualitative effects completely preventing infection by only some genotypes in the genetically mixed inoculum. RAD markers facilitated rapid construction of new genetic maps in this outcrossing species and will enable development of sequence-based markers linked to stem rust resistance in L. perenne.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anhalt UCM, Heslop-Harrison P, Byrne S, Guillard A, Barth S (2008) Segregation distortion in Lolium: evidence for genetic effects. Theor Appl Genet 117:297–306
Armstead IP, Turner LB, King IP, Cairns AJ, Humphreys MO (2002) Comparison and integration of genetic maps generated from F2 and BC1-type mapping populations in perennial ryegrass. Plant Breed 121:501–507
Arumuganathan K, Tallury SP, Fraser ML, Bruneau AH, Qu R (1999) Nuclear DNA content of thirteen turfgrass species by flow cytometry. Crop Sci 39:1518–1521
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS One 3:e3376
Bert PF, Charmet G, Sourdille P, Hayward MD, Balfourier F (1999) A high-density molecular map for ryegrass (Lolium perenne) using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:445–452
Brazauskas G, Pasakinskiene I, Asp T, Lubberstedt T (2010) Nucleotide diversity and linkage disequilibrium in five Lolium perenne genes with putative role in shoot morphology. Plant Sci 179:194–201
Brueggeman R, Rostoks N, Kudrna D, Kilian A, Han F, Chen J, Druka A, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2002) The barley stem rust-resistance gene Rpg1 is a novel disease-resistance gene with homology to receptor kinases. PNAS 99:9328–9333
Brueggeman R, Druka A, Nirmala J, Cavileer T, Drader T, Rostoks N, Mirlohi A, Bennypaul H, Gill U, Kudrna D, Whitelaw C, Kilian A, Han F, Sun Y, Gill K, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2008) The stem rust resistance gene Rpg5 encodes a protein with nucleotide-binding-site, leucine-rich, and protein kinase domains. PNAS 105:14970–14975
Calenge F, Faure A, Goerre M, Gebhardt C, Van de Weg WE, Parisi L, Durel CE (2004) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis reveals both broad-spectrum and isolate-specific QTL for scab resistance in apple progeny challenged with eight isolates of Venturia inaequalis. Phytopathology 94:370–379
Chutimanitsakun Y, Nipper RW, Cuesta-Marcos A, Cistue L, Corey A, Filichkina T, Johnson EA, Hayes PM (2011) Construction and application for QTL analysis of a restriction site associated DNA (RAD) linkage map in barley. BMC Genomics 12:4
Cogan NOI, Ponting RC, Vecchies AC, Drayton MC, George J, Dracatos PM, Dobrowolski MP, Sawbridge TI, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2006) Gene-associated single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Mol Gen Genomics 276:101–112
Dumsday JL, Smith KF, Forster JW, Jones ES (2003) SSR-based genetic linkage analysis of resistance to crown rust (Puccinia coronata f. sp lolii) in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Plant Pathol 52:628–637
Faville MJ, Vecchies AC, Schreiber M, Drayton MC, Hughes LJ, Jones ES, Guthridge KM, Smith KF, Sawbridge T, Spangenberg GC, Bryan GT, Forster JW (2004) Functionally associated molecular genetic marker map construction in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:12–32
Fischer BM, Salakhutdinov I, Akkurt M, Eibach R, Edwards KJ, Töpfer R, Zyprian EM (2004) Quantitative trait locus analysis of fungal disease resistance factors on a molecular map of grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 108:501–515
Gill GP, Wilcox PL, Whittaker DJ, Winz RA, Bickerstaff P, Echt CE, Kent J, Humphreys MO, Elborough KM, Gardner RC (2006) A framework linkage map of perennial ryegrass based on SSR markers. Genome 49:354–364
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Hampton JG (1986) Fungicidal effects on stem rust, green leaf area and seed yield in ‘Grasslands Nui’ perennial ryegrass. NZ J Exp Agric 14:7–12
Jensen LB, Muylle H, Arens P, Andersen CH, Holm PB, Ghesquiere M, Julier B, Lubberstedt T, Nielsen KK, De Riek J, Roldan-Ruiz I, Roulund N, Taylor C, Vosman B, Barre P (2005) Development and mapping of a public reference set of SSR markers in Lolium perenne L. Mol Ecol Notes 5:951–957
Jo YK, Barker R, Pfender W, Warnke S, Sim SC, Jung G (2008) Comparative analysis of multiple disease resistance in ryegrass and cereal crops. Theor Appl Genet 117:531–5434
Jones ES, Mahoney NL, Hayward MD, Armstead IP, Jones JG, Humphreys MO, King IP, Kishida T, Yamada T, Balfourier F, Charmet G, Forster JW (2002) An enhanced molecular marker based genetic map of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) reveals comparative relationships with other Poaceae genomes. Genome 45:282–295
Kantety RV, Rota ML, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Khedikar YP, Gowda MVC, Sarvamangala C, Patgar KV, Upadhyaya HD, Varshney RK (2010) A QTL study on late leaf spot and rust revealed one major QTL for molecular breeding for rust resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 121:971–984
Lauvergeat V, Barre P, Bonnet M, Ghesquiere M (2005) Sixty simple sequence repeat markers for use in the Festuca–Lolium complex of grasses. Mol Ecol 5:401–405
Lewis ZA, Shiver AL, Stiffler N, Miller MR, Johnson EA, Selker EU (2007) High-density detection of restriction-site-associated DNA markers for rapid mapping of mutated loci in Neurospora. Genetics 177:1163–1171
Mago R, Miah H, Lawrence GJ, Wellings CR, Spielmeyer W, Bariana HS, McIntosh RA, Pryor AJ, Ellis JG (2005) High-resolution mapping and mutation analysis separate the rust resistance genes Sr31, Lr26 and Yr9 on the short arm of rye chromosome 1. Theor Appl Genet 112:41–50
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Nouhra ER, Gokirmak T, Bassil NV, Kubisiak TL (2006) A genetic linkage map for hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) based on RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 49:122–133
Miller MR, Dunham JP, Amores A, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2007) Rapid and cost-effective polymorphism identification and genotyping using restriction site associated DNA (RAD) markers. Genome Res 17:240–248
Muylle H, Baert J, Van Bockstaele E, Petris J, Roldan-Ruiz I (2005) Four QTLs determine crown rust (Puccinia coronata f. sp. lolii) resistance in a perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) population. Heredity 95:348–357
Nipper RW, Atwood TS, Boone JQ, Gribbin JM, Johnson EA (2009) SNP discovery in Zea mays using sequenced restriction-site associated DNA markers. Acta Hortic 859:129–133
O’Donoughue LS, Chong J, Wright CP, Fedak G, Molnar SJ (1996) Localization of stem rust resistance genes and associated molecular markers in cultivated oat. Phytopathology 86:719–727
Pfender WF (2001) A temperature-based model for latent period duration in stem rust of perennial ryegrass and tall fescue. Phytopathology 91:111–116
Pfender WF (2003) Prediction of stem rust infection favorability, by means of degree-hour wetness duration, for perennial ryegrass seed crops. Phytopathology 93:467–477
Pfender WF (2009a) A damage function for stem rust of perennial ryegrass seed crops. Phytopathology 99:498–505
Pfender WF (2009b) Demonstration of pathotype specificity in stem rust of perennial ryegrass. Phytopathology 99:1185–1189
Rose-Fricker CA, Meyer WA, Kronstad WE (1986) Inheritance of resistance to stem rust (Puccinia graminis subsp. graminicola) in six perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) crosses. Plant Dis 70:678–681
Saha MC, Mian R, Eujayl I, Zwonitzer JC, Wang L, May GD (2004) Tall fescue EST-SSR markers with transferability across several grass species. Theor Appl Genet 109:783–791
Saha MC, Mian R, Zwonitzer JC, Chekhovskiy K, Hopkins AS (2005) An SSR- and AFLP-based genetic linkage map of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). Theor Appl Genet 110:323–336
Schejbel B, Jensen LB, Xing Y, Lubberstedt T (2007) QTL analysis of crown rust resistance in perennial ryegrass under conditions of natural and artificial infection. Plant Breed 126:347–352
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat Biotechnol 18:233–234
Sim S, Chang T, Curley J, Warnke SE, Barker RE, Jung G (2005) Chromosomal rearrangements differentiating the ryegrass genome from the Triticeae, oat, and rice genomes using common heterologous RFLP probes. Theor Appl Genet 110:1011–1019
Sim S, Diesburg K, Casler M, Jung G (2007) Mapping and comparative analysis of QTL for crown rust resistance in an Italian × perennial ryegrass population. Phytopathology 97:767–776
Sim S, Yu J, Jo Y, Sorrells ME, Jung G (2009) Transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to ryegrass. Genome 52:431–437
Spielmeyer W, Sharp PJ, Lagudah ES (2003) Identification and validation of markers linked to broad-spectrum stem rust resistance gene Sr2 in wheat (Triticum aesetivum L.). Crop Sci 43:333–336
Steiner JJ, Poklemba CJ, Fjellstrom RG, Elliot LF (1995) A rapid one-tube genomic DNA extraction process for PCR and RAPD analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 23:2569–2570
Studer B, Boller B, Bauer E, Posselt UK, Widmer F, Kolliker R (2007) Consistent detection of QTL’s for crown rust resistance in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) across environments and phenotyping methods. Theor Appl Genet 115:9–17
Studer B, Kolliker R, Muylle H, Asp T, Frei U, Roldan-Ruiz I, Barre P, Tomaszewski C, Meally H, Barth S, Skot L, Armstead IP, Dolstra O, Lubberstedt T (2010) EST-derived SSR markers used as anchor loci for the construction of a consensus linkage map in ryegrass (Lolium spp.). BMC Plant Biol 10:177
Thorogood D, Kaiser WJ, Jones JG, Armstead I (2002) Self-incompatibility in ryegrass 12. Genotyping and mapping the S and Z loci of Lolium perenne L. Heredity 88:385–390
Thorogood D, Armstead IP, Turner LB, Humphreys MO, Hayward MD (2005) Identification and mode of action of self-compatibility loci in Lolium perenne L. Heredity 94:356–363
Tsilo TJ, Chao S, Jin Y, Anderson JA (2009) Identification and validation of SSR markers linked to the stem rust resistance gene Sr6 on the short arm of chromosome 2D in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 118:515–524
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL5, software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma B.V., Wageningen, Netherlands
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma B.V., Wageningen, Netherlands
Van Tassell CP, Smith TPL, Matukumalli LK, Taylor JF, Schnabel RD, Lawley CT, Haudenschild CD, Moore SS, Warren WC, Sonstegard TS (2008) SNP discovery and allele frequency estimation by deep sequencing of reduced representation libraries. Nat Methods 5:247–252
Warnke SE, Barker RE, Jung G, Sim SC, Rouf Mian MA, Saha MC, Brilman LA, Dupal MP, Forster JW (2004) Genetic linkage mapping of an annual × perennial ryegrass population. Theor Appl Genet 109:294–304
Wilcox PL, Amerson HV, Kuhlman EG, Liu BH, O’Malley DM, Sederoff RR (1996) Detection of a major gene for resistance to fusiform rust disease in loblolly pine by genomic mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3859–3864
Zhou WC, Kolb FL, Bai GH, Domier LL, Boze LK, Smith NJ (2003) Validation of a major QTL for scab resistance with SSR markers and use of marker-assisted selection in wheat. Plant Breed 122:40–46
Acknowledgments
We thank Sheila Seguin and Lori Evans-Marks (USDA-ARS) and Konstantin Chekhovskiy (Noble Foundation) for their technical assistance in this research, and acknowledge the assistance of Rick Nipper (Floragenex).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Luebberstedt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2011_1546_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1 RAD tag linkage maps of the stem rust susceptible female (S20) and rust resistant male (R2) parents. Linkage group numbering conforms to standard Lolium maps and was determined by co-segregation of RAD tag markers and previously mapped Lolium SSR markers (Gill et al. 2006) (PDF 56 kb)
122_2011_1546_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 2 SSR/STS linkage maps of the stem rust susceptible female (S20) and rust resistant male (R2) parents. Linkage group numbering conforms to standard Lolium maps, based on common SSR markers (Gill et al. 2006) (PDF 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfender, W.F., Saha, M.C., Johnson, E.A. et al. Mapping with RAD (restriction-site associated DNA) markers to rapidly identify QTL for stem rust resistance in Lolium perenne . Theor Appl Genet 122, 1467–1480 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1546-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1546-3