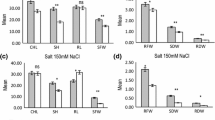
Abstract
Allotetraploid (2n = 4x = 32) white clover (Trifolium repens L.) is the most commonly cultivated legume component of temperate pastures, sown in swards with a companion grass species. Genetic control of growth performance of white clover on saline land is highly important for dairy industries, due to increasing soil salinity problems. The objective of this study was to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for salinity tolerance in terms of vegetative growth under stress. Two parental genetic maps consisting of 213 and 159 marker loci and spanning 1,973.0 and 1,837.6 cM, respectively, were constructed using simple sequence repeat (SSR) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers from a two-way pseudo-test cross F1 population derived from pair-crossing of the Haifa2 and LCL2 genotypes. A total of 8 unique genomic regions on 8 linkage groups (LGs) of the Haifa2 parental map and 6 unique regions on 5 LGs in the LCL2 parental map were associated with plant growth under salt stress and relative growth under stress, as compared to control conditions. The results of this study indicate that salt tolerance in white clover is controlled by multiple QTLs, some at common locations, but each of limited magnitude. Location of these QTLs provides the genetic basis and potential for pyramiding of salt tolerance genes in breeding improvement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel GH (1969) Inheritance of the capacity for chloride inclusion and chloride exclusion by soybeans. Crop Sci 9:697–698
Ab-Shukor NA, Kay QO, Stevens DP, Skibinski DO (1988) Salt tolerance in natural populations of Trifolium repens L. New Phytol 109:483–490
Asins MJ (2002) Present and future of quantitative trait locus analysis in plant breeding. Plant Breed 121:281–291
Barnard C (1972) Register of Australian herbage plant cultivars. CSIRO, Canberra. http://www.pi.csiro.au/ahpc/legumes/pdf/haifa.pdf)
Barrett B, Griffiths A, Schreiber M, Ellison N, Mercer C, Bouton J, Ong B, Forster J, Sawbridge T, Spangenberg G, Bryan G, Woodfield D (2004) A microsatellite map of white clover. Theor Appl Genet 109:596–608
Barrett B, Baird I, Woodfield D (2005) A QTL analysis of white clover seed production. Crop Sci 45:1844–1850
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB (1994) Zmap-a QTL cartographer. In: Smith C, Gavora JS, Chesnais BBJ, Fairfull W, Gibson JP, Kennedy BW, Burnside EB (eds) Proceedings of the 5th world congress on genetics applied to livestock production: computing strategies and software, vol 22. Guelph, Ontario, Canada, pp 65–66
Cogan NOI, Abberton MT, Smith KF, Kearney G, Marshall AH, Williams A, Michaelson-Yeates TPT, Bowen C, Jones ES, Vecchies AC, Forster JW (2006) Individual and multi-environment combined analyses identify QTLs for morphogenetic and reproductive development traits in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:1401–1415
Cogan NOI, Drayton MC, Ponting RC, Vecchies AC, Bannan NR, Sawbridge TI, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2007) Validation of in silico-predicted genic single nucleotide polymorphism in white clover (Trifolium repens L.), an outbreeding allopolyploid species. Mol Genet Genom 277:413–425
Ellis RP, Forster BP, Waugh R, Bonar N, Handley LL, Robinson D, Gordon DC, Powell W (1997) Mapping physiological traits in barley. New Phytol 137:149–157
Ellis RP, Forster BP, Gordon DC, Handley LL, Keith RP, Lawrence P, Meyer R, Powell W, Robinson D, Scrimgeour CM, Young G, Thomas WTB (2002) Phenotype/genotype associations for yield and salt tolerance in a barley mapping population segregating for two dwarfing genes. J Exp Bot 53:1163–1176
Ellison NW, Liston A, Steiner JJ, Williams WM, Taylor NL (2006) Molecular phylogenetics of the clover genus (Trifolium–Leguminosae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:688–705
Febrer M, Cheung F, Town CD, Cannon SB, Young ND, Abberton MT, Jenkins G, Milbourne D (2007) Construction, characterization, and preliminary BAC-end sequencing analysis of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Genome 50:412–421
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Flowers TJ, Koyama ML, Flowers SA, Sudhakar C, Singh KP, Yeo AR (2000) QTL: their place in engineering tolerance of rice to salinity. J Exp Bot 51:99–106
Foolad MR, Chen FQ, Lin GY (1998) RFLP mapping of QTLs conferring salt tolerance during germination in an interspecific cross of tomato. Theor Appl Genet 97:1133–1144
Foolad MR, Zhang LP, Lin GY (2001) Identification and validation of QTLs for salt tolerance during vegetative growth in tomato by selective genotyping. Genome 44:444–454
Forster JW, Cogan NOI, Dobrowolski MP, Francki MG, Spangenberg GC, Smith KF (2008) Functionally-associated molecular genetic markers for temperate pasture plant improvement. In: Henry RJ (ed) Plant genotyping II: SNP technology. CABI Press, Wallingford, pp 154–187
George J, Sawbridge TI, Cogan NOI, Gendall AR, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2008) Comparison of genome structure between white clover and Medicago truncatula supports homoeologous group nomenclature based on conserved synteny. Genome 51:905–911
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff RR (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross: mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Grattapaglia D, Bertolucci FL, Sederoff RR (1995) Genetic mapping of QTLs controlling vegetative propogation in Eucalyptus grandis and E. urophylla using a pseudo-testcross strategy and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:933–947
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324
Hand ML, Ponting RC, Drayton MC, Lawless KA, Cogan NOI, Brummer EC, Sawbridge TI, Spangenberg GC, Smith KF, Forster JW (2008) Identification of homologous, homoeologous and paralogous sequence variants in an outbreeding allopolyploid species based on comparison with progenitor taxa. Mol Genet Genom 280:293–304
Hand ML, Cogan NOI, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2009) Comparative structural analysis of gene clusters between sub-genomes of white clover and with model legume species. Plant and Animal Genome XVII, San Diego, California, p 353. http://www.intl-pag.org/17/abstracts/P05f_PAGXVII_353.html
Jones ES, Hughes LJ, Drayton MC, Abberton MT, Michaelson-Yeates TPT, Bowen C, Forster JW (2003) An SSR and AFLP molecular marker-based genetic map of white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Plant Sci 165:531–539
Kölliker R, Jones ES, Drayton MC, Dupal MP, Forster JW (2001) Development and characterisation of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Theor Appl Genet 102:416–424
Kölliker R, Enkerli J, Widmer F (2006) Characterisation of novel microsatellite loci for red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) from enriched genomic libraries. Mol Ecol Notes 6:50–53
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner RMD, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 125:406–422
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lee GJ, Boerma HR, Villagarcia MR, Zhou X, Carter TE, Li Z, Gibbs MO (2004) A major QTL conditioning salt tolerance in S-100 soybean and descendent cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 109:1610–1619
Lee SY, Ahn JH, Cha YS, Yun DW, Lee MC, Ko JC, Lee KS, Eun MY (2006) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at the seedling stage in rice. Mol Cells 21:192–196
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108:253–260
Ma LQ, Zhou EF, Huo NX, Zhou RH, Wang GY, Jia JZ (2007) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in a recombinant inbred population of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 153:109–117
Mano Y, Takeda K (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at germination and the seedling stage in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Euphytica 94:263–272
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
McFarlane NM, Ciavarella TA, Smith KF (2003) The effects of waterlogging on growth, photosynthesis and biomass allocation in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) genotypes with contrasting root development. J Agric Sci 141:241–248
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167:645–663
Munns R, James RA (2003) Screening methods for salinity tolerance: a case study with tetraploid wheat. Plant Soil 253:201–218
Payne RW, Murray DA, Harding SA, Baird DB, Soutar DM (2007) GenStat for Windows (10th edition) introduction. VSN International, Hemel Hempstead
Phang TH, Shao G, Lam HM (2008) Salt tolerance in soybean. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1196–1212
Prasad SR, Bagali PG, Hittalmani S, Shashidhar HE (2000) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with seedling tolerance to salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr Sci 78:162–164
Quarrie SA, Steed A, Calestani C, Semikhodskii A, Lebreton C, Chinoy C, Steele N, Pljevljakusic D, Waterman E, Weyen J, Schondelmaier J, Habash DZ, Farmer P, Saker L, Clarkson DT, Abugalieva A, Yessimbekova M, Turuspekov Y, Abugalieva S, Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Hollington PA, Aragues R, Royo A, Dodig D (2005) A high-density genetic map of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from the cross Chinese Spring X SQ1 and its use to compare QTLs for grain yield across a range of environments. Theor Appl Genet 110:865–880
Quesada V, Garcia-Martinez S, Piqueras P, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2002) Genetic architecture of NaCl tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130:951–963
Rogers ME, Noble CL, Nicolas ME, Halloran GM (1993) Variation in yield potential and salt tolerance of selected cultivars and natural-populations of Trifolium Repens L. Aust J Agric Res 44:785–798
Rogers ME, Noble CL, Halloran GM, Nicolas ME (1997) Selecting for salt tolerance in white clover (Trifolium repens): chloride ion exclusion and its heritability. New Phytol 135:645–654
Sato S, Isobe S, Asamizu E, Ohmido N, Kataoka R, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Sakurai N, Okumura K, Klimenko I, Sasamoto S, Wada T, Watanabe A, Kohara M, Fujishiro T, Tabata S (2006) Comprehensive structural analysis of the genome of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). DNA Res 12:301–364
Sewell MM, Bassoni DL, Megraw RA, Wheeler NC, Neale DB (2000) Identification of QTLs influencing wood property traits in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) I. Physical wood properties. Theor Appl Genet 101:1273–1281
Sewell MM, Davis MF, Tuskan GA, Wheeler NC, Elam CC, Bassoni DL, Neale DB (2002) Identification of QTLs influencing wood property traits in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) II. Chemical wood properties. Theor Appl Genet 104:214–222
Tozlu I, Guy CL, Moore GA (1999a) QTL analysis of morphological traits in an intergeneric BC1 progeny of Citrus and Poncirus under saline and non-saline environments. Genome 42:1020–1029
Tozlu I, Guy CL, Moore GA (1999b) QTL analysis of Na+ and Cl− accumulation related traits in an intergeneric BC1 progeny of Citrus and Poncirus under saline and non-saline environments. Genome 42:692–705
Villalta I, Bernet GP, Carbonell EA, Asins MJ (2007) Comparative QTL analysis of salinity tolerance in terms of fruit yield using two solanum populations of F7 lines. Theor Appl Genet 114:1001–1017
Villalta I, Reina-Sanchez A, Bolarin MC, Cuartero J, Belver A, Venema K, Carbonell EA, Asins MJ (2008) Genetic analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in leaf and stem as physiological components of salt tolerance in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 116:869–880
Wang J, Dobrowolski MP, Cogan NOI, Forster JW, Smith KF (2009) Assignment of individual genotypes to specific forage cultivars of perennial ryegrass based on SSR markers. Crop Sci 49:49–58
Williams WM, Griffiths AG, Hay MJM, Richardson KA, Ellison NW, Rasmussen S, Verry IM, Collette V, Hussain SW, Thomas RG, Jones CS, Anderson C, Maher D, Scott AG, Hancock K, Williamson ML, Tilbrook JC, Greig M, Allan A (2009) Development of Trifolium occidentale as a plant model system for perennial clonal species. In: Yamada T, Spangenberg G (eds) Molecular breeding of Forage and Turf: the Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on the Molecular Breeding of Forage and Turf. Springer, New York, USA, pp 45–53
Zang JP, Sun Y, Wang Y, Yang J, Li F, Zhou YL, Zhu LH, Jessica R, Mohammadhosein F, Xu JL, Li ZK (2008) Dissection of genetic overlap of salt tolerance QTLs at the seedling and tillering stages using backcross introgression lines in rice. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci 51:583–591
Zeng Z (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang Y, Sledge MK, Bouton JH (2007) Genome mapping of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) and comparative analysis within the Trifolieae using cross-species SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 114:1367–1378
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Department of Primary Industries, Victoria, Dairy Australia, the Geoffrey Gardiner Dairy Foundation, and Meat and Livestock Australia through the Australian Molecular Plant Breeding Cooperative Research Centre (MPB CRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Varshney.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Drayton, M.C., George, J. et al. Identification of genetic factors influencing salt stress tolerance in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) by QTL analysis. Theor Appl Genet 120, 607–619 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1179-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1179-y